PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate how a 10-week online live Pilates training held during the COVID-19 pandemic affected body composition, cardiovascular function, and physical fitness in sedentary middle-aged obese women. METHODS Thirty obese women, aged 30 to 49 years (BMI : 25kg/m2 or more; waist circumference: 85cm or more) who were leading a sedentary lifestyle for more than 8 hours a day were assigned to one of two groups—that is, the Pilates training group (TR) and the control group (CON). Four participants were dropped from the study during the intervention period. Participants in the TR group (n=13) performed online live mat Pilates exercises (3 sessions per week; 60 minutes per session for 10 weeks, whereas participants in the CON group (n=13) were asked to maintain their normal lifestyles during the same intervention period. Independent variables related to body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, physical fitness, and 1-RM (repetition maximum) were measured at pre-test and post-test, and data were compared between the two groups and between the two tests. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, fat mass, and waist circumference decreased significantly in the TR group. 2) Regarding cardiovascular function, stroke volume and cardiac output increased significantly in the TR group, and total peripheral resistance decreased significantly in the TR group. 3) Regarding venous function in the lower body, blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of the parenchyma area increased significantly in the TR group. 4) Regarding physical fitness, cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, flexibility, and balance improved significantly in the TR group. 5) 1RM of biceps curl, lat pull-down, leg curl, and leg extension increased significantly in the TR group. CONCLUSIONS It was concluded that the 10-week online live Pilates training had positive effects on the body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, and physical fitness of middle-aged obese women leading sedentary lifestyles.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the dynamic posture stabilization and kinematic variables between visual feedback and Y-balance training groups during jump-landing. METHODS Thirty-eight male players (age: 22.6 ± 1.12 years, height: 175 ± 3.54 cm, weight: 65.5 ± 5.11 kg) were included in this study, and chronic ankle instability was checked using Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) and Balance Error Scoring System (BESS). They were randomly assigned to the Visual biofeedback (Training group: TG, n = 19) and Y-balance groups (Control group: CG, n = 19) for four weeks. TG performed balance training using the Biodex balance system (BBS) and CG performed training using the Y-balance system. During jump landing, time to stabilization (TTS), force plate (COP, GRF); joint angle and moment were collected and analyzed. All analyses were performed with SPSS 21.0, and Bonferroni was used for repeated measured ANOVA and post-hoc. RESULTS The results indicated that there was an interaction between TG and CG in terms of AP and ML directions of TTS (p < 0.05). AP/ML TTS of the TG for the post-test was smaller than that for CG (AP: p = 0.000; ML: p = 0.046). ML TTS of the TG for post-test was smaller than at pre-test (p = 0.041), and AP TTS of the CG for ankle joint moment (p < 0.05). There was an interaction between TG and CG in terms of dorsiflexion (DF) and plantarflexion (PF) of joint moment (p < 0.05). Ankle moment of the CG for post-test decreased than at pre-test (DF: p = 0.040, PF: p = 0.032), and ankle dorsiflexion moment of the CG for post-test was decreased than at pre-test (p = 0.046). CONCLUSIONS Balance ability was achieved more effectively through visual biofeedback training than Y-balance training. Therefore, we recommend balanced training with visual feedback on chronic ankle instability.
PURPOSE Blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive individuals is reduced by the accumulation of post-exercise hypotension (PEH) induced by a long period of training. This study aimed to investigate the effects of intensity of two different aerobic exercises with identical energy expenditure on post-exercise blood pressure and cardiovascular function in prehypertensive men. METHODS Eleven prehypertensive men in their 30s participated in two trials repeatedly. In the first trial, the exercise was moderate in intensity and continuous (MICE) with 70% of VO2max, and the exercise in the second trial was high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) with 50% and 90% of VO2max. Each exercise was performed for 30 min, and the variables related to BP and cardiovascular function were measured at certain times for 1 hr during the recovery phase. RESULTS Our main findings are as follows: (1) Systolic blood pressure was significantly lower at 30 and 45 min of recovery time than the baseline in the HIIE trial, and systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 10, 15, and 30 min of recovery time. (2) The rate pressure product was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (3) The heart rate was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (4) Stroke volume was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 30 min of recovery time. (5) Cardiac output was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 min of recovery phase. (6) Total vascular conductance was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. (7) Total peripheral resistance was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. CONCLUSIONS The HIIE shows a higher cardiovascular stress than MICE; however, HIIE contributes to the augmentation of PEH and improvement of cardiovascular function. Therefore, HIIE rather than MICE should be suggested in BP control and enhancement of cardiovascular function in prehypertensive males.

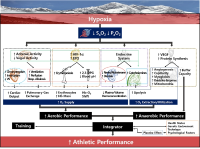
Purpose The purpose of this study is to emphasize the need for the establish and the use of altitude training center via examining exercise training method in natural or artificial altitude environment that is applied to various elite athletes in various advanced countries to maximize exercise performance and its effectiveness. Results Altitude training in natural or artificial altitude environment enhances aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance baesd on the hematological and nonhematological adaptations to hypoxic conditions. These altitude training methods can be classified into living high training high (LHTH), living high training low (LHTL), and living low training high (LLTH). LHTH (i.e., developed since the 1968 Mexico Olympics) and LHTL (i.e., developed in the 1990s by Levine and Stray-Gundersen) improve exercise performance via hematologic changes through erythropoiesis such as increased hemoglobin mass and erythrocyte volume. On the other hand, LLTH (i.e., has been developed variously since the 2000s) is composed continuous hypoxic training (CHT), intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) and repeated sprint training in hypoxia (RSH), and the altitude environment is constructed using a vacuum pump and a nitrogen generator. In general, LLTH method dose not induce hematological change in a short time within 3 hours. However, CHT and IHT enhance aerobic exercise capacity by improved exercise economy, supply and utilization of blood to tissues, capillary and mitochondrial densities, and oxidative enzyme activity through various biochemical and structural changes in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. RSH enhances anaerobic power and repetitive sprint performance by improving glycolytic enzyme, glucose transport, and pH control. In Korea, however, there are almost no facilities for altitude training that is applied to enhance athletic performance in advanced sports countries and recognition of the need for altitude training is also very poor. Conclusions Therefore, it is very urgent to develop altitude training for maximizing athletic performance in Korea and a lot of support and efforts are needed from the government and local governments.


Purpose The present study compared physical fitness, metabolic syndrome risk factors, and resting metabolic rate (RMR) according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Methods Fifty-one women in their 20s were recruited and assigned into three groups, i.e., normal group (n=18), normal weight obesity (NWO) group (n=18), and obesity group (n=15) according to BMI and %BF. Physical fitness, metabolic syndrome risk factors, and RMR were measured and compared among three groups. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Physical fitness were not significantly different among three groups. 2) Regarding 1-RM, arm curl and leg extension were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group. Leg press was significantly lower in normal group than obesity group. 3) Regarding metabolic syndrome risk factors, there were significant differences in waist circumference, ordering from low to high such as normal, NWO, and obesity groups. Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group, while HDL-C was significantly higher in normal group than NWO group and obesity group. 4) Regarding RMR, absolute values of RMR such as VO2(㎖·min-1), RMR (Kcal·min-1), RMR (KJ·min-1), and RMR (Kcal·day-1) were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group. On the other hand, relative value of RMR such as RMR (KJ·kg-1FW·h-1) was significantly higher in normal group than NWO group and obesity group. Conclusions It was concluded that obese women showed increased risk of metabolic syndrome and low relative RMR level, and NWO had similar problems. Active health management through physical activity and dietary control should be committed to NWO individuals because the NWO has possibility of high risk of metabolic syndrome and reduction of metabolic rate from 20s even though there was no problem in their external appearance.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of a 10-week aerobic exercise training on cardiovascular function, atherosclerosis, and vascular endothelial function in elderly women. Methods Twenty impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and normoglycemic elderly women volunteered to participate in the study. The participants in aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=9) completed 20-40 minutes of aerobic exercise program at 30-50% HRR for 3 times per week during 10 weeks. The participants in control group (CON: n=11) were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) There were no significant main effect or interaction in body weight, fat-free mass, fat mass, percent body fat, and body mass index. 2) There were no significant main effect or interaction in heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance (TPR), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial blood pressure, pulse pressure, and rate pressure product. However, interaction between group and test in TPR was close to statistically significant level (P =.054), and it tended to be decreased in TR group. 3) There was a significant main effect of test in high sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP), it tended to be decreased in TR group. There were no significant changes in total cholesterol(TC)/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, triglyceride/HDL-C ratio, and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol/HDL-C ratio. 4) There were significant main effect of group, main effect of test, as well as interaction between group and test in % flow mediated dilation(FMD), and it increased significantly (P<.01) in TR group. Nitric oxide tended to be increased in TR group, even though it did not change significantly in both groups. Conclusions It was concluded that the 10-week aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of vascular endothelial function, resulting from the decrement of total peripheral resistance.
This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.
Purpose The valuable impacts of exercise-intervention in diverse type of cancer patients were rationally well-prescribed, though many experimental and review researches already performed in this fields. Generally, cancer-related fatigue and pain remains one of the most prevalent problems for cancer populations. Therefore, exercise has become increasingly significant in cancer prevention and progression. The purpose of this recent study was to analyze the combined exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, pain, quality of life and cancer prognosis in diverse type of cancer patients. This study analyses the safety and feasibility of exercise intervention in diverse stages of cancer patients such as early stage, advanced stage and even metastatic periods in cancer populations. we also wanted to know the impacts of dose-response trial of aerobic and resistance exercise on quality of life in cancer survivors. Methods we conducted a comprehensive PubMed/MEDILINE electronic database from Jan 2015 to August 2020. The reference lists of eligible experimental research articles and relevant systemic review articles were checked. Inclusion criteria were adult cancer survivors from randomized controlled trials performing well-tailored exercise intervention programs to diverse type of cancer patients, Using predefined search items ‘exercise-intervention, cancer & immunology’. Based on reference search, more than 100 articles were identified whereas 30 research papers met the inclusion criteria and were well connected with exercise-intervention and cancer progression. we analyzed the connections between physical exercise and cancer intervention in the main text. Results Moderate to vigorous exercise (aerobic and resistance exercise) revealed to decreased level of cancer-related fatigue, pain, and cancer-related symptoms, however increased level of sleep quality, activities of daily living, exercise performance and health- related quality of life. Exercise intervention reduced pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress as well as insomnia, fatigue, pain symptoms whereas it enhanced the antioxidant systems and immune functions. In addition, home-based aerobic physical exercise might enhance muscular strength and quality of life in many types of cancer survivors. Psychological intervention also effective for reducing cancer-related fatigue and pain during and after cancer treatment. they might be the much better intervention than available pharmaceutical options. we believe that it is the related mechanisms of immune cell mobilization and activation such as NK cells which is induced by the activation of sympathetic system during and after physical exercise. Conclusion According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that implementation of exercise intervention appear to be the best non-pharmaceutical interventions for cancer populations, and also revealed to be safe and feasible in early and advanced stages, although not in the metastatic periods. Sometimes, psychological intervention such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) might be useful in reducing anxiety, depression, fatigue, pain and enhancing quality of life, quality of sleep for cancer populations. we can conclude, exercise-intervention might not just be prevention effect but might be therapeutics, however more studies are urgently needed to confirm the exercise intervention on the NK-receptors activation and immune connection of cancer populations.