
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.







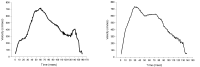

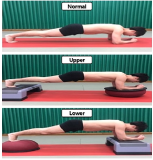
Purpose This study was to analyze and compare series of muscle activities during plank exercises with use of togu-jumper. Methods Ten male subjects (age 26.9±1.7 yrs, height 172.2±5.7 cm, weight 66.5±7.5 kg) who have no musculoskeletal disorder with one's upper or lower limb were selected as subjects. To analyze and compare series of muscle activity, five of surface EMG electrodes were attached to the upper rectus abdominis (URA), lower rectus abdominis (LRA), external abdominal oblique (EO), erector spinae (ES) and gluteus maximus (GM). Each subject did plank exercise on stable support surfaces (normal surfaces) and unstable support surfaces with the togu-jumper. For each dependent variable, one-way ANOVA with repeated measures were performed with significance level p<.05. Contrasts were performed to execute post tests for results with statistical significance. Results The study showed that the average IEMG values of URA and LRA increased in Upper (Togu-jumper used upper limb) compared to normal surfaces. This is perhaps because the effects of URA more than any other muscles for body stability. Furthermore, the peak IEMG values of LRA increased in Upper and Lower (Togu-jumper used lower limb) compared to normal surfaces. In addition, peak IEMG values of EO increased in Upper compared to Normal. This may have resulted due to momentary strong muscle activity in LRA and EO to correct body posture and balance. Therefore, using Togu-jumper on upper limb maximizes the performance of core training in plank exercise. Conclusions The study may be further applied to a method for effective training. It is considered that research and analysis has to be further done on modified plank exercise. Additionally, it is necessary to analyze not only global muscle but also local muscle, as a comprehensive research, to suggest ideal method for plank exercise.



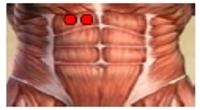
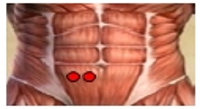
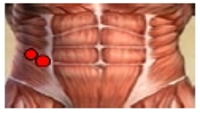

Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of detachable forefoot outsole on muscle activity of the lower extremity during downhill walking. Methods Thirteen male university students (age: 23.5±2.1 yrs, height: 175.7±4.6 cm, weight: 651.9±55.5 N) who have no musculoskeletal disorder were recruited as the subjects. Each subject walked down 20° ramp with forefoot’s design for the detachable outsole’s angle(5°, 10° and 20°) and type(A and B). To assess the myoelectric activities of selected muscles, six of surface EMG(QEMG8, Laxtha Inc. korea, sampling frequency = 1,024 Hz, gain = 1,000, input impedance > 1012 Ω, CMRR > 100 dB) electrodes with on-site pre-amplification circuitry were attached to ES, RF, BF, TA, LG, and MG. For each dependent variable, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to determine whether there were significant differences among forefoot’s design for the detachable outsole’s angle and type (p<.05). When correlation effect was not statistically significant, post hoc analyses were performed using the multiple comparison through bonferroni, and if correlation effect was statistically significant, one-way ANOVA was performed as for the form of outsole which is an inter-group variable in order to find out simple main effect, and the paired t-test was performed to find out the angle of outsole, which is an intra-group variable. Results In IDLS phase, In terms of Rectus Femoris, 10°-B outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 5°-B, 5°-A outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 5°-B, 20°-A outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 20°-B. Among these outsoles, Conclusion 5°-B outsole was found to the most useful outsole for improving stability and controlling the bodily movement due to the body weight load when walking down the ramp.







