Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical activity and depression according to the presence of disease. Methods A survey and basic assessment were conducted for 2,754 (Male=1,025 and Female=1,729) aged 40 and over who participated in the rural-based cohort study. The survey included physical activity, depression scale and disease preservation. The basic assessment measured height, weight, and body fat percentage. The measured data were analyzed by using logistic regression to examine the relationship between physical activity and depression prevalence. Results First, physical activity reduced the prevalence of depression by 33% and 51%, respectively, in the general population and in patients with the disease. Second, physical activity once or twice per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 51%, and at least three physical activities reduced the prevalence of depression by 37% in the general population and 33% of patients with disease. Third, physical activity less than 150 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 43%, and physical activity of more than 150 minutes and less than 300 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of 43% of the general population and 52% of patients with disease. Physical activity over 300 minutes per week had a 38% reduction in the prevalence of depression in the general population. Conclusions This study suggests that the level of physical activity suggested by the ACSM guidelines is appropriate to reduce the prevalence of depression. In addition, the patients with the disease was found to be effective with less frequency and amount of physical activity than the general person.
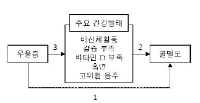
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between depression and bone mineral density in Korean elder men (55+), and test mediating role of health behaviors. Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2006-2011 data were analyzed. Bone mineral density was measured using DXA. Depression was measured by whether a participant had diagnosed depression, depressed mood lasted longer than 2 weeks, and/or suicidal thinking. Mediating health behaviors were serum vitamine D, calcium intake, high-risk drinking, endurance physical actiity, and resistance exercise. The associations among depression, health behaviors, and bone mineral density with demographic covariates were tested by linear regression, logistic regression, and path analysis. Diagnosed depression was not significantly associated with bone mineral density. Men who experienced substantial depressed mood and suicidal thinking has significantly lower bone mineral density than non-experienced counterparts. The effect of suicidal thinking on bone mineral density was mediated by endurance physical activity only. This study results suggest that elder men who experienced severely depressed mood and suicidal thinking were at-risk population for osteopenia. Also, physical activity intervention seems to be a priority to prevent osteoporosis comorbidity in depressed people.

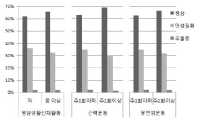
This study examined the association between physical activity (PA) and the prevalence of chronic disease and chronic depression. Additionally, the relationships between PA and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among general population, categorized by healthy, chronic disease and depression were investigated. Cross-sectional data includes 9,739 participants (4,351 males, 5,659 females, over 19 years old) who completed physical activity, chronic disease and HRQoL questionnaires from The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Complex samples frequency, descriptive, cross-tab and logistic analysis were used. Estimated prevalence of chronic disease and depression were significantly different between PA levels and frequency. Based on odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), participating in lower levels of daily PA including less resistance and flexibility exercise were associated with an increased likelihood of chronic disease. Less frequency of resistance PA was also associated with an increased likelihood of depression. Estimated prevalence of HRQoL was different according to PA in the healthy and chronic disease populations. Adjusted OR and confidence intervals represented through lower levels of daily PA and less frequency of resistance PA were associated with an increased likelihood of poor HRQoL in the chronic disease population. No significant OR between PA and HRQoL in the depression population was observed.

PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze factors associated with physical activity (PA) in older adults based on social ecological theory. METHODS Secondary analysis was conducted using raw data from the 2021 Community Health Survey. after excluding 129 non-responses in the PA domain, a total of 74,363 individuals were included in the final analysis. A total of eight factors, including personal (level of depression, history of falls), relational (relationships with neighbors, living alone), community (satisfaction with the local community system, safety), and environmental factors (living environment, natural environment), were selected in accordance with the key points of social ecological theory. To analyze social ecological factors related to the PA of older adults, we conducted a decision tree analysis using Chi-square automatic interaction detection (CHAID). RESULTS The average PA level among older adults was approximately 136 minutes, but the mode and median were both 0 minutes. A total of 20.2% of older adults met the physical activity recommendations, while 79.8% did not. According to the first split of the decision tree, living alone was the most relevant factor associated with the PA of older adults, followed by depression and falls. Older adults living alone, with a depression score of 10 or higher, and who had experienced a fall within the past year, were least likely to meet the PA recommendations. CONCLUSIONS This study urgently suggests that PA programs should target older adults living alone, experiencing depression, and falls.
PURPOSE This study investigated the associations between mental health and physical activity with all-cause mortality in persons with disability. METHODS A total of 595 participants (39.3% women) aged 45≥ years, who participated in the Korean longitudinal study of aging (KLoSA) were included in this study. The Korean version of mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) and the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale (CES-D) were used to assess cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms, respectively. The participants were classified into active and inactive groups based on physical activity of 150 min/week. Cox’s proportional regression analyses were used to determine the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of mental health and physical activity relating to all-cause mortality. RESULTS During the follow-up period (11.8±4.1 years), a total of 218 (36.6%) deaths occurred from all-causes. Participants in the inactive group had significantly higher cognitive impairment (p =0.046), depressive symptoms (p =0.001), and all-cause mortality (p=0.037) than those in the active group. Compared to participants in the normal (HR=1), cognitive impairment (HR=2.229, 95% CI=1.645-3.020, p<0.001), and depressive symptoms groups (HR=1.542, 95% CI=1.136-2.091, p<0.001), those in the inactive group had significantly higher HR related to all-cause mortality. However, in the active group, cognitive function and depressive symptoms were not associated with all-cause mortality. CONCLUSIONS The current finding suggests that the promotion of physical activity may play an important role in preventing premature death from all-causes in persons with disability, especially among those with mental health problems.