축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에서 경기력평가요인 반영의 일치도
Performance Evaluation Factors Reflecting Player and Casting Judgments of Football Coaches
Article information
Abstract
[목적]
본 연구는 축구지도자의 선수 경기력평가요인 범주를 추출하고, 추출한 경기력평가요인에 대한 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에서 반영 특징을 검토할 목적으로 진행하였다.
[방법]
본 연구에서는 AFC C 이상 지도자 80명을 대상으로 개방형설문과 범주화를 통해 경기력평가요인을 추출하였다. 계층분석을 통해 선수판단과 기용판단의 반영도를 산출하였으며, SPSS21.0을 활용해 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영의 일치도를 검토하였다.
[결과]
첫째, 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인은 신체지능, 심리지능, 성장잠재력, 경기지능 등 4개의 일반영역으로 범주화되었다. 둘째, 축구지도자는 선수판단에 축구지능, 상황판단, 축구재능, 전술이해, 전술운용, 기술, 자기주도, 태도, 매개기술, 승부근성, 체력, 열정, 자신감, 소통자원, 헌신, 체격 순으로 반영한다. 기용판단에 선수의 전술이해, 매개기술, 체력, 전술운용, 상황판단, 기술, 축구지능, 자신감, 축구재능, 체격, 승부근성, 태도, 헌신, 자기주도, 열정, 소통자원의 순으로 반영한다. 셋째, 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에 경기력평가요인 일치도가 다르다. 축구지도자는 심리지능과 경기지능 요인, 하위요인으로 기술, 체격, 태도, 열정 등에서 선수판단과 기용판단의 중요도를 일치시키는 반면, 신체지능과 성장잠재력 요인, 하위요인으로 매개기술, 체력, 축구재능, 전술이해에서 선수판단과 기용판단의 중요도를 다르게 판단한다.
[결론]
지도자의 선수판단에서는 성장을 향한 이상 원리가, 기용판단에서는 승리를 향한 현실 원리가 작동하며 이러한 차이는 축구지도자의 이상과 현실 차이로 인한 내적갈등의 크기이기도 하다.
Trans Abstract
PURPOSE
This study aimed to extract football coaches’ categories of performance evaluation factors (PEF) and examine the reflective characteristics of the football coaches’ player and casting judgments.
METHODS
PEF were extracted through an open-ended questionnaire and categorization from 80 AFC C or higher football coaches. Reflection was calculated in player and casting judgments through an analytic hierarchy process. The difference between the football coaches’ player and casting judgments was examined using SPSS 21.0.
RESULTS
First, the PEF of football coaches were categorized into four general categories: physical intelligence, psychological intelligence, growth potential, and competition intelligence. Second, the importance of football coaches’ player judgments were reflected by the PEF as football intelligence, situation judgment, football talent, tactical understanding, tactical operation, etc. The importance of the casting judgment were reflected by the PEF as tactical understanding, mediative skills, fitness, tactical operation, situation judgment, etc. Third, a statistically significant difference was noted between player and casting judgments. Football coaches tended to value growth potential and talent as sub-factors in the player evaluations. Football coaches’ PEF were aligned with the importance of player and casting judgments in psychological and competition intelligence as sub-factors such as skills, physical, attitude, passion, etc., but differed from physical intelligence and growth potential as sub-factors including mediative skills, physical, football talent, and tactical understanding.
CONCLUSIONS
In the football coaches’ player evaluations, the idealistic principle centered on growth potential. However, in the casting evaluation, the realistic principle centered on victory takes effect.
서론
축구지도자는 훈련 프로그램에 따라 훈련을 진행하면서 선수를 평가하고, 선수의 특징을 판단해 경기에 기용한다. 이 과정에서 지도자 개인의 경기력 구성 요소 정의는 선수의 경기력 장단 분석과 판단의 준거가 된다. 일반적으로 지도자의 선수판단은 훈련과 경기에 따라 다른 기준이 반영되는데, 훈련에서는 선수의 성장가능성이 중시되는 반면 경기에서는 팀승리 기여 가능성이 중시된다. 이러한 지도자의 판단 경향성은 가능성이 추정되어 왔을 뿐 실증의 영역에 이르렀다고 보기는 어렵다. 훈련과 경기에서 축구지도자의 선수판단에 어떤 요소가 반영되고 있을까?
개인의 정보 기반 판단 과정에서 나타나는 정박과 조정, 대표성 휴리스틱 등은 판단 과정에 대한 이해를 돕는다(Kahneman & Tversky, 1973; Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). 의사결정에서 의사 결정 주체의 내부는 물론 외적환경 정보는 판단에 영향을 미치는 요인(Hong & Na, 2020)으로 선호에 따라 결정에 다른 방식으로 영향을 미친다. 개인의 판단은 개인의 내면적 과정이라기보다 상황과 반영(Kim & Han, 2016)된 개인 내부의 소통 과정이다. 이러한 개인 내부의 소통 양상은 정보 지각 과정이나 다양한 선택안을 결정할 때 효율적으로 판단하려는 경향(Sohn & Park, 2003)으로 이어진다. 판단 과정의 효율은 간결한 의사결정 과정과 무관하지 않은데, 선택 과정에서 개인은 판단의 선택지를 최소화하고(Lee & Park, 2017), 실제로 의사결정을 간결하게 진행하려는 경향이 있다(Kim et al., 2005).
평가는 개인이나 사물의 속성에 대한 가치판단으로, 평가 상황에는 판단의 기준(Kim et al., 2005)이 필요하다. 개인의 판단에는 사회적 바람직성이나 상황, 개인의 경험, 맥락(Kim & Yang, 2020) 또는 초기정보, 개인의 경험과 전문성, 상황과 맥락이 판단 결과의 차이(Kim & Choi, 2010) 등으로 반영된다. 개인은 판단 과정에서 이득보다 손실에 민감하고 보수적으로 손익을 계산해 판단(Kahneman & Tversky, 1979)한다. 또한 사법판단에는 상황이나 목표, 정보 선택의 초점에 따라 결과가 달라지기도 한다(Yoon et al., 2021). 판단에는 정보를 해석하는 개인의 성향이나 정보 선호도가 반영되기도 하고(Gwon & Kim, 2021), 시간이나 공간 등의 압박(Alt et al., 2021; You & Yun, 2021)이 반영되기도 한다. 이처럼 개인의 판단에는 다양한 요인과 맥락이 반영된다.
스포츠는 전략과 전술을 기반으로 하고 있는데, 이를 감안하면 경기와 훈련은 판단 과정의 연속이다. 스포츠에서 판단은 개인의 내적 자원과 상대의 상황, 경기 환경이나 맥락 등 다양한 변수를 반영해 이루어진다. 그리고 스포츠에는 판단의 결과가 다음 판단에 영향을 미치는 맥락적 연속성이 작동한다. 스포츠에서는 맥락에 따라 정보 해석이 달라지거나(Yun, 2005), 승부 예측 방향에 따라 경기결과 평가가 달라지기도 하며(Kim & Hwang, 2005), 맥락에 따라 자신의 판단을 감추기도 한다(Hwang, 2004). 또한 자기고양으로 인한 사후과잉확신(Hwang & Kim, 2007)을 보이는 등 스포츠에서 판단과 의사결정에는 맥락적 영향이 작동한다.
특히 지도자의 판단은 경기결과와 직접적으로 연결된다(Musculus et al., 2021). 지도자의 의사결정에는 팀운영 전반의 요소가 고려된다(Jeon & Yun, 2015). 실제로 지도자는 지도철학(Kramers et al., 2019)이나 선수의 경기력 발전, 팀의 분위기, 선수의 성장을 위한 판단을 반복적으로 진행하면서 팀을 운영한다(Preston & Fraser-Thomas, 2018). 또한 지도자는 선수와 원활한 관계(Danielsen et al., 2019)나 팀 구성원 소통과 구성원 배려 분위기 조성을 위한 판단(Gano-Overway & Sackett, 2021), 팀운영, 선수의 인성이나 선수 성장 지원을 위한 판단을 반복한다(Winter et al., 2019). 팀운영과 지도에서 지도자 판단의 다양성은 선수를 판단하는 과정에서 지도자가 고려해야 할 변수의 다양성을 방증한다.
축구에서 지도자는 선수 선발이나 기용에 핵심 주체로 이 과정에서 지도자의 심리적 펀더멘틀(Yun, 2008)이 중시된다. 팀운영과 경기에서 지도자는 선수의 성장을 고려(Kim & Shin, 2021)하는 동시에 팀이 성과를 거둘 수 있도록 지도역량(Ha & Choi, 2016)을 발휘해야 한다. 이 과정에서 지도자는 선수를 파악(Chung, 2004)하고 특징을 분석해 선수와 팀의 상황과 맥락에 적절한 판단(Preston & Fraser-Thomas, 2018)을 한다. 축구지도자의 평가와 판단은 팀의 현재 전력이나 상태, 상황과 맥락, 대회 성격이나 상대팀의 전력에 따라 달라진다(Roberts et al., 2021). 판단과 결정은 선수평가에서도 동일한 방식으로 작동할 가능성이 있다.
지도자는 시합이나 훈련에서 선수를 관찰해 경기력을 판단하고 판단 결과를 팀운영에 반영한다. 이러한 과정에서 선수 기용에 지도자의 주관적 판단(Johansson & Fahlén, 2017)이 중시되는데, 이로 인해 지도자의 경기력 판단 준거는 선수의 경기력영향요인(Roberts et al., 2021)으로 수렴될 개연성이 있다. 축구경기력은 선수의 내적 자원과 외적환경은 물론 사회문화적 맥락이 반영된다(Yun, 2015). 여기에 ESG로 구현된 지속가능성이 경기력평가 요소로 논의(Yun, 2022)되기도 한다. 선수의 경기력은 체력, 기술, 전술, 심리의 함수라는 고전적 관점에서 선수의 성과 관리(Ivarsson et al., 2020), 지능 논의의 확장(Gould et al., 2002), 선수 재능계발(Orosz & Mezo, 2015), 최적의 수행(Anshel & Payne, 2006) 등으로 경기력에 대한 정의를 넘어 과정으로 관심이 확장되고 있다.
실제로 선수의 경기력평가에 경기력의 내적자원인 경기지능(Roberts et al., 2019), 심리지능(Durand-Bush et al., 2022), 신체지능(Yun, 2011)을 비롯해 외적환경인 지도자, 성장경험, 주요타자(Yun & Jeon, 2013), 가치와 평판(Yun, 2015) 등이 맥락적으로 반영(Yun et al., 2021)되고 있다. 이는 선수 경기력평가가 조건이나 환경에 따라 달라질 수 있음을 시사한다. 뿐만 아니라 경기력은 훈련이나 경험, 기술, 지도자와 원활한 관계(Anderson et al., 2014), 신체최적화(Louie et al., 2020), 정서적 균형(Cooper et al., 2021) 등에 따라 다르게 발현된다. 이처럼 경기력은 내적요인은 물론 외적 요인에 따라 다르게 발현되는 가변적 속성이 있다.
축구지도자의 선수판단은 훈련과 경기 맥락에 따라 달라질 개연성이 있다. 선수판단 준거로 훈련에서는 선수의 성장가능성이 반영되는 반면, 경기에서는 경기에서의 활약 여부가 반영된다. 이는 선수판단에 성장가능성이, 기용판단에는 경기에서 활약 가능성이 고려될 개연성을 시사한다. 이상에 따라 본 연구에서는 축구지도자의 경기 력평가요인을 추출하고, 추출한 경기력평가요인을 선수판단과 기용 판단에 반영하는 특징을 이해할 목적으로 진행하였다. 이를 위하여 첫째, 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인을 추출하였다. 둘째, 지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에 경기력평가요인 반영도를 산출하였다. 셋째, 경기력평가요인의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영 일치도를 검토하였다.
연구방법
자료제공자
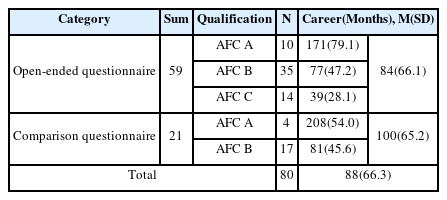
본 연구에서는 경기력평가요인 탐색을 위하여 축구지도자 59명을 대상으로 개방형설문을, 선수판단과 기용판단 반영도 산출을 위하여 축구지도자 21명에게 이원비교설문을 진행하였다. 축구지도자는 경력에 따라 D, C, B, A, P 등 자격의 급수가 다르고, 자격급수에 따라 지도 가능 대상이 차별화되어 있다. 자료제공자 80명의 선수경력의 평균은 148개월이며, 표준편차는 58.3개월이다. 구체적 지도경력 특징은 <Table 1>과 같다.
조사도구
본 연구에서는 개방형설문과 이원비교설문을 활용해 자료를 수집하였다. 개방형설문은 “귀하께서 선수를 평가할 때 중시하는 요소는 무엇인가요?” 로 문항을 구성하여, 지면설문과 google form을 제작하였다. 이원비교설문은 개방형설문의 범주화 결과를 토대로 9점 비율척도를 적용한 이원비교설문으로 구성하여 온라인방식(www.ssra.or.kr)과 지면방식으로 <Figure 1>과 같이 제작하였다.
연구 절차
본 연구는 경기력평가요인 탐색 단계, 선수판단과 기용판단의 반영도 산출 단계, 선수판단과 기용판단의 일치도 검증 단계 순으로 진행하였다. 먼저 경기력평가요인 탐색 단계에서는 경기력평가요인 탐색을 위하여 개방형설문을 제작하였으며, 개방형설문 제작과정에서 연구진, 스포츠심리학 박사 2인, 스포츠심리학 박사과정 2인 등 6인을 대상으로 내용타당도를 검토하였다. 축구지도자를 대상으로 개방형설문을 진행하여 선수평가에서 중시하는 요인을 수집하였다. 수집된 자료는 귀납적범주화 후 스포츠심리학 박사 5인과 스포츠심리학 박사과정 1인 등 6인이 참여한 전문가회의를 개최해 귀납적범주화 결과가 만장일치에 이르기까지 검토를 진행하였으며, 범주의 빈도비율을 산출하였다.
선수판단과 기용판단의 반영도 산출 단계에서는 경기력평가요인 탐색 결과를 토대로 선수판단과 기용판단을 내용으로 하는 이원비교설문을 진행하였다. 이원비교설문은 선행연구(Yun & Lee, 2006; Yun et al., 2021) 설문을 토대로 경기력평가요인의 세부영역과 일반영역을 내용으로 지면설문을 제작한 후, 지면설문의 구성과 동일하게 사회과학연구 자동화 홈페이지에서 온라인설문을 제작하였다. 이원비교설문은 COVID-19 봉쇄를 감안하여 사회과학연구 자동화의 온라인 설문링크나 지면설문을 모바일로 발송하면 자료제공자가 온라인 설문링크에 응답하거나 ᄒᆞᆫ글2020 형식의 지면설문에 응답해 모바일메신저로 재송부하는 비대면 방식으로 진행하였다. 이 과정에서 선수판단 상황과 기용판단 상황을 분리해 설문을 반복하였다. 계층분석은 일관성지수 .2를 기준으로, 채택된 자료의 기하평균 산출 후 이원비교와 비교결과 통합을 진행하였다.
선수판단과 기용판단의 일치도 검증 단계에서는 선수판단과 기용판단의 반영도 계층분석 결과를 토대로 선수판단과 기용판단의 일치도를 검증하였다. 자료제공자별 선수판단과 기용판단의 계층분석 결과를 대상으로 대응표본 t-검증을 진행하였다. 선수판단과 기용판단 반영도의 대응표본 t-검증 결과에서 유의차가 없는 경우 일치요인으로, 유의차가 나타나는 경우 불일치요인으로 분류하고 논의를 진행하였다. 이상의 연구절차는 <Figure 2>와 같다.
자료 분석
본 연구에서는 수집한 자료의 분석을 위하여 귀납적내용분석, Excel 2019, EC-2000, SPSS 21.0을 활용하였다. 귀납적내용분석은 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인 도출에 활용하였다. 개방형설문 결과 수집된 원자료를 의미의 유사성에 따라 세부영역으로 유목화하고, 세부영역은 내용과 의미의 유사성에 따라 일반영역으로 범주화하였다. Excel 2019는 범주화 결과의 빈도비율 산출과 이원비교설문 응답의 기하평균 산출(삽입/함수/GEOMEAN)에 활용하였다. EC-2000은 경기력평가요인의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영도 산출을 위한 계층분석에 활용하였다. SPSS 21.0은 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영 일치도 검증을 위한 대응표본 t-검증(p<.5)에 활용하였다.
결과 및 논의
축구지도자의 경기력평가요인 범주
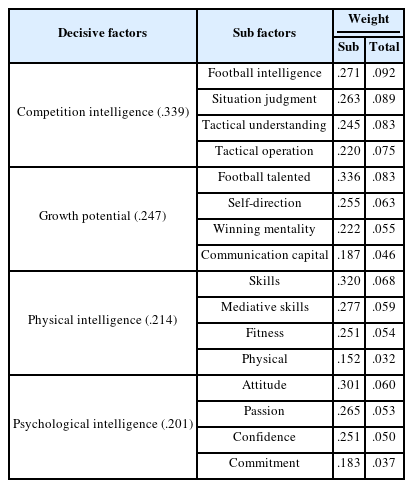
축구지도자의 경기력평가요인은 개방형 설문결과, 323개의 원자료가 수집되었다. 수집된 원자료는 16개 세부영역으로, 세부영역은 신체지능, 심리지능, 성장잠재력, 경기지능 등 4개 일반영역으로 <Table 2>와 같이 범주화하였다.
신체지능은 선수가 몸을 원하는 대로 조절하는 능력으로 기술, 체력, 체격, 매개기술로 구성된다. 심리지능은 선수 스스로 자신의 심리를 조절하는 능력으로 태도, 열정, 헌신, 자신감으로 구성된다. 성장잠재력은 선수의 장기적인 성취에 대한 지도자의 기대로 승부근성, 축구재능, 자기주도, 소통자원으로 구성된다. 경기지능은 훈련에서 경기력을 자기화시키는 동시에 경기를 풀어가는 능력으로 축구지능, 상황판단, 전술이해, 전술운용으로 구성된다.
축구지도자의 경기력평가요인으로 신체지능, 경기지능, 심리지능과 더불어 성장잠재력이 도출되었는데, 이는 축구선수의 내적자원(Yun, 2015)과 선수의 성장가능성(Musculus et al., 2021)을 포함하고 있다. 축구 경기력에 영향을 미치는 요인으로 체력, 기술, 전술운용(Yun & Lee, 2006)이나 승부근성, 축구재능, 자기주도성, 소통자원(Kang & Yun, 2021) 등이 제시되고 있다. 여기에 심리기본기, 정서조절, 경기지능, 소통역량이 경기력에 영향을 미치는 심리요인(Yun et al., 2021)으로 논의되고 있다. 경기력영향요인과 경기력 영향심리요인은 지도자의 선수 경기력평가요인과 유사하다.
선수판단과 기용판단에 경기력평가요인의 반영도
축구지도자의 선수판단에 경기력평가요인 반영도는 <Table 3>과 같다.
축구지도자는 선수판단에 축구지능, 상황판단, 축구재능, 전술이해, 전술운용, 기술, 자기주도, 태도, 매개기술, 승부근성, 체력, 열정, 자신감, 소통자원, 헌신, 체격 순으로 경기력평가요인을 반영한다.
축구지도자는 선수판단에 경기지능, 성장잠재력, 신체지능, 심리지능 요인 순으로 경기력평가요인을 반영하고 있다. 특히 경기지능과 성장잠재력의 비중 있는 반영은 지도자의 선수판단에서 현재보다 미래(Musculus et al., 2021)를 염두에 두고 있음을 방증한다. 실제로 경기지능은 선수 성장의 예측지표(Roberts et al., 2019; Yun, 2010)이면서 동시에 경기력영향요인으로 중시(Johansson & Fahlén, 2017; Roberts et al., 2021; Yun et al., 2021)되고 있다.
축구지도자의 기용판단에서 경기력평가요인 반영도는 <Table 4>와 같다.
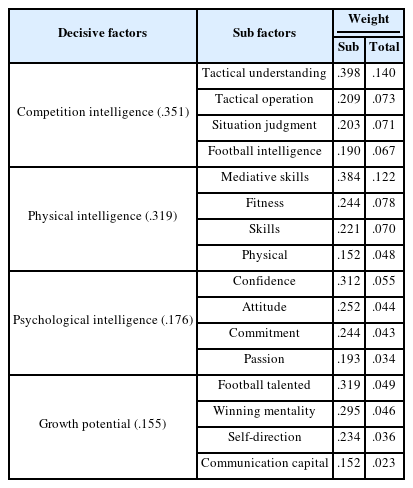
축구지도자는 기용판단에 전술이해, 매개기술, 체력, 전술운용, 상황판단, 기술, 축구지능, 자신감, 축구재능, 체격, 승부근성, 태도, 헌신, 자기주도, 열정, 소통자원의 순으로 경기력평가요인을 반영한다.
축구지도자는 기용판단에 경기지능, 신체지능, 심리지능, 성장잠재력 순으로 경기력평가요인을 반영하고 있다. 특히 경기지능과 신체지능의 비중 있는 반영은 기용판단에서 팀전술을 이해하고 경기에 구현을 요구하는 지도자의 의도(Chung, 2019)가 반영된다. 실제로 선수평가에서 신체지능이 중시(Nurjaya et al., 2020)되는 경향이 나타나는데, 축구에서 매개기술 활용을 위해 체력이 전제(Yun & Lee, 2006) 되어야 하는 현실적 고려가 반영된 결과로 해석된다. 이는 현재 시점에서 성장가능성이 기대되는 선수보다 경기에서 빠르고 강하면서 오래 달릴 수 있는 선수가 팀에 이득인 현실(Oh & Kim, 2002)을 반영한 결과이다.
축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영의 일치도
축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에서 경기력평가요인 반영의 일치도와 판단을 위한 대응표본 t-검증 결과는 <Table 5>와 같다.
축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에서 심리지능과 경기지능 요인, 하위요인으로 기술, 체격, 태도, 열정 등은 선수판단과 기용판단에서 일치요인이다. 반면, 신체지능과 성장잠재력 요인, 하위요인으로 매개기술, 체력, 축구재능, 전술이해는 불일치요인이다. 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에 일치와 불일치요인은 <Table 6>과 같이 정리된다.
축구지도자의 경기력평가요인은 지도상황과 맥락에 따라 선수판단에 다르게 반영되고 있다. 선수판단과 기용판단에서 일치요인은 축구지도자가 선수판단 전반에 걸쳐 요구하는 경기력평가요인의 공통속성이다. 반면, 불일치요인은 훈련이나 경기 등의 맥락이 반영된다. 구체적으로 성장잠재력 요인과 하위요인의 축구재능은 선수판단에 고려되는 특징이다. 또한, 신체지능 요인과 하위요인의 매개기술, 체력, 전술이해는 기용판단에 고려된다. 선수판단에는 선수의 미래와 성장 맥락이 반영(Kim & Yang, 2020)되고, 기용판단에는 성과를 지향하는 지도자의 현실(Oh & Kim, 2002)이 신체지능에 비중있는 반영(Hong & Na, 2020)으로 나타난다. 이는 축구지도자의 선수판단에 선수의 성장을 위한 바람이, 기용판단에는 승리를 향한 현실이 반영된다.
결론 및 제언
축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단의 일치도를 도출한 본 연구의 결론은 다음과 같다.
첫째, 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인 원자료는 16개 세부영역과 신체지능, 심리지능, 성장잠재력, 경기지능 등 4개의 일반영역으로 범주화하였다. 신체지능은 선수 스스로 자신의 신체 조절 능력으로 기술, 매개기술, 체력, 체격으로 구성된다. 심리지능은 선수의 심리적항상성 유지 조절 능력으로 태도, 헌신, 자신감으로 구성된다. 성장잠재력은 지도자의 선수 성취에 대한 기대로 승부근성, 축구재능, 자기주도, 소통자원으로 구성된다. 경기지능은 경기력을 자기화시켜 경기를 풀어가는 능력으로 축구지능, 상황판단, 전술이해, 전술운용으로 구성된다.
둘째, 선수판단과 기용판단에 축구지도자의 경기력평가요인 반영도를 산출하였다. 축구지도자는 선수판단에 경기지능, 성장잠재력, 신체지능, 심리지능 요인 순으로 중시하며, 하위요인은 축구지능, 상황판단, 축구재능, 전술이해, 전술운용, 기술, 자기주도, 태도, 매개기술, 승부근성, 체력, 열정, 자신감, 소통자원, 헌신, 체격 순으로 중시한다. 한편, 기용판단에는 선수의 경기지능, 신체지능, 심리지능, 성장잠재력 순으로 중시하며, 하위요인은 전술이해, 매개기술, 체력, 전술운용, 상황판단, 기술, 축구지능, 자신감, 축구재능, 체격, 승부근성, 태도, 헌신, 자기주도, 열정, 소통자원의 순으로 중시한다.
셋째, 경기력평가요인에 대한 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단 반영도의 대응표본 t-검증 결과, 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단은 일치요인과 불일치요인으로 구분된다. 구체적으로 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단에서 심리지능과 경기지능 요인, 하위요인으로 기술, 체격, 태도, 열정 등은 일치요인이다. 반면, 신체지능과 성장잠재력 요인, 하위요인으로 매개기술, 체력, 축구재능, 전술이해는 불일치요인이다. 축구지도자의 선수판단에는 선수의 성장을 위한 이상 원리가, 기용판단에는 승리를 향한 현실 원리가 작동하며 이러한 차이는 축구지도자의 이상과 현실 차이로 인한 내적갈등의 크기이기도 하다.
본 연구 진행과 결과를 토대로 후속 연구에 다음과 같이 제언한다.
첫째, 선수나 선수부모, 축구행정가 등 축구계 전반으로 선수판단과 기용판단 차이의 경향을 검토할 필요가 있다. 본 연구 결과 선수판단과 기용판단이라는 맥락에 따라 지도자의 경기력평가요인 반영도가 달라지는데 이는 맥락이 확장되어 다른 기준이 적용되면 적용 기준에 따라 경기력평가요인의 반영도가 달라질 개연성을 내포한다. 또한 이러한 결과는 축구지도자는 물론 선수, 선수부모, 행정가 등 축구계 주체의 경기력평가요인 반영도나 중요도 평가 등에 이견 가능성을 시사한다. 따라서 축구계 구성주체들의 경기력평가요인 반영도 차이를 이해한다면 축구계 구성원 간의 소통증진에 기여할 것이다.
둘째, 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단의 경기력평가요인이 일부 다른 결과가 지도자교육 프로그램에 활용되기를 기대한다. 축구지도자는 선수판단에서 성장을 향한 이상을, 기용판단에서 승리를 향한 현실을 반영하고 있다. 이러한 불일치는 축구지도자의 판단 과정에서 상황맥락이 반영된 결과로 축구지도자에게 선수평가 과정에서 발생하는 내적갈등이나 외적갈등의 유발 요인이 된다. 따라서 지도자 판단의 불일치가 선수평가 과정의 이상과 현실의 맥락이 반영된 결과임을 이해할 수 있도록 지도자교육에서 이해를 제공할 필요가 있다. 이를 통해 축구지도자 스스로 지도자의 선수평가로 인해 유발되는 내외적 갈등에 유연한 대응 방안을 모색하는 단초를 마련할 수 있을 것이다.
셋째, 축구지도자의 선수판단과 기용판단 일치도에서 일치요인과 불일치요인 차이에 대한 심층적 검토가 필요하다. 실제로 일치요인에서 경기지능, 축구지능, 상황판단, 전술운용, 기술 등의 가시적으로 드러나는 경기력영향요인이나, 심리지능, 소통자원, 자신감 등의 비가시적 경기력영향요인이 반영된다. 일치요인에는 선수의 경기력 전반과 태도요인이 포함되고, 불일치요인에는 경기력영향요인이 포함된다. 일치요인에는 지도자이면서 동시에 선생님, 부모의 역할을하는 축구지도자의 환경맥락이, 불일치요인에는 축구를 지도하는 축구지도자로서 역할이 반영된 것으로 추정된다. 선수판단과 기용판단에 대한 심층적 이해는 선수 육성과 훈련에서 단기적 관심요인과 장기적 관심요인에 대한 이해를 제공할 것이다. 이러한 이해는 훈련프로그램 개발의 원칙과 방향 설정에 반영할 수 있을 것이다.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
논문 작성에 있어서 어떠한 조직으로부터 재정을 포함한 일체의 지원을 받지 않았으며 논문에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 어떠한 관계도 없음을 밝힌다.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Young-Kil Yun & Ji-Hun Kang, Data curation: Ji-Hun Kang, Formal analysis: Ji-Hun Kang, Funding acquisition: Ji-Hun Kang, Methodology: Young-Kil Yun, Projectadministration: Ji-Hun Kang, Visualization: Ji-Hun Kang, Writing-original draft: Ji-Hun Kang, Writingreview&editing: Young-Kil Yun