
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.







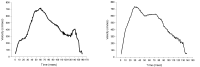
Purpose The purpose of this study is to compare the maximal strength, isokinetic muscle function and anaerobic capacity according to the position of college and professional rugby players. Methods Subjects for this study were 54 athletes and randomly divided into 4 groups: the forwards group in college rugby players (FCRP, n = 10), backs group in college rugby players (BCRP, n = 16), forwards group in professional rugby players (FPRP, n = 16), and backs group in professional rugby players (BPRP, n = 12). Physical fitness was consisted of squat, bench press, bilateral grip strength. Isokinetic knee and trunk muscle functions were measured by Humac Norm device, and anaerobic pedaling power was analyzed by Wingate test. Significant differences between groups were determined with one-way repeated ANOVA. Results As the result of this study, there was no statistically significant difference between the absolute and relative values of the squat and bilateral grip strengths, but bench press was significantly higher in FPRP and BPRP compared to other groups. Isokinetic knee and trunk extensor and flexor muscle strength showed stronger in FPRP and BPRP than those in FCRP and BCRP. In addition, the anaerobic pedaling power was also the highest in FPRP and BPRP. Conclusions Our findings suggest important information that the college rugby players and forwards in professional rugby team should be given scientific training to improve their maximum strength, isokinetic strength and anaerobic power.
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to provide the physiological characteristics of female adults in their 30s by comparing the body composition and the maximal strength of the knee extension and flexion and bilateral ratio and ipsilateral ratio(H/Q: Hamstring and Quadriceps ratio) depending on age. [Methods] Body composition was measured by Hv-ps 7681(GE medical systems Lunar, USA). Isokinetic lower limb muscular strength was measured by Isomed2000(D&R Ferstl GMBH, Germany). 92 volunteers who were chosen by our selection criteria agreed to participate in our study. The participants were divided into three groups depending on age and classified as female adults in twenties(n=30), in thirties(n=34), in forties(n=28). To evaluate differences according to age, One-way ANOVA was used. [Results] The result in the test for female adults is as follows. In body composition, there were significant differences in lean mass, bone mineral density in the legs area among groups(p<.05). In isokinetic test, there were significant differences in muscular strength among groups in extensor of knee(p<.05). [Conclusion] The finding revealed that strength training based on the characteristics depending on age is required and ipsilateral ratio needs to be improved.