PURPOSE This study compared the spatiotemporal gait parameters and kinetic variables of lower extremity joints during gait between normal and presarcopenia groups of middle-aged women. METHODS Middle-aged women participants (n=24) were divided into two groups based on the Appendicular Lean Mass Index (ALMI): a normal group (n=12) and a presarcopenia group (n=12). During walking by each group, spatio-temporal gait variables and the maximum moments and net joint power of the ankle, knee, and hip joints in different directions were calculated and compared using independent samples t-tests with IBM SPSS 27.0 software. RESULTS The normal group and the presarcopenia group showed no statistically significant differences in spatiotemporal gait variables. However, during the shock absorption phase of gait, the presarcopenia group showed significantly higher maximum knee abduction, maximum knee internal rotation, and maximum hip external rotation moments than the normal group. Additionally, the presarcopenia group exhibited significantly higher maximum net knee power during the shock absorption phase. Conversely, during the propulsion phase of gait, the normal group exhibited significantly higher maximum net ankle power than the presarcopenia group. CONCLUSIONS Middle-aged women with presarcopenia experienced higher knee joint loading and lower ankle joint propulsion during walking, indicating the need for training to improve lower limb strength.
Purpose The study was designed to compare physical fitness, indices of lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle according to sarcopenia and obesity in elderly women. Methods One hundred elderly women were alloted to one of four groups, i.e., sarcopenia+obesity (SO: n=20) group, sarcopenia (S: n=20) group, obesity (O: n=29) group, and normal (N: n=31) group. Criterion for sarcopenia was 'appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM)/height2<5.4 kg/㎡', and criterion for obesity was 'percent body fat>35%'. Dependent variables regarding physical fitness, lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle were measured and compared among four groups. Results 1) Regarding daily living fitness, grip strength, upper arm flexion, sit-and-reach, up and go, and VO2max in SO group and S group were significantly lower than N group. Regarding isokinetic function, peak torque and average power in SO group and S group were significantly lower, and relative values to body weight in SO group and O group were significantly lower than N group. 2) Regarding hypertension, resting HR and RPP in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding hyperlipidemia, HDL-C in SO group and O group were significantly lower than S group and N group. Regarding atherosclerosis, TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. 3) Regarding biochemical property of muscle, IL-6 in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Conclusion It was concluded that physical fitness was declined in sarcopenia elderly, and that relative value of isokinetic function, indices of lifestyle disease, and inflammation markers were deteriorated in obesity elderly. Especially, the decline and deterioration of physical fitness and indices of lifestyle disease were even more severe in the elderly who had the both status. Therefore, the efforts should be made to prevent and improve sarcopenia and/or obesity.

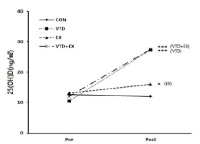
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of 12-weeks of vitamin D supplementation and circuit training on skeletal muscle mass in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency. Forty eight elderly women with type-2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency were randomly assigned to control(n=10), vitamin D supplement(n=11), exercise(n=12), and vitamin D supplement+exercise(n=15) groups. Dependent variables were measured before and after the 12-week interventions. Major outcomes included body composition, fasting glucose, insulin, and 25(OH)D concentration. ASM(apeendicular skeletal muscle mass), SMI(skeletal muscle mass), and HOMA-IR (homeostasis model for insulin resistance) were calculated. Women assigned to the vitamin D supplement consumed 1,200 IU of vitamin D orally per week for 12 weeks. Women assigned to the exercise intervention performed a circuit training at an intensity of 60%~80% of HRmax with a frequency of 3 days per week for 12 weeks. Compared to control group, all groups had significant loss of body weight and increases in serum 25(OH)D after the 12-week intervention. ASM and SMI increased significantly in only vitamin D+exercise group. Regardless of treatments, no significant group differences were found in changed scores of fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR. In conclusion, vitamin D + exercise would improve the loss of ASM and SMI compared with vitamin D or exercise alone.

PURPOSE This study investigated the impact of underweight and hand grip strength (HGS) levels on the risk of all-cause mortality in older adults. METHODS Data from the 2006 baseline and 2020 follow-up assessments of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA), involving 3,009 older Koreans (≥65 years) were used in the study. Participants were categorized based on body mass index (BMI) as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese and grouped according to the Asian Working Group Sarcopenia criteria into high or low HGS. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of all-cause mortality according to BMI and HGS categories. RESULTS During the 11.3±4.0 years follow-up period, 1,334 deaths from all causes occurred. The risk of death by BMI and HGS level was analyzed. The results showed that the risk of death in the overweight and high HGS group (HR=0.773, p=.016) was significantly lower than that in the normal weight & high HGS group (HR=1). In comparison, the risk of death in the underweight & low HGS group (HR=1.930, p<.001) and the normal weight & high HGS group (HR=1.225, p=.014) were significantly higher than normal weight & high HGS. However, the risk of death in the underweight and high HGS group showed no significant difference compared to the normal weight and high HGS group. CONCLUSIONS The current findings suggest that improving muscle strength through regular exercise may be important in preventing the risk of all-cause mortality due to being underweight.