
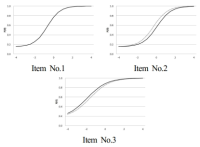
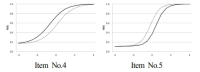
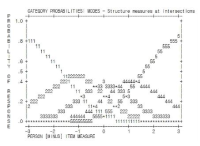
The purpose of this study was to analyze and confirm whether the items used in final paper and pencil test was determined to DIF when school sports clubs in each school operated by discriminatory curriculum in accordance with gender. Participants were 8th middle school students(male=135, female=141). They joined in school sports club every week from freshman to sophomore 1st semester. At that time, boys of them participated in soccer and basketball, and girls played dodge ball. They studied soccer unit at sophomore 1st semester, and had a final examination consisting of 5 soccer items. Using the data, differentially functioning item by the population difference between male and female were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. The results showed that Mantel-Haenszel method(using classical test theory), comparison of item characteristic curve and likelihood ratio test(using IRT) determined item number 4 and 5 to differentially functioning item. Finally, item number 4 were identified differentially functioning item in favor of male students in intensive qualitative analyses. That item have low content validity and application-level of cognitive behavior classification. The result provides that application-level item can be functioning differentially to female students with little sports experience than male students in paper and pencil test of PE.





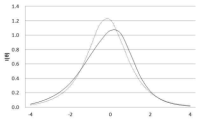

Sport Imagery Questionnaire of Hall et al.(1998) was developed to investigate the imagery type of athletes objectively. The purpose of this research is to verify validity and reliability of Korean SIQ by using Rasch Model, in order to make up for complement drawback of SIQ which was developed only using factorial analysis. This research conducted first and second questionnaire survey. Second survey was conducted targeting different study participants from those of first survey. The participants of first survey was 265 athletes of Chungcheong Province, and the participants of second survey was 169 athletes of Chungcheong Province. SPSS 21, Winstep 3.62, and AMOS 18 was used for date analysis. The result of Rasch Model verification for the data of first survey revealed that 8 items of SIQ were unfit. Thus, 5 factors and 22 items were determined. 7 point Likert scale was revealed to be a good fit. The result of Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data of second survey revealed that Construct Validity of 5 factors and 22 items was valid and reliability was high by recording Cronbach’α value .954. External Validity was revealed to be high by showing that correlation between sport confidence and MG-M imagery was high.

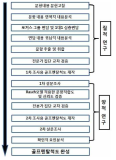
The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.
Purpose Based on Haidt's social-intuitionist theory, this study analyzes the differences in ethical decision-making between sport athletes and the general public in order to understand the ethical judgment tendencies of athletes and examine the determining factors influencing their judgment from the perspective of their environment. In so doing, this study hopes to motivate education for enhancing ethical consciousness as well as institutional policy. Methods To this end, 200 elite athletes in their twenties registered for more than 10 years at the Korean Sports Association and 200 college students in their twenties from five universities in Seoul were selected for comparison. Response trends for each item were analyzed by percentage, and differences between groups were confirmed by the χ2 test method. Results The results are as follows. First, in general ethical situations, athletes usually showed a compulsory ethical view that emphasized principles, whereas in a sports situation, they showed a double consciousness and revealed a very strong consequential ethical view which put much emphasis on outcome. Second, athletes strongly maintained a Confucian ethical view that recognized ethics as a norm compared to the general public and, as a result, it was found that paternalism was relatively stronger than rationalism in their ethical decision making. Third, athletes regarded other people's thoughts and group interests as important criteria for ethical decision-making rather than individual thoughts and interests, and showed a group-centered mindset which emphasized group harmony and relationship. Fourth, while the general public viewed excellent athletes as those with excellent skills and good personality, and valued their morality, athletes thought relatively little of the influence and importance of morality in their success. Finally, it was found that coaches and managers were fundamental to the formation of the athlete’s moral view. Conclusion An in-depth understanding of sports participants' ethical awareness should come first in order to enhance ethical consciousness in sport. I hope this study will work as a catalyst for research which approaches athletes' ethical consciousness from a socio-cultural context.