Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.
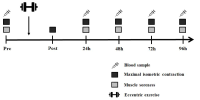
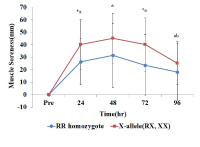
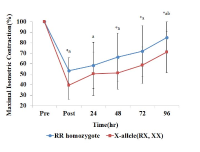
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the change of muscle damage markers after maximal eccentric exercise and to verify the difference of recovery according to ACTN3 gene polymorphism. [Methods] Fifty healthy males participated in this study. Subjects performed 25 times/1 set (total 2 set) maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexor muscles on a modified preacher curl machine with a between-sets rest time of 5 min. Maximal isometric contraction (MIC) was measured 6 times (pre, post, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Muscle soreness (SOR) was measured 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Blood samples were collected 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). ACTN3 gene polymorphisms were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Data were analyzed using a 2-way repeated measure ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test. [Results] Analysis of ACTN3 gene polymorphism revealed the following distribution: 22% RR (n=11), 50% RX (n=25), and 28% XX (n=14). Individuals were classified into the RR homozygote group (n=11) and the X-allele group (n=39). MIC showed a significant difference between groups and interaction (p<.05). The groups differed significantly in MIC at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after exercise and the X-allele group decreased more than the RR homozygote group. The groups differed significantly in muscle soreness and interaction (p<.05). SOR in the X-allele group was significantly higher than in the RR homozygote group at 24 h after exercise. Although blood CK activity was lower in the RR homozygote group than in the X-allele group, but there was no significant difference between the groups (p>.05). [Conclusion] The RR homozygote group showed lower muscle strength reduction rate, muscle soreness and blood CK activity than the X-allele group. This indicates that RR individuals have a lower risk of exercise-induced muscle damage than those with an X-allele.

PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of an 8-week gluteus medius strengthening exercise on back pain, balance, and strength in female office workers with low back pain. METHODS The participants of this study were female office workers aged 30 to 48 years old who reported low back pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS) ranging from 3 to 7. Twenty-six participants were randomly assigned to the exercise (n=13) and control (n=13) groups. The study applied a gluteus medius strengthening program to the exercise group for 8 weeks, three times a week, and 60 minutes per session. The participants in the control group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns during the period of intervention. Data collected from the test were analyzed through repeated two-way ANOVA, paired t-test, and independent t-test. RESULTS First, there has been a significant decrease in the pain level, as evidenced by VAS and Korean oswestry disability index (KODI) scores. Second, there was a statistically significant improvement in both static and dynamic balance capabilities. Last, back strength also significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Application of the gluteus medius strengthening exercise appears to be effective for low back pain, static and dynamic balance capabilities, and back strength.
Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of a single corrective exercise (CEX) and corrective kinesio taping (CKT) on gait patterns, plantar pressure, balance, and pain in 20~30s female patients with moderate hallux valgus. Methods Twenty-one participants (age: 30.1±5.1 yrs; height: 164.1±4.8 cm; body weight: 56.7±6.8 kg; body mass index: 21.2±5.7 kg·m-2; hallux valgus angle: 27.2±6.1°) with hallux valgus was recruited and participated in three trials, i.e., CEX trial, CKT trial, and combined CEX and CKT (CEX+CKT) trial, repeatedly in a counter-balanced order. One week of wash-out period was placed between the trials to minimize the effect of the previous treatment on the next treatment. Variables related to gait pattern, plantar pressure, balance, and pain were measured during each treatment. We carried out repeated two way ANOVA on measured variables. Results 1) Regarding gait patterns, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant increases in the length of patients strides, the single support line during the stance phase, and significant reduction of the cadence. 2) Regarding gait cycle, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant reductions in the contact times of forefoot, midfoot, and heel. There was a significant reduction of double stance phase in CEX treatment. 3) Regarding foot pressure on gait, CEX+CKT treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of midfoot and heel. CEX treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of forefoot. 4) Regarding balance, CEX treatment and CKT treatments significantly increased one leg standing with eyes closed. 5) Pain was significantly reduced in CKT treatment and CEX+CKT treatments. Conclusions According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that a single CKT treatment was effective in reducing pain when walking and that plantar pressure, gait pattern, gait cycle, and balance were improved through a single bout of CEX treatments. Therefore, treatments by stage, starting with CKT treatments to reduce the pain, and then treating CEX to improve the gait pattern, gait cycle, foot pressure when walking, and balance ability, would be effective. Future research is warranted to identify the effects of long-term treatments.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of field and on-ice performances of ice-hockey players and the relationship of performance with subjective joint pain and dysfunction. METHODS A total of 25 male college icehockey players were evaluated for 19 items of performance. Pain and dysfunctions in the lower extremities and lower back were confirmed through the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score, Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, Hip Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, and Osweatry Disability Index questionnaire. Players with similar performance characteristics were classified through a cluster analysis, and differences in performance and patient-reported outcomes between clusters were analyzed with a one-way analysis of variance. RESULTS The ice-hockey players were classified into “lower muscular strength and performance (cluster 1),” “lower cardiorespiratory endurance (cluster 2),” and “high muscular strength and performance (cluster 3).” Players in cluster 1 had more frequent ankle and knee joint dysfunctions and pain compared to those in cluster 3. Several performance test items affected the subjective joint score, and the related performance items were more in the proximal joint than in the distal joint. CONCLUSIONS Ice hockey players should perform training to supplement their individual lack of on-ice and field performance. Since performance may be limited because of joint dysfunction and pain, a joint-specific intervention strategy should be applied to improve physical and athletic performances.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to analyze the type of and interest in home training video contents using the YouTube platform. METHODS Web crawling was performed using Python and a total of 3,937 sets ofvideo information (title, content, number of views, upload date) were obtained, 3,155 of which were finally selected for the study material. Overlapping and unrelated content were excluded. The data of text underwent 3 stages of preprocessing, the TF and TF-IDF of the keywords were calculated to identify the main keywords, and the LDA algorithm was applied in the topic modeling to successfully identify the types. In order to understand the level of interest by type, the number of views was subdivided into the percentage of the assigned type. RESULTS First, the types of home training videos were classified into bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, Pilates exercise for core and upper body strengthening, upper body exercise using tools, lower body line exercise, posture correction and upper body stretching exercise for pain relief, hip-up exercise, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet, and bare body exercise for core and lower body strengthening. Second, it was found that the proportion and interest were high in the contents of bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study may provide baseline data about the development of the active online home training videos in the market.
The purpose of this study was to describe psychological changes and variables of injured elite athletes during sport injury rehabilitation. 5 injured elite athletes were selected as participants, and open-ended questionnaires, participant observation, and in-depth interview were used for collecting data. Results from the data were analyzed through transcription, coding, and categorization with inductive method. To validate the results of this study, triangulation, in-depth description, member checks, and peer debriefing were used, and findings of this study were as follow. The participants showed negative psychological state such as fear of return to play and anxiety during the initial rehabilitation program, but their psychological state was changed positively such as recovery of confidence and desire of return to play at the end of program. However, the specific psychological changes of each participant showed several differences according to participant's surrounding environment and situation during the rehabilitation program. All findings have important implications for implementing and developing rehabilitation program, so needs to be investigated further.
Purpose The valuable impacts of exercise-intervention in diverse type of cancer patients were rationally well-prescribed, though many experimental and review researches already performed in this fields. Generally, cancer-related fatigue and pain remains one of the most prevalent problems for cancer populations. Therefore, exercise has become increasingly significant in cancer prevention and progression. The purpose of this recent study was to analyze the combined exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, pain, quality of life and cancer prognosis in diverse type of cancer patients. This study analyses the safety and feasibility of exercise intervention in diverse stages of cancer patients such as early stage, advanced stage and even metastatic periods in cancer populations. we also wanted to know the impacts of dose-response trial of aerobic and resistance exercise on quality of life in cancer survivors. Methods we conducted a comprehensive PubMed/MEDILINE electronic database from Jan 2015 to August 2020. The reference lists of eligible experimental research articles and relevant systemic review articles were checked. Inclusion criteria were adult cancer survivors from randomized controlled trials performing well-tailored exercise intervention programs to diverse type of cancer patients, Using predefined search items ‘exercise-intervention, cancer & immunology’. Based on reference search, more than 100 articles were identified whereas 30 research papers met the inclusion criteria and were well connected with exercise-intervention and cancer progression. we analyzed the connections between physical exercise and cancer intervention in the main text. Results Moderate to vigorous exercise (aerobic and resistance exercise) revealed to decreased level of cancer-related fatigue, pain, and cancer-related symptoms, however increased level of sleep quality, activities of daily living, exercise performance and health- related quality of life. Exercise intervention reduced pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress as well as insomnia, fatigue, pain symptoms whereas it enhanced the antioxidant systems and immune functions. In addition, home-based aerobic physical exercise might enhance muscular strength and quality of life in many types of cancer survivors. Psychological intervention also effective for reducing cancer-related fatigue and pain during and after cancer treatment. they might be the much better intervention than available pharmaceutical options. we believe that it is the related mechanisms of immune cell mobilization and activation such as NK cells which is induced by the activation of sympathetic system during and after physical exercise. Conclusion According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that implementation of exercise intervention appear to be the best non-pharmaceutical interventions for cancer populations, and also revealed to be safe and feasible in early and advanced stages, although not in the metastatic periods. Sometimes, psychological intervention such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) might be useful in reducing anxiety, depression, fatigue, pain and enhancing quality of life, quality of sleep for cancer populations. we can conclude, exercise-intervention might not just be prevention effect but might be therapeutics, however more studies are urgently needed to confirm the exercise intervention on the NK-receptors activation and immune connection of cancer populations.