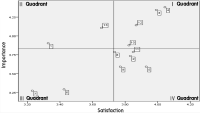
Purpose The purpose of this study is to grasp consumers' perception of badminton racket brand image using MDS and ISA. Methods To do this, we conducted questionnaires on those who participated in badminton and had experience of participating for 6 months or more in Seoul and Gyeonggi province from April 12 to 28, 2017, selected and analyzed a total of 313 copies as valid samples of this study. Results The results of study are as follows. First, as a result of MDS analysis, it showed that only the price of brand image attributes were in order of Trion > Joobong > Lining > Victor > Yonex, and the other attributes(Design, Functionality, Quality, Awareness, Advertising image, Event, Color, Popularity, Sophistication, Originality, Trust, Service) were in order of Yonex > Victor > Lining > Joobong > Trion. Second, as a result of ISA analysis, in I quadrant, Yonex showed functionality, quality, sophistication, and trust and Trion showed price, design, functionality and quality, Victor showed price, design, functionality, quality, color, sophistication, trust, service, and Joobong showed price, functionality, quality, and trust in this area. In quadrant Ⅱ as concentrated area, Yonex showed price and service, Trion showed color, trust, service, Victor showed price, Lining showed trust and service, and Joobong showed service in this area. In quadrant Ⅲ as low rank, Yonex showed advertising image, event, Trion showed awareness, advertising image, event, popularity, sophistication, originality, Victor showed advertising image, event, popularity, originality, Lining showed awareness, advertising image, event, popularity, originality, and Joobong showed design, advertising image, color, popularity, sophistication in this area. In quadrant IV as excess avoidance, Yonex showed design, awareness, color, popularity, originality, Victor showed awareness, Joobong showed awareness, event, originality in this area.







PURPOSE This study seeks to contribute to the enhancement of the performance of domestic wheelchair racers by producing 3D-printed customized gloves and verifying their application effect. METHODS A total of three male wheelchair racers who belong to the T54 and have won gold medals in the National Para Games within the last three years were selected as subjects. Each subject performed three session s of muscle activity and maximum speed measurements before and after applying a 3D-printed glove during the stroke and recovery phases of wheelchair racing, focusing on the pectoralis major (PM), triceps brachii (TB), and erector spinae (ES) muscles. To standardize the muscle activity measurement data, the relative muscle activity level (%) for each section was calculated by maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) for each subject. All maximum speeds of each round of driving were calculated by the average record for comparative analysis. In addition, to verify the effectiveness of applying the 3D-printed glove, the Wilcoxon signed rank test, which is a non-parametric test method, was performed on all measured values using SPSS 24.0. RESULTS This study derived the following results. First, a statistically significant difference was observed in the muscle activity of each major muscle before and after using the 3D-printed glove. In common, an increase in muscle activity of the PM, TB, and ES was confirmed in the stroke section, and an increase in muscle activity of the TB was confirmed in the recovery section. Second, a statistically significant difference was documented in the maximum speed before and after using the 3D-printed glove. When using 3D-printed gloves, the maximum speed increased by 4.57, 3.63, and 1.06km/h for Payer A, and by 5.9, 6.04, and 7.86km/ h for Player B. In the case of Player C, the speed increased by 6.73, 2.27, and 0.83km/h, and all three players improved their maximum speed through the 3D-printed gloves. CONCLUSIONS Our study suggests that the application of 3D-printed customized gloves can have a positive impact on the performance of wheelchair racers. If the application of 3D-printed customized equipment is extended to athletes in a wider range of sports in the future, this could significantly contribute to the improvement of performance in domestic disability sport.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to find effective skin scuba activation factors and to provide basic data that extend the scope of research related to skin scuba. Methods Delphi method was used and the experts were categorized by experts to analyze the results. The questionnaires collected through the 2nd and 3rd delphi surveys were SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Microsoft Office Excel 2013 to calculate mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. The concrete conclusions are as follows. Conclusions First, in terms of organization sub-factor, fostering sports-for-all participants and college club came out to be very effective and followed by cooperation system with Ministry of Public Safety and Security and Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, strengthening cooperation and exchange with other education organizations, initializing new scuba diving education organization management and inspection institution and establishing scuba diving education organization. Second, in terms of facility/equipment sub-factor, factors that cause most effectiveness came out as expanding scuba-diving installation, developing connection system with medical department, enlarging indoor-diving education facilities, improving scuba diving equipment, consecutively. Third, in terms of leader sub-factor, training instructor through leader personality education and verification came out to be the most effective, followed by objectifying professional education institution leader training system, improving leader treatment. Fourth, in terms of program sub-factor, it is found that safety education program as the most effective factor, coming next with environment education/professional manpower training program, developing various programs, lastly, inventing insurance product. Fifth, in terms of advertisement sub-factor, as in order of guiding publics to change their view towards scuba-diving, expanding scuba-diving related events and establishing advertisement system had its effectiveness. Sixth, in terms of policy sub-factor, establishing cooperation system among administration departments came out to be most effective and then improving related law-system.
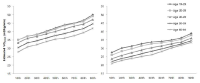
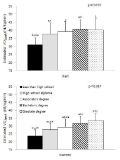
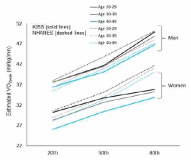
To provide the distribution of cardiorespiratory fitness including Bruce treadmill exercise time and estimated peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and investigate association with cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic syndrome, sedentary lifestyle, or education level among Korean adults. Analysis of data on 2,006 adults (19-64 yr) who had completed a maximal grade treadmill exercise test, from the Sports Institute of Sports Science Fitness Standards (KISS FitS) project 2014-2015. The mean maximal exercise time was 11’26’‘, 11’18’‘, 11’06’‘, 10’03’‘ and 8’51’‘ (minutes and seconds) for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, for women, it was 9’49’‘, 9’09’‘, 8’42’‘, 8’01’‘ and 7’33’‘ for the corresponding age groups. The mean peak oxygen uptake was estimated as 42.3, 41.8, 41.2, 37.6 and 33.6 ml/kg/minute for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, For women, it was 34.0, 31.8, 30.3, 28.0 and 26.4 ml/kg/minute for the corresponding age groups. A positive association between cardiorespiratory fitness level and education level was observed for both men and women. Furthermore, participants with sedentary lifestyle had a significantly lower cardiorespiratory fitness than participants with activity lifestyle. Finally, Men with moderate and high fitness level had 50% and 87% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, and women had 48% and 50% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, respectively, than the ones with low fitness level after adjustment for age, smoking, alcohol intake, and sedentary lifestyle. These results can be used to track future Korean assessments and to evaluated interventions. The differences in fitness status by education level, sedentary lifestyle or metabolic syndrome can also be used to develop health policies, program and educational services.

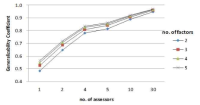
The purpose of this study which is follow up study of Lee and Kim(2015b)'s was to analyse error sources and estimation of reliability in peer review of forced connection method-sportscasting by applying generalizability theory. Generalizability theory quantify error sources of the data measured under certain specific situation set by the researchers. It is an analysis method that the relative influences of each error sources taking from score is determined(G-study), and the effective measurement condition future applicable is provided(D-study). Participants were 10th high school students(N=216). Data were collected from student's peer review results and analyzed using univariate and multivariate generalizability theory. Results showed that error source for video have a more significant impact than other error sources. But the result by analyzing the gender difference was that error source for the interaction of video and participants have a more significant impact than other error source in the case of girls. Peer review used in this study showed high generalizability coefficient and even when reducing the number of video or participants it can maintain the adequate reliability. But generalizability coefficient of boys was higher than girls and specific measurement conditions leading to enhanced reliability were different when analyzing by gender difference. Also, method of analysis which cannot reflect measurement conditions properly estimates the reliability excessive. Discussions were provided in term of the relative influences of each error sources, the effective measurement condition maintaining the Generalizability coefficient of a certain level, and the comparison the Generalizability coefficient with the way of estimation traditional reliability applying univariate and multivariate Generalizability theory taking from score in peer review of forced connection method-sportscasting.