Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect of push-up plus exercise(PUPE) on stabilization of the scapula and to use it as basic data for shoulder rehabilitation program. Methods In this study, research papers were collected using Research Information Sharing Service(RISS) and Pub-Med Central.(PMC) as a search term for scapular stabilization, push - up plus, shoulder joint injury rehabilitation and scapular stabilization exercise. Also, it was used as basic data of literature analysis. The collected data were classified into the structure and movement of the scapula and shoulder, kinesiologic relation of the scapula and the mechanism of injury, and the effect of push-up plus Results Serratus anterior is a typical stabilizing muscle, and it forms a force couple with the upper and lower trapezius to control the movement of the scapula. The PUPE is an effective exercise method to selectively strengthen serratus anterior, which are the stabilizing muscles of the scapula, and is an exercise method that is also useful for correcting the wrong postures and movements because of hypertonus upper trapezius. In addition, various conditions such as application posture, arm position, and ground instability were suggested during PUPE. Conclusion The results of this study confirmed that PUPE is an effective program for scapula stabilization in the rehabilitation of shoulder injuries and injured patients and athletes. The PUPE will be used as a rehabilitation exercise program for patients and athletes who need rehabilitation of the shoulder joint.

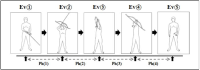
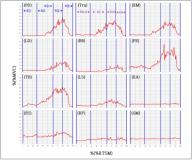
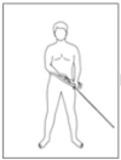
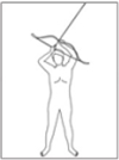
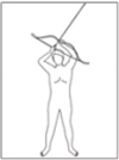
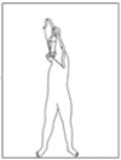
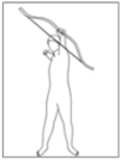
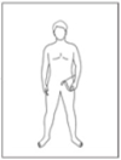
The past few decades has seen increasing kinematic studies using surface electoromyography (EMG) in archery, however there has been no such specific study in Korean traditional archery. The purpose of this study was to evaluate EMGs during archery shooting motion in Korean traditional archers. Ten men Korean traditional archers were participated, and divided into two groups according to the shooting stance; parallel stance group(PSG, n=5) and oblique stance group(OSG, n=5). The surface EMGs were measured 12 muscles during shooting motion of five events including Junbi(Set), Geogung(Set up), Manjak(Full draw), Balsi(Release), Machigi(Ending). At the result, muscle activity of posterior deltoid, trapezius, rhomboid major, latissimus dorsi, biceps brachii, forearm extensor bundle, triceps brachii, levator scapulae significantly increased at event of full draw and release, then significantly decreased again at event of ending, respectively(p<.01, p<.001). The muscle activity of erector spinae(ES) was also significantly increased at event of full draw and release(p<.01, p<.001), while no significant changes in muscles of rectus abdominis, rectus femoris(RF), gluteus maximus. As a result of comparing PSG and OSG, muscle activity of RF in OSG was higher than PSG at event of release(p<.05), it remained until event of ending(p<.05). On the other hand, the higher the tension of the bow, the higher the muscle activity of the draw arm at event of release(p<.05). These results suggest that when Korean traditional archery shooting, both side arm and back muscles are more activated than the abdomen, leg and hip muscles. The parallel stance might suppress the muscle activity of the lower extremities to twist the upper body. And the higher bowstring tension needs to increase of muscle strength in BB of draw arm.