PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop the estimating equations for 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting. METHODS 80 male elite athletes performed 4 trials of the Wingate Anaerobic test by each type. Subjects were conducted the retest one week later. Data collected from the Wingate Anaerobic test included mean power, peak power, and power drop for 30s were measured. Coefficient of correlation was used for validity of type 1(DOS version) and the other types(ver. 2.24, 3.3.0, and 3.2.1). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to examine the reliability of test and retest. Simple regression analysis was used for calculating the estimating equation. RESULTS There was significant correlation for absolute value(Watt, p<.01) and relative value(Watt/kg, p<.01) of mean power, absolute value(W, p<.01), relative value(Watt/kg, p<.05), and power drop rate(%, p<.01). Test and retest reliability was excellent for all test variables(p<.01). CONCLUSIONS From the all results, the estimating equation was calculated to convert all outputs from each type to the other types of the Wingate Anaerobic test setting. These findings suggest that the estimating equations are compatiable to 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting.
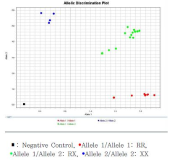
The ACTN3 R577X polymorphism has been associated with an elite athletes status. Several studies have determined that the R allele is connected with power-oriented athletic performance, whereas the nonfunctional XX genotype may give some beneficial effect for endurance performance. The main aim of the study was to determine the possible interaction between the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism and an power-oriented athlete status in Korean elite athletes(wrestling 31, judo 13, boxing 16, fencing 6, cycle 16, ≤400m athlete 18). Each athletes performed a 30-second WAPtest with a resistance equal to 7.5% for male and 5% for female body weight. Genotyping for the ACTN3 R577X (rs1815739) polymorphism was performed using the TaqMan approach. The ACTN3 R577X genotypes exhibited a HardyWeinberg equilibrium distribution in our population. The relative and absolute average power results of the 30-second Wingate test did not differ significantly among the genotypes. However, the relative peak power result of the Wingate test was significantly higher in the R-allele- dominant model groups than in the XX group in male but not female athletes. These results suggest that the ACTN3 R allele is associated with the relative peak power during the Wingate test in male Korean elite athletes.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of six-weeks intermittent hypoxic training at 3,000 m hypobaric hypoxic condition on aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity in competitive swimmers. Methods South Korean swimmers (n=20) were randomly assigned into training at sea-level (n=10, intermittent normoxic training group; INT) and training at 526 torr corresponding to 3,000 m hypobaric hypoxic condition (n=10, intermittent hypoxic training group; IHT). The participants completed an aerobic continuous treadmill training (30 min) within 80%HRmax and anaerobic interval bicycle training (10 times; 2 min of exercise and 1 min of rest) for 30min within 90%HRmax in each environment. We compared their aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity before and after six-weeks of training. Exercise frequency was 1 hour, 3 days per a week, and during 6 week. Results In aerobic exercise capacity, PWC at 75%HRmax, estimated VO2 max, and exercise time were increased by training in only the IHT group. Estimated VO2 at 75%HRmax was increased by training in both groups, but presented a larger increase tendency in the IHT group compared with the INT group. In anaerobic exercise capacity, peak anaerobic power and fatigue index were increased by training in only the IHT group. Blood lactate level after wingate test were decreased by training in both groups, but the IHT group have a lower blood lactate level in after training compared with the INT group. Conclusion In our study, we did not measure to various dependent variables for support to enhancement of aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance. However, these results showed that the IHT method may be effective in improvement of exercise performance in competitive swimmers who participates in a variety of events from short to long distance.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to compare the maximal strength, isokinetic muscle function and anaerobic capacity according to the position of college and professional rugby players. Methods Subjects for this study were 54 athletes and randomly divided into 4 groups: the forwards group in college rugby players (FCRP, n = 10), backs group in college rugby players (BCRP, n = 16), forwards group in professional rugby players (FPRP, n = 16), and backs group in professional rugby players (BPRP, n = 12). Physical fitness was consisted of squat, bench press, bilateral grip strength. Isokinetic knee and trunk muscle functions were measured by Humac Norm device, and anaerobic pedaling power was analyzed by Wingate test. Significant differences between groups were determined with one-way repeated ANOVA. Results As the result of this study, there was no statistically significant difference between the absolute and relative values of the squat and bilateral grip strengths, but bench press was significantly higher in FPRP and BPRP compared to other groups. Isokinetic knee and trunk extensor and flexor muscle strength showed stronger in FPRP and BPRP than those in FCRP and BCRP. In addition, the anaerobic pedaling power was also the highest in FPRP and BPRP. Conclusions Our findings suggest important information that the college rugby players and forwards in professional rugby team should be given scientific training to improve their maximum strength, isokinetic strength and anaerobic power.
The purpose of this study was to examine whether the difference between ingestion of nutrition supplements for 8 weeks can regulate physical activities and fatigue recovery. Fifty one middle-aged women participated in this study and were divided into placebo, ingestion of 20g energy supplement and ingestion of 40g energy supplement groups. Energy supplement mainly consists of carbohydrates and proteins. All subjects take in this supplement one time per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity and fatigue recovery were measured before and after ingestion of energy supplement for 8 weeks by using the Wingate anaerobic and a blood tests. In the Wingate anaerobic test, the peak power(p<.01) and average power(p<.05) were significantly increased in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group. Although concentrations of lactate and growth hormone in the blood didn’t show a significant differences among groups, blood concentrations of cortisol and ammonia were further enhanced in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group(p<.001). The results of present study provide evidence that energy supplement mixed with carbohydrates and proteins may be effective to increase physical activity as well as to reduce blood concentration of fatigue-related factors after exercise.
PURPOSE This study sought to investigate the effects of passive warm-up on flexibility, exercise performance, and lactate oxidation rate in track and field athletes. METHODS A total of eight male athletes with more than three years of athlete experience were recruited as participants, and passive warm-up (PW) and active warm-up (AW) treatments were conducted in a single-group crossover study design. The participants performed thermal stimulation at 40°C for 20 minutes as a PW and performed a 60-70% HRmax cycle as an AW. Flexibility and exercise performance were measured after each treatment. Anaerobic power was measured using the Wingate test, and lactic acid concentration was measured. RESULTS Body temperature significantly increased in both PW and AW, and no significant difference was observed in exercise performance between treatments. Flexibility and lactic acid oxidation rate were significantly higher in PW than in AW. CONCLUSIONS In track and field sprinters, PW did not exhibit any significant difference in anaerobic power and exercise performance compared to AW even though no physical exercise was performed, and PW was effective in body temperature, lactic acid oxidation rate, and flexibility. PW suggests the possibility of replacing AW.