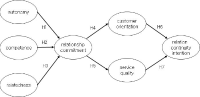
[Purpose] The purpose of this research is to empirically analyze the relationship between self-determination and relationship commitment, customer orientation, service quality, and relation continuity intention of fitness center customers through structural equation model analysis. [Methods] For this purpose, this study set 242 members at the five fitness centers located in Seoul as the research subjects. In an effort to verify the proposed structural model, this study used IBM SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. [Results] As a result, first, autonomy had a positive effect on relationship commitment. Second, competence didn’t had a positive effect on relationship commitment. Third, relatedness had a positive effect on relationship commitment. Fourth, relationship commitment had a positive effect on customer orientation. Fifth, relationship commitment had a positive effect on service quality. Sixth, customer orientation had a positive effect on relation continuity intention. Seventh, service quality had a positive effect on relation continuity intention

Purpose This study examines the regional differences in fall-related physical fitness and fall experience characteristics between Korean and Japanese elderly people. Methods The study includes 176 elderly residents of Gifu(35 male, 73.5yrs; 141 female, 72.4yrs) and 147 residents of Ulsan(46 male, 75.6yrs; 101 female, 75.6yrs). One-legged stance, hand grip strength, knee extension strength, 10 m gait, timed up and go test, 30-s chair stand, sit and reach, and reaction time were measured to examine the fall-related physical fitness. A questionnaire survey was also conducted to investigate the characteristics of the fall experiences. Results The elderly in Ulsan experienced a lot of falls compared to those in Gifu. Many of the fallers in Ulsan have fallen forward due to tripping, and they have often fallen backwards by losing balance. In addition, 14% of them suffered a bone fractured. The one-legged stance, hand grip strength, 10m gait, timed up and go, 30-s chair stand, and reaction time of the elderly in Gifu were superior to those in Ulsan. Conclusion In order to reduce the fall rate through improvements to fall related physical fitness and the awareness of fall prevention, various professional fall prevention programs and policies should be proposed, and they should be implemented systematically for community living elderly people.
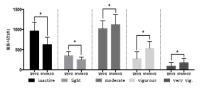
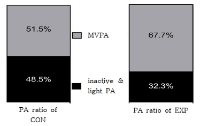
Active participation in Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity(MVPA) is the indicator of healthy development for adolescents. However, Korean adolescents’ MVPA have continuously declined, and Korean adolescents have lower levels of MVPA compared to adolescents in other countries. Considering this issue, the purpose of this study is to examine the effectiveness of SPARK M-SPAN program to promote adolescents’ MVPA in P.E. classes and to understand how the promotion of adolescents’ MVPA occurs. To collect data, this study used Sequential Mixed Method and GT3X accelerometers. A total of 168 adolescents (84 in an experimental group and 84 in a control group) participated in this study for the quantitative data analysis, and six students and a teacher were interviewed for the qualitative data analysis. Paired t-test showed that students in SPARK P.E. classes experienced the significant decreases of sedentary behaviors(-339.6 sec) and low intensity P.A.(-96.9 sec) at p<.05 and the significant increases of moderate(+99.3 sec), vigorous(+252.4 sec), and very vigorous intensity P.A.(+84.7 sec) regardless of gender difference at p<.05 except for female students’ moderate intensity P.A.. The qualitative data analysis showed that SPARK classes gave students positive learning environments and led them to experience enjoyment and achievement-orientated learning Key teaching strategies of SPARK program and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion section.

The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship of obesity index, fitness and cardiovascular risk index in middle and high school students. Obesity index, fitness score and cardiovascular risk index were measured from 1,044 middle and high school students. The results of relation between obesity index and fitness showed that the higher obesity index had significantly lower fitness score for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.05) The results of relation between obesity index and cardiovascular risk index indicated that the higher obesity index had significantly higher cardiovascular risk index for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.001). Moreover, The lower fitness index showed significantly higher cardiovascular risk index regardless of gender in middle school students (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.01). Therefore, the results of this study indicated that obese adolescents had the lower fitness level and high possibility of cardiovascular risk.
It has been known that β-alanine supplementation induce the increment of carnosine in vivo and was effective in delaying fatigue by buffering the hydrogen which was formed during exercise. This study was designed to investigate the effects of 4 weeks of β-alanine supplementation on physical fitness and blood lactate concentration in middle school soccer players. Nineteen middle school soccer players were randomly assigned to either one of two groups, i.e., β-alanine group (n=10) and placebo group (n=9). Subjects in β-alanine group consumed β-alanine 2 g/day during 1st and 2nd week, as well as 3 g/day during 3rd and 4th week, whereas subjects in placebo group consumed maltodextrin in the same manner. All subjects ate same menu and trained same amount at the same training camp during the intervention period. Body composition, aerobic capacity, anaerobic capacity, isokinetic function, and blood lactate concentration during maximal GXT were measured at pre- and post-test. Main results of the present test were as follows: 1) Fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in β-alanine group. 2) No significant changes were found in variables related to aerobic capacity in both groups. 3) Average power increased significantly in β-alanine group. 4) Isokinetic muscular endurance increased significantly in β-alanine group. 5) Blood lactate concentration did not change in eithet group; however, blood lactate concentration immediately after maximal GXT in β-alanine group tended to be increased more than placebo group. It was concluded that β-alanine supplementation would have positive effects for improvement of body composition, anaerobic capacity, and muscular endurance in middle school soccer players.

The purpose of this study was to investigate basal physical fitness and smash speed of elite national badminton players. To perform this study, total forty six korea national badminton player were participated : twenty two male players(age : 20.90±2.24years, height : 179.30±5.40cm, weight : 73.80±7.12kg, career : 11.27±1.88years) and twenty four female players(age : 19.45±1.95years, height : 167.83±4.36cm, weight : 61.39±3.60kg, career : 9.50±2.47years). Each subjects performed the 6 basal physical fitness trials : agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, balance and cardiorespiratory endurance. And the speed of badminton smash were analysis by using radar gun when players were standing smash success. To determine the difference between two groups, independent samples test was used. As a result, we found that there was a large difference male players and female players in basal physical fitness and smash speed. First, male players were significantly strong in agility(side step 10%), muscular endurance(repetitional jump 12%), muscular strength(left grasping power 3%, right grasping power 31%) and cardiorespiratory endurance(20m suttle run 31%). On the other hand, female players were relatively strong in flexibility(sit and reach 27%) and balance(standing on one leg with eyes closed 51%). Second, maximum smash speed show that male players were about 57km/h(24%) faster than female players(male : 247.72km/h, female : 190.37km/h). Based on the findings, we shall be applicable training program to improve flexibility, balance of male athletes and agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, and cardiorespiratory endurance of female athletes. our results will be appliable to improve the athletic performances of national badminton players by the coaches in the future.

PURPOSE This study assessed Taekwondo’s impact on functional fitness and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in older women from South Korean multicultural families. METHODS Through purposive sampling, 16 participants were divided into an experimental group that underwent a 12-week Taekwondo training program and a control group without this intervention. RESULTS Pre- and post-intervention assessments showed that the Taekwondo group experienced significant improvements in both functional fitness and HRQoL. These findings suggest that Taekwondo could be an effective physical activity for enhancing the well-being of older women in multicultural families, advocating for inclusion of culturally sensitive physical activities in health promotion programs targeting this demographic. CONCLUSIONS This study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting physical activity’s benefits for elderly populations, particularly in multicultural family dynamics.
PURPOSE This study investigated the effects of 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox training on physical fitness, badminton skills, and fatigue in male badminton, grade A (top grade) club members aged 20–30s, with over 5 years’ experience. METHODS Participants in a training group (TR: n=15) engaged in 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox circuit training involving maximum 8–12 reps of clubbell exercises and stepbox exercises at over 77% of HRmax for 50–55 min/sessions three times a week. Participants in a control group (CON: n=15) maintained their normal lifestyle pattern during the same intervention period. Dependent variables were measured and compared using repeated measures two-way ANOVA. RESULTS The main results were as follows: 1) The groups showed no significant differences in body composition. 2) Regarding physical fitness, VO2max, relative peak power, relative average power, grip strength, push ups, repeated jump squats, SSPT (seated single-arm shot-put test), 10 m sprint, and hexagon agility increased significantly in the TR, while push ups decreased significantly in the CON. 3) As for badminton skills, forehand clear accuracy, badminton agility, badminton endurance, and smash speed increased significantly in the TR. Forehand clear accuracy decreased significantly in the CON, but badminton agility and smash speed increased significantly. 4) The groups showed no significant differences in fatigue. CONCLUSIONS In male badminton club members aged 20–30s, 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox circuit training effectively improved physical fitness and badminton skills. However, lack of any improvement in body composition and fatigue warranted further research in these areas.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of accelerated rehabilitation exercise on physical fitness, lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables in older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. METHODS A total of 29 older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis residing in G city participated in the study, and 19 participants, excluding dropouts, took part in the experiment. They underwent exercise twice a week for 60 minutes per session over a period of 12 weeks. Pre- and post-experiment, the older adult fitness assessment (SFT), lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables were measured. Data analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0, and paired sample t-tests were conducted to examine the effects before and after exercise. RESULTS The study results showed significant differences in body mass index (BMI) before and after exercise (p<0.05), and the older adult fitness assessment (SFT) showed significant differences in all items (p<0.01). Lower extremity isometric strength showed significant differences in absolute (Nm) and relative (%BW) values of 20° right flexion muscle (p<0.01). In terms of blood variables, significant differences were observed in creatine and ESR before and after exercise (p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS This study’s results suggest that regular physical activity and rehabilitation exercise programs can positively impact the muscular strength, cardiovascular endurance, exercise function, and blood composition of older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. It is indicated that conducting future research, including periodic exercise programs, could be beneficial in promoting sustained exercise participation.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of continuous exercise and the accumulation of short-duration exercise for 12 weeks on body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices in overweight men in their 30s. METHODS Participants in the continuous exercise group (CE; n=13) performed a circuit exercise program of 30 min/session, 3 sessions/week for 12 weeks. Participants in the accumulation of short duration exercise group (ASE; n=12) performed the same exercise time of 30 min per day, divided into three sessions of 10 min. Body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices were measured pre- and post-test and were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, skeletal muscle mass, waist circumference, and fat mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the CE group. Waist circumference and skeletal muscle mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the ASE group. 2) Regarding physical fitness, right grip strength, sit and reach, sit up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in both groups. 3) Regarding hypertension indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but they showed a tendency to improve. 4) Regarding hyperlipidemia indices, triglycerides (TG) decreased significantly in both groups, and total cholesterol (TC) decreased significantly in the CE group. 5) Regarding diabetes indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but a tendency to improve was noticed. 6) Regarding arteriosclerosis indices: TG/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in both groups, and the TC/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in the CE group. CONCLUSIONS We concluded that both the accumulation of short duration exercise and continuous exercise can be effective in improving body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease in overweight men.