The purpose of the study was to determine relationship of abdominal fat, adipocytokine, bone mineral density, and bone turnover markers in obese male adolescents. Twenty four male adolescents (obese: 12, normal: 12) volunteered to participate in the study. Anthropometry and skeletal maturity were measured. Body composition and bone mineral density were estimated by DXA (Hologic, QDR-4500, USA). Abdominal fat with total adipose tissue (TAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT), and visceral adipose tissue to subcutaneous adipose tissue ratio (VSR) were estimated by computed tomography (ECLOS, HITACH, Japan). Blood samples were obtained for and analysis of adipocytokines including leptin and adiponectin. Bone turnover markers, osteocalcin (OC), bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BALP) for bone formation markers and N-terminal telopeptide (NTx), C-terminal telopeptide (CTx) for bone resorption markers were analysed. All data were analyzed utilizing SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute, NC, USA). Independent t-test was used to evaluate the differences between obese adolescents and normal adolescents. Pearson correlation analysis was applied to figure out the relationship between abdominal fat, adipocytokines, bone mineral density, and bone turnover markers. Multiple regression analysis was used to find out the factors of abdominal fat which influence on bone mineral density. A level of significance was set at p<.05. The results of the study indicated that fat tissue (p<.001), percent body fat (p<0.001), TAT (p<.001), VAT (p<.001), and SAT (p<0.001) were significantly higher in obese adolescents than normal adolescents. However bone mineral contents were significantly higher in normal adolescents. Normal adolescents have significantly higher whole body BMD and lumber BMD than obese adolescents. Abdominal fat including VAT and SAT related negatively with whole body BMD and lumbar BMD. Leptin related negatively with BMD whereas adiponectin related positively with BMD. NTx for bone resorption marker related positively with abdominal fat. Visceral adipose tissue was a predictor for whole body BMD and lumbar BMD in explaining 46% and 32% in adolescents. In conclusion, obese male adolescents have lower whole body BMD and lumbar BMD than normal adolescents. Abdominal fat including VAT and SAT related negatively with whole body BMD and Lumbar BMD. And leptin and adiponectin were closely related with BMD. Finally, visceral adipose tissue was a predictor for whole body and lumbar BMD in adolescents.
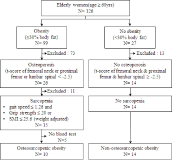
Purpose The purpose of this study were to assess physiological and biochemical characteristics in elderly women with osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO), and to analyze relationships among irisin, adipokines and bone metabolism markers. Methods 126 elderly women were selected and among them 10 women were classified into OSO group (76.9±5.2 yrs) and 14 women were classified as a NOSO group (72.9±5.6 yrs). Physique, body composition and bone mineral density were measured. Senior fitness tests were 30-s chair stand, 30-s arm curl, chair sit-and-reach, back scratch, 8-foot up-and-go, grip strength, and 2-min step test. Isokinetic muscle strength was measured by isokinetic dynamometer (Cybex 770, USA). Nutrition intake and physical activity were administered. Biochemical parameters including irisin, FNDC-5, leptin, adiponectin, CTx, 25(OH)D, osteocalcin, and PTH were measured. All data were analyzed by SAS 9.4. Independent t-test was applied to compare between OSO and NOSO groups. Multiple regression analysis was used. The level of significance was set at .05. Results The results of the study showed that there were significantly high for waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and BMI in OSO group compared to those of NOSO group. Higher results were also obtained for fat tissue and percent body fat but significantly low for lumbar bone mineral density. OSO group showed significant lower results for grip strength and 2-min step test compared to NOSO group. Peak torque, and relative peak torque at 60° were significantly lower for left and right knee flexion in OSO group. Protein intake was significantly low in OSO group, but no difference was obtained in level of physical activity between two groups. Irisin was significantly related to adiponectin, FNDC-5 and osteocalcin in explaining 35.2%, 81.5% and 92.1% of the variance, respectively. Conclusions This study shows that elderly women with OSO have higher results for physique and body composition parameters except body height. However, lower values were obtained for functional fitness, and isokinetic muscle strength. OSO may have more risks for metabolic syndrome, bone fractures, fall, lack of daily physical activity and limit of locomotion due to the imbalance of quadriceps and biceps femoris in non dominant leg. This study suggests that criteria and mechanism of OSO should be clarified by follow-up study.
