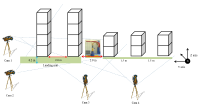
Purpose The purpose of the study was to perform a comparative analysis of the YANG Hak Seon technique carried out by "K" athlete with the kinematical data of "Y" athlete and propose a method to improve the YANG Hak Seon technique of "K" athlete. Method The subject recruited for the study was a male athlete from Korean national team (Age: 21, height: 1.65 m, body weight: 59.6 kg, and career: 11 years). Four high - speed cameras were used to analyze the 3D motion of the YANG Hak Seon technique performed by "K" athlete. The variables selected for analysis were the velocity of COM, displacement of COM, the rotational & torsional angle of the trunk and rotational & torsional angular velocity of the trunk. The results obtained were compared to the preexisting data of the "Y" athlete (data set from the published research). Results Firstly, the horizontal displacement of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the "K" athlete was observed to be shorter along with lower vertical displacement during landing compared to “Y” athlete. In addition, the overall horizontal velocity was low and vertical velocity was not generated which rises during the BC (board contact) phase. Although the rotational angular velocity of the trunk was lower during the BC, HC (horse contact) phase and LD (landing) phase, torsional angular velocity was higher during the LD. Conclusion In order to improve the completeness of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the K player, it is necessary to enter with a fast and low posture on the footplate during the initial phase. In the BC phase, it is essential to raise the COM simultaneously while landing on the footplate and increase the rotational angular velocity of the trunk.

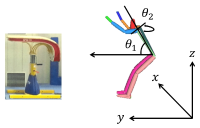

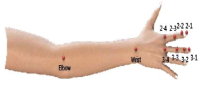
The purpose of this study was to determine how acute active pc-video game affects kinematic variables and muscle activities of adolescents. Fourteen middle school students(age: 15.9±0.7 yrs, height: 171.3±6.1cm, weight: 60.0±5.4 kg, right handed) who have no musculoskeletal disorder were recruited as the subject according to having experience in using the pc-video game for more than six months. Maximum angle, angular velocity, and muscle activity of the upper extremity were determined for each trial. For each dependent variable, a paired t-test was performed to test if significant difference existed between pre- and post a 60 minute active pc-video game(p<.05). This study found that one hour pc-video game hour may not affect on movement and ROM of the finger and the wrist, whereas it may have an effect on muscle activity of the upper extremity. It seems that repetitive movement pattern during an active pc-video game may hinder muscle activity of adolescents’ upper extremity. Part of the increase in musculoskeletal disorders is linked to the amount of time adolescents are allowed to play video games. This study found that an active pc-video game appears to have negative effects on the upper extremity muscles. Since wrist movements are continually repeated throughout the video game, carpal tunnel syndrome may possibly be caused by long-term exposure to video games.


[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of complex exercise and chromium supplement on healthe-related physical fitness, appetite regulating hormones, and diabetes risk factors in obese elementary school students. [Methods] The subjects were 32 obese elementary students over 25 kg/m2 to BMI, 8 complex exercise with high chromium supplement group (CE+HC), 8 complex exercise with low chromium supplement group (CE+LC), 8 complex exercise with placebo group (CE+PL), and 8 placebo group (PL). The subjects have performed the exercise program for 70 minutes a day and 3 times a week with aerobic and anaerobic exercise during 12 weeks. Also, low and high chromium supplement group took a peel 50 ug and 400 ug respectively at the same time and place. [Results] There were significant decreases in body fat to CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and significant increase in muscle mass compared with CE+PL (p<.05). However, there were no significant differences in body weight, BMI, muscular strength, muscular endurance, and flexibility between groups. For appetite regulating hormones, there is a significant difference to ghrelin in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and there were significant differences to glucose and insulin significantly decreased in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) in diabetes risk factors. [Conclusion] In conclusion, there were positive responses for body composition and diabetes risk factors for the twofold cases through complex exercise and high chromium supplement, but not for physical fitness and appetite regulating hormones.
Purpose Sperm quality and function are reduced by environmental factors (e.g., obesity), leading to increased infertility worldwide. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate the effects of obesity and exercise training on sperm quality and function in animal and human models. Methods In order to determine the effects of obesity and exercise on sperm quality, motility, morphology, testosterone, oxidative stress, inflammation, we reviewed previous literatures with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results The most important factor to control the sperm motility is calcium ion, which is performed by the protein of CatSper (Cation Channel of Sperm). Obese men showed the decrease of number, concentration, motility, and volume in sperm, resulting in delayed or failed fertility. However, regular exercise training increased sperm-mediated factors including number, motility, and morphology, and festicular function-mediated factors including sperm concentration and serum testosterone. Conclusions While obesity exacerbates sperm quality and function in men, regular exercise training with moderate intensity increases sperm number and motility and reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to the improvement of men’s fertility.
PURPOSE This study analyzed the difference in lower extremity joint angle and shock absorption patterns at the point of maximum ground reaction force during single-leg drop landing with or without anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR). METHODS Forty adult males were recruited for this study, with 19 in the ACLR group (age: 20.52±1.43years, height: 179.26±5.18cm, weight: 74.91±6.29kg) and 21 in the control group (age: 21.42±1.61years, height: 174.97±6.83cm, weight: 69.27±7.56kg). Participants performed single-leg landings on a 30cm tall box. An independent sample t-test was used to analyze the difference in kinetics variables at the point of maximum ground reaction force upon landing, with significance set at p=0.05. RESULTS The lower limb joint angle showed significant differences in hip flexion, hip abduction, knee flexion, and knee valgus (p<0.05) between groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the results of kinetics variables during single-leg landing (maximum ground reaction force, lower extremity stiffness, and shock absorption time). CONCLUSIONS The ACLR group showed a clear difference in kinematics compared to the control group, but no significant difference in kinetic results was found. The two groups compensated for the same impact with different movements, though movements in the ACLR group may increase the risk of ACL re-injury. Those with ACLR should strive to reduce the risk of re-injury by training to use correct movements.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the sport biomechanics questions in the ‘Secondary Physical Education Teacher Recruitment 1st Exams’ and find the orientation for future exams. METHODS Twenty-one sports biomechanics questions (49 detailed questions) in the last 7 years (2016-2022) were classified into four types (evaluation content factors, classification of educational goal, sports application or not, classroom connection, and including calculation) and analyzed. RESULTS The recruitment exams had the following characteristics. First, only approximately 22.4% of the questions were related to the secondary physical educational field. Second, only 34% were sports-applied questions. In addition, according to Bloom's classification of educational evaluation, 36.7% of knowledge-level questions, 40.8% comprehension-level questions, and 22.4% application-level questions were accounted for. Finally, the questions tended to be considerably biased towards specific items (kinetics and kinematics understanding and application of linear and angular motion). CONCLUSIONS Sport biomechanics questions in the ‘Secondary Physical Education Teacher Recruitment 1st Exams’ should be based on questions that are likely to occur in the field of secondary physical education, to occur in real sports situations, and to be asked by students. Additionally, rather than asking for simple knowledge or comprehension, the proportion of questions in the application level should be increased.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency that can guarantee the student athletes' right to study and performance, and to derive the ranks of setting proper training duration of frequency of student athletes by school level. Consequently, to provide basic data for the development of training guidelines for the growth period of Korean student athletes. Methods Delphi and Analytic Hierarchical Process(AHP) techniques were used. The Delphi survey was conducted in three phases, and collected data through Delphi survey were computed by SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Excel, using the mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. Using the AHP technique, we classified the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency derived through Delphi survey, and calculated the importance by using Microsoft Excel 2010. Conclusion First, elementary students should be guaranteed regular class participation, have basic after school training, and be provided with adequate rest so that they do not lose interest in the exercise. Second, middle school students are required to decide whether to continue exercise based on their ability to exercise and abundant experience. Therefore, when abandoning the exercise, students should be able to faithfully carry out their academic performance. Third, high school students are directly related to college entrance and employment, so they have to concentrate on performance rather than on academic performance.
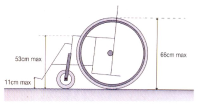
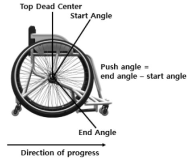
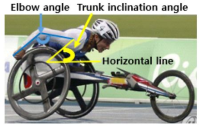
[Purpose] A potential issue for wheelchair sports are the characteristics of wheelchair design. The purpose of this review was to investigate the characteristics of design in wheelchair sports including the height of seat, camber and handrim size for improving the performance. [Results] The optimum height of seat related to trunk, arm length and handrim size. The lower seat showed the push efficient highly, while higher seat increased the energy expenditure. In energy expenditure, the optimum height of seat was 100-120° of elbow angle. Handrim size play the role in gear. The smaller handrim size acts like high gear, it gains disadvantages in acceleration, it gains advantages in maximum velocity. On the contrary, the higher handrim size acts like low gear, it gains disadvantages in maximum speed, it gains advantages in acceleration. The ratio of gear consideration in power and velocity. When increased camber enhanced the lateral stability, easier catch the handrim and easier arm motion. So it improved the energy expenditure and push technique. When increased camber enhanced the mechanical efficiency and stability, but it decreased the power. The racing wheelchair camber using the 8° and 10°. [Conclusion] Athletes, coaches and wheelchair experts are provided with insight in the performance effect of key wheelchair design settings, and they are offered a proven sensitive method to apply in sports practice, in their search for the best wheelchair-athlete combination.



The purpose of this study is to investigate the further direction of molecular biological studies, the advantages and limitations of assaying samples, and variables in figuring out the details of domestic and overseas studies verified through cell and molecular biological analysis in order to analyze the effect of concurrent training. The analysis study was limited to domestic and overseas literature, which investigated the effect of combined training using molecular biological analysis among studies to date. The study was reclassified by specialty, composed of professors of physical education and doctors of exercise physiology. The final selected study analyzed the subject and the trend of studies in terms of comprehensive perspectives. In detail, it analyzed hormonal and enzymatic changes in criteria such as leptin, 5-HT, ACTH(adrenocorticotropic hormone), cortisol, testosterone, GH(growth hormone), LDH(lactate dehydrogenase), CPK(creatine phosphokinase), antioxidants in blood samples and protein, and enzymatic and morphologic changes in for CRP, VEGF(vascular endothelial growth factor), PAI-1(plasminogen activator inhibitor-1), MAD(malondialdehyde), carnosin, and SDH(succinate dehydrogenase), the area of muscle fibers, ratio of type Ⅰ/Ⅱ muscle fiber and capillary proportion per muscle fiber in the extracted muscle by biopsy, for example. Finally, urine samples, and hormonal changes (like cortisol), were analyzed. The results of the analysis of domestic and overseas studies according to combined training has shown that this training has more varied effects than single training and lower improvement by interference effect or magnifying the effect of one type of training amongst the combined training types appears, rather than higher improvement through combined trainings. Therefore, it should be investigated in view of performance improvements relating to the characteristic of sports.