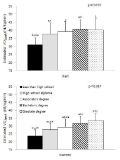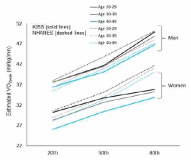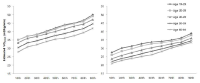
To provide the distribution of cardiorespiratory fitness including Bruce treadmill exercise time and estimated peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and investigate association with cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic syndrome, sedentary lifestyle, or education level among Korean adults. Analysis of data on 2,006 adults (19-64 yr) who had completed a maximal grade treadmill exercise test, from the Sports Institute of Sports Science Fitness Standards (KISS FitS) project 2014-2015. The mean maximal exercise time was 11’26’‘, 11’18’‘, 11’06’‘, 10’03’‘ and 8’51’‘ (minutes and seconds) for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, for women, it was 9’49’‘, 9’09’‘, 8’42’‘, 8’01’‘ and 7’33’‘ for the corresponding age groups. The mean peak oxygen uptake was estimated as 42.3, 41.8, 41.2, 37.6 and 33.6 ml/kg/minute for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, For women, it was 34.0, 31.8, 30.3, 28.0 and 26.4 ml/kg/minute for the corresponding age groups. A positive association between cardiorespiratory fitness level and education level was observed for both men and women. Furthermore, participants with sedentary lifestyle had a significantly lower cardiorespiratory fitness than participants with activity lifestyle. Finally, Men with moderate and high fitness level had 50% and 87% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, and women had 48% and 50% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, respectively, than the ones with low fitness level after adjustment for age, smoking, alcohol intake, and sedentary lifestyle. These results can be used to track future Korean assessments and to evaluated interventions. The differences in fitness status by education level, sedentary lifestyle or metabolic syndrome can also be used to develop health policies, program and educational services.