The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship of obesity index, fitness and cardiovascular risk index in middle and high school students. Obesity index, fitness score and cardiovascular risk index were measured from 1,044 middle and high school students. The results of relation between obesity index and fitness showed that the higher obesity index had significantly lower fitness score for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.05) The results of relation between obesity index and cardiovascular risk index indicated that the higher obesity index had significantly higher cardiovascular risk index for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.001). Moreover, The lower fitness index showed significantly higher cardiovascular risk index regardless of gender in middle school students (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.01). Therefore, the results of this study indicated that obese adolescents had the lower fitness level and high possibility of cardiovascular risk.
Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.

Purpose This study was designed to investigate the effects of weight-bearing exercise and CareRing treatment on cardiovascular responses, popliteal vein functions, and vascular elasticity of 30-40s women who had worked longer than eight hours a day in a standing position. Methods Thirteen subjects participated in 30 min of standing up treatment (STAND), weight-bearing exercise treatment (EX), and weight-bearing exercise with CareRing treatment (EX+RING). Each subject took part in the three trials repeatedly in a counter-balanced order and proceeded with a wash-out period of at least one week between the respective trials. Results The main results were as follows: 1) Significant reduction in EDV, no change in the diameter of popliteal vein, trend of reduction in blood flow of popliteal vein, and increased baPWV, indicating reduction of vascular elasticity of whole body, were shown in the STAND. 2) CO and EF increased significantly, and TPR decreased significantly in the EX. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of popliteal vein increased significantly, and baPWV decreased significantly from immediately after the treatment throughout the recovery phase in the EX. 3) HR, CO, and EF increased significantly in the EX+RING. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume increased significantly in the EX+RING. Diameter of popliteal vein increased significantly immediately after the treatment and decreased significantly at 40 minutes of recovery. TPR and baPWV decreased significantly immediately after treatment compared to the STAND. Conclusions It was concluded that weight-bearing exercises would be effective in preventing venous or cardiovascular diseases occurred due to long-standing in 30-40s women, who are at high risk for such diseases. Furthermore, it would be more effective to combine pressure treatment with CareRing during weight-bearing exercises.

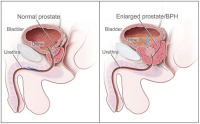
Purpose Prostate problems, such as prostate cancer, and benign prostate hyperplasia have been recognized as problems largely related to androgens and genetic factors. They affect a large fraction of the elderly population, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate a therapeutic strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Methods In order to determine the therapeutic exercise strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia, previous literature was reviewed with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results Prostate cancer and its associated treatments can cause significant and lasting morbidities, such as cardiovascular and sexual dysfunctions. Various interventions have attempted to prevent or mitigate these dysfunctions. This review summarizes the available evidence concerning the effects of exercise training on male sexual health in the cancer prevalent population. Smoking cessation, regular exercise, and maintaining healthy weight are important public health targets for intervention. Importantly, several lifestyle modifications may lower the risk of developing more aggressive cancer or offer survival benefits to prostate cancer patients. Conclusions In this review article, physical exercise training can increase apoptosis markers in the prostate, suggesting exercise training as a potential novel therapeutic strategies for treating prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Future studies in more advanced and varied prostate cancer populations are required to ascertain the duration, intensity and frequency of exercise that optimizes the effects of exercise training on prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia.
