The purpose of this study was a investigate the endothelial function of prehypertensive during dynamic exercise. Hypothesis of this study was to impair the endothelial function in prehypertensive compared to normtensive during dynamic handgrip exercise. Eleven healthy prehypertension (24±2 yrs) and ten healthy normotensive (25 ± 2 yrs) were recruited in this study. Participants were performed dynamic handgrip exercise in one contraction per second at 30% of maximum voluntary contraction for three minutes. Vascular (blood vessel diameter, blood flow) and cardiar response (stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output) were measured at rest and during exercise. Flow mediated dilation (FMD) was decrease significantly in prehypertensive less than normotensive (p<0.05) at rest, and vasodilation of prehypertensive was reduced significantly less than normitensive during exercise (p<0.05). All the cardiovascular responses were aot significantly different at rest and during exercise between prehypertensive and normotensive. These results suggest that endothelial function is impaired in prehypertensive compared to in normotensive

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of a 10-week aerobic exercise training on cardiovascular function, atherosclerosis, and vascular endothelial function in elderly women. Methods Twenty impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and normoglycemic elderly women volunteered to participate in the study. The participants in aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=9) completed 20-40 minutes of aerobic exercise program at 30-50% HRR for 3 times per week during 10 weeks. The participants in control group (CON: n=11) were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) There were no significant main effect or interaction in body weight, fat-free mass, fat mass, percent body fat, and body mass index. 2) There were no significant main effect or interaction in heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance (TPR), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial blood pressure, pulse pressure, and rate pressure product. However, interaction between group and test in TPR was close to statistically significant level (P =.054), and it tended to be decreased in TR group. 3) There was a significant main effect of test in high sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP), it tended to be decreased in TR group. There were no significant changes in total cholesterol(TC)/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, triglyceride/HDL-C ratio, and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol/HDL-C ratio. 4) There were significant main effect of group, main effect of test, as well as interaction between group and test in % flow mediated dilation(FMD), and it increased significantly (P<.01) in TR group. Nitric oxide tended to be increased in TR group, even though it did not change significantly in both groups. Conclusions It was concluded that the 10-week aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of vascular endothelial function, resulting from the decrement of total peripheral resistance.
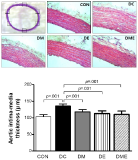
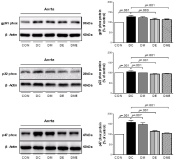
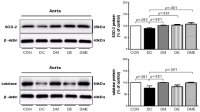
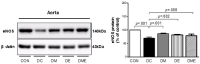
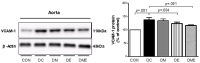
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment on NADPH oxidase, antioxidation and vascular function-related factors in aortic of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Methods To induce the animal model of aging, D-galactose was diluted in saline, and a dose of 100mg /kg was intraperitoneally injected into Sprague-Dawley rats once a day for a total of 10 weeks. Rats were divided into five groups: Control group (CON, n=9), D-galactose control group (DC, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ group (DM, n=9), D-galactose+Exercise group (DE, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ + Exercise group(DME, n=9), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 5 days/week during 8 weeks with gradual increase of intensity. MitoQ treatment was intraperitoneally injected at a concentration of 100μM/kg twice a week for 8 weeks during the research period. Results The result showed that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment decreased the expression of NADPH oxidase level and increased antioxidant enzyme such as SOD-2, catalase. It lead to positive effects such as increasing the level of eNOS, a protein involved in vascular function while decreasing the level of VCAM-1. In addition, as a result, it showed the structurally reduced intima-media thickness. Conclusions It can be concluded that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment are effective in ameliorating and treating vascular dysfunction resulting from aging.