
Purpose The purpose of this study is to empirically inquire into the relationship between a commercial sports center employee's humor orientation & customer orientation and employees' trust, service quality, sports center relationship quality and relationship retention through structural equation model analysis. Methods For this purpose, the survey targeted 224 adult men and women who have used any one of the three commercial sports centers in Chungcheong for over three months. For sampling method, convenience sampling method was used, while the questionnaire was self-administered. In an effort to verify the proposed structural model, this study used IBM SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. Results First, humor orientation was found to have a positive influence on employees' trust. Second, customer orientation was found to have a positive influence on employees' trust. Third, employees' trust was found to have a positive influence on service quality. Fourth, employees' trust was found not to have a positive influence on sports center relationship quality. Fifth, employees' trust was also found not to have a positive influence on relationship retention. Sixth, service quality was found to have a positive influence on sports center relationship quality. Seventh, service quality was also found not to have a positive influence on relationship retention.


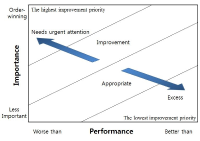
Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify the importance and satisfaction of service quality of visitors to screen baseball using the Importance-Performance Analysis. Methods Selected visitors who participated in screen baseball using convenience sampling of non-probability sample method from January 26 to May 27, 2017, and conducted a questionnaire survey to a total of 213 data were used in this study except 17 data which were untrustworthy responses or non-responses. SPSS 21.0 statistical program were used to exploratory factor analysis, reliability analysis, frequency analysis and IPA. Results The results were as follows. first of all,Ⅰquadrant derives 7 items including modernized facilities and equipments. Next, Ⅱ quadrant, there are 5 credibility of the program and continuous service provision. Also, in the quadrant Ⅲ, the service promised to the customer and the interest and effort of the staff in case of trouble were confirmed.. In the quadrant IV, four items were analyzed such as the interest in the members and the matching of the members' use time. In the analysis of Slack's(1994) diagonal model, twelve kinds of improvements such as costumes, appearance, internal facilities and services promised to customers were derived. In addition, there are 5 appropriately provided properties such as modern facilities and equipment, and facilities suitable for enjoying baseball. Finally, in the attributes that are provided in excess, four attributes are indicated, attention to members and matching of members' use time. Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it is meaningful to be a marketing and management practice data for operating the screen baseball.



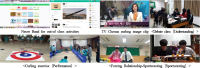
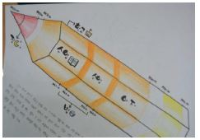
Purpose The purpose of this study was (1) to develop and to apply flipped learning strategies in Physical Education(PE) classes based on Sportscasting Model and (2) to examine the responses of students after PE lesson. Methods Participants were 10th high school students(N=216, male=115, female=101) in high school. Instruction strategies of flipped learning was developed after theoretical investigation, and the unit plans for curling and instructional materials were developed and applied. Open-ended questionnaires and in-depth interviews were used to collect the data. Qualitative content analysis combined with of structures in lesson was used to analyze the data. Results Results showed that (1) 11 instruction strategies of flipped learning were developed, (2) and the unit plan combining out-of class activities and in-class activities organically based on Sportscasting Model and instructional materials for unit of curling were developed and applied. In step of sportscasting, forcing relationship method-sportscasting based on the survey of students was developed and applied. (3) And 31 factors of Sportscasting Model and 15 factors of flipped learning were drawn from the analysis of questionnaires and interviews. Conclusion And to conclude, this research has a value of early study to develop and apply instruction strategies of flipped learning, the unit plan and instructional materials for combining Sportscasting Model with flipped learning organically. Discussions were provided in terms of the development of flipped learning applied in PE classes and responses of students.


The purpose of this study was to explore Physically Activity Lifestyle pattern & constraints of high school girl in city, and then to propose P.A. promotional ways. I used International Physical Activity Questionnaire Long version and accelerometer to examine outline of P.A. pattern, and photo-voice as qualitative research techniques. The results were as followings. First, sedentary lifestyles of students in G girls' high school was terrible. Accelerometer was said that their inactive time were about 92.4%, however their moderate to vigorous time about 0.76% of the total time of a week. And, school domain of four domains(school, transportation, leisure, domestic chores) were the most active domain of all. Second, P.A. constraints were analyzed as 'because of something no'(time, effort, will, space, physical skills and person) and 'because of something'(smart phone, car, gaze, rules). The key cause were a shortage of time caused by academic based on school curriculum, sedentary leisure and transportation culture. Lastly, I proposed high school girl' P.A. promotional ways in basis of social ecological model.










PURPOSE This study examined the cultural experiences of tennis club members that have changed due to COVID-19, specifically emphasizing the accepted culture within these clubs. METHODS Seven tennis club members, with over five years of experience, active participation in two or more clubs, and a history of active participation, were interviewed using in-depth interviews and a semi-structured questionnaire. RESULTS Firstly, the tennis club members accepted the “no contact” culture that has emerged since COVID-19. Secondly, social distancing made getting together in large groups difficult, and tennis club activities became more limited. This has led to weakening the tennis club community, which is different from what we have seen before. Lastly, the growing interest in non-traditional content has led to an increase in participants enjoying tennis through social media. The information and experiences gained through social media have changed the perception of coaching. CONCLUSIONS The cultures that tennis players have adopted due to COVID-19 are expected to continue in the future. The findings from this study may provide evidence for understanding the changing culture of sports in the future.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of field and on-ice performances of ice-hockey players and the relationship of performance with subjective joint pain and dysfunction. METHODS A total of 25 male college icehockey players were evaluated for 19 items of performance. Pain and dysfunctions in the lower extremities and lower back were confirmed through the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score, Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, Hip Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, and Osweatry Disability Index questionnaire. Players with similar performance characteristics were classified through a cluster analysis, and differences in performance and patient-reported outcomes between clusters were analyzed with a one-way analysis of variance. RESULTS The ice-hockey players were classified into “lower muscular strength and performance (cluster 1),” “lower cardiorespiratory endurance (cluster 2),” and “high muscular strength and performance (cluster 3).” Players in cluster 1 had more frequent ankle and knee joint dysfunctions and pain compared to those in cluster 3. Several performance test items affected the subjective joint score, and the related performance items were more in the proximal joint than in the distal joint. CONCLUSIONS Ice hockey players should perform training to supplement their individual lack of on-ice and field performance. Since performance may be limited because of joint dysfunction and pain, a joint-specific intervention strategy should be applied to improve physical and athletic performances.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to compare the dynamic postural control of youth athletes with and without a history of lateral ankle sprains. METHODS Twenty-eight youth athletes (14 lateral ankle sprain, 14 healthy control) participated in this study. All participants answered the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure questionnaire and were subject to the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) for dynamic postural control evaluation to collect the joint angles of the lower extremity, a center of pressure (COP) path, and COP velocity. Independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test were performed to analyze the difference between the groups. RESULTS The lateral ankle sprain group (LAS) was found to have a long experience in participating in sports, and low Foot and Ankle Ability Measure scores were identified when compared to the healthy control (CON; p<0.05). LAS was observed with a short reach distance, less hip flexion, and dorsiflexion angles during the anterior direction of SEBT when compared to CON (p<0.05). Furthermore, LAS showed a slower anteroposterior and mediolateral center of pressure velocities in the posteromedial aspect of SEBT and a slower anteroposterior COP velocity in the posterolateral aspect of SEBT when compared to that of CON (p<0.05). There were no differences between the groups with respect to the other variables (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, decreased anterior reach distance of SEBT may be affected by changing the dynamic posture control strategy of the lower extremity joint on the sagittal plane in LAS.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify movement pattern differences in the running of youth soccer players with and without lateral ankle sprain (LAS) histories. METHODS A total of 12 participants were recruited and assigned to the LAS group or the control group. All participants were assessed for anthropometric data, and they filled in the subjective ankle function questionnaires. Then, reflective markers were attached to their bodies, and they were instructed to run at the preferred speed on the 9-m runway thrice. 3D joint angles for ankle, knee, and hip joints were exported, and their mean values and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Ensemble curve analysis was conducted to compare running kinematics between the groups. RESULTS The LAS group exhibited fewer dorsiflexion angles and more inversion angles compared to the control group. Excluding the dorsiflexion deficits and more inverted ankles, there were no significant differences between the groups. CONCLUSIONS Although the ankle kinematic patterns found in this paper are not considered LAS risk factors, it will be able to identify precise LAS risk factors with prospective design (e.g., lower extremity movement patterns) as well as intrinsic risk factors.
PURPOSE Taekwon gymnastics is expected to be a program that can overcome the management difficulties currently faced by Taekwondo gyms and contribute to the expansion of Taekwondo base. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship among organizational identification, flow experience, intention to continue participation, and recommendation intention of Taekwon gymnastics participants. METHODS In this study, data was collected from 313 teenagers participating in Taekwon gymnastics at Taekwondo gyms in the metropolitan area from September 10 to 24, 2021. A total of 267 questionnaires were selected as the final sample, and data analysis was conducted using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. RESULTS Organizational identification had a significant effect on flow experience, challenge only had a positive effect on intention to continue participation, flow experience did not significantly affect recommendation intention, and intention to continue participation had a significant effect on recommendation intention. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study confirmed that organizational identification can contribute to improving inner pleasure and self-esteem, and it is necessary to examine the role of factors that can mediate the relationship between flow experience and behavioral intention in the future. Furthermore, managers of Taekwondo gyms should hold various events that can inspire teenagers’ sense of challenge to encourage intention to continue participation.
PURPOSE This study was conducted to investigate changes in stress before and after elite shooting athletes participate in a match, and to find out the effect on the match score. METHODS Thirty-wight elite shooting athletes were sampled, questionnaires were distributed to measure psychological stress before and after the match, and saliva was collected before and after the match to measure cortisol. In addition, psychological stress and changes in cortisol before and after the game were investigated, and how psychological stress before and after the game and cortisol affect the score of the game were investigated. Accordingly, a statistical analysis based on data analysis was conducted, and the following research results were obtained. RESULTS The pre-match analysis of psychological stress and cortisol revealed statistically significant changes; both post-match stress and cortisol decreased compared to before the match. Increased psychological stress and cortisol both before and after the match had a negative effect on the match score. CONCLUSIONS These findings confirmed that shooters experience very strong psycho-physiological stress before the match, and the stronger the psychological stress, the lower the game score.