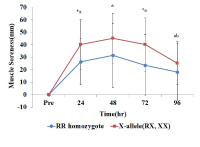
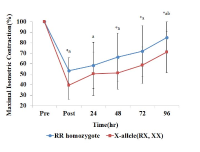
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the change of muscle damage markers after maximal eccentric exercise and to verify the difference of recovery according to ACTN3 gene polymorphism. [Methods] Fifty healthy males participated in this study. Subjects performed 25 times/1 set (total 2 set) maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexor muscles on a modified preacher curl machine with a between-sets rest time of 5 min. Maximal isometric contraction (MIC) was measured 6 times (pre, post, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Muscle soreness (SOR) was measured 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Blood samples were collected 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). ACTN3 gene polymorphisms were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Data were analyzed using a 2-way repeated measure ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test. [Results] Analysis of ACTN3 gene polymorphism revealed the following distribution: 22% RR (n=11), 50% RX (n=25), and 28% XX (n=14). Individuals were classified into the RR homozygote group (n=11) and the X-allele group (n=39). MIC showed a significant difference between groups and interaction (p<.05). The groups differed significantly in MIC at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after exercise and the X-allele group decreased more than the RR homozygote group. The groups differed significantly in muscle soreness and interaction (p<.05). SOR in the X-allele group was significantly higher than in the RR homozygote group at 24 h after exercise. Although blood CK activity was lower in the RR homozygote group than in the X-allele group, but there was no significant difference between the groups (p>.05). [Conclusion] The RR homozygote group showed lower muscle strength reduction rate, muscle soreness and blood CK activity than the X-allele group. This indicates that RR individuals have a lower risk of exercise-induced muscle damage than those with an X-allele.

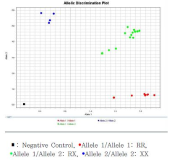
The ACTN3 R577X polymorphism has been associated with an elite athletes status. Several studies have determined that the R allele is connected with power-oriented athletic performance, whereas the nonfunctional XX genotype may give some beneficial effect for endurance performance. The main aim of the study was to determine the possible interaction between the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism and an power-oriented athlete status in Korean elite athletes(wrestling 31, judo 13, boxing 16, fencing 6, cycle 16, ≤400m athlete 18). Each athletes performed a 30-second WAPtest with a resistance equal to 7.5% for male and 5% for female body weight. Genotyping for the ACTN3 R577X (rs1815739) polymorphism was performed using the TaqMan approach. The ACTN3 R577X genotypes exhibited a HardyWeinberg equilibrium distribution in our population. The relative and absolute average power results of the 30-second Wingate test did not differ significantly among the genotypes. However, the relative peak power result of the Wingate test was significantly higher in the R-allele- dominant model groups than in the XX group in male but not female athletes. These results suggest that the ACTN3 R allele is associated with the relative peak power during the Wingate test in male Korean elite athletes.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine the differences in physique and physical fitness factors affecting exercise performance according to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) FokI gene polymorphism in athletic gifted children. Methods FokI VDR polymorphisms were genotyped in 82 boys (9.1±0.9 years) and 55 girls (9.3±0.9 years). Basic physical fitness (basketball throw, half-squat jump, standing long jump, 15m pacer, 50m run, handgrip strength, side-step, trunk forward flexion, sit-up) and physique were measured and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with bonferroni’s correction. Results No association was found between the VDR FokI genotypes and all the physical fitness variables as well as physique variables in boys and girl. However, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium results for VDR polymorphism distribution showed significant differences (χ2= 6.516, df=2, p=.038). Conclusion Although there was no significant difference in the fitness variables according to the VDR Fok1 genotype, it was difficult to exclude the potential for predicting fitness in that the H-W equilibrium test showed a significant difference. Therefore, in order to confirm the true potential of the VDR Fok1 gene to predict physical fitness, it is considered that additional studies on general children should be conducted.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify ACTN3 gene polymorphisms amongprofessional ssireum players by weight class and between elite and non-elite players,and to select genotype that matches the characteristics of the sport. METHODS The subjects of this study were 148 male athletes currently working as professionalssireum players. Chi-square test cross-tabulation analysis was conducted to examinethe differences in ACTN3 genotypes between weight classes and between elite andnon-elite players. RESULTS There were no significant differences in allele or genotypebetween ssireum players, but there were significant differences in R-allele and XXgenotype. CONCLUSIONS Players with the R-allele type of the ACTN3 gene weremore often classified as elite. Using this marker as a basis for organizing a playerselection and training programs would be more effective in training those that matchthe characteristics of elite players of the game.