The purpose of this study is to investigate the further direction of molecular biological studies, the advantages and limitations of assaying samples, and variables in figuring out the details of domestic and overseas studies verified through cell and molecular biological analysis in order to analyze the effect of concurrent training. The analysis study was limited to domestic and overseas literature, which investigated the effect of combined training using molecular biological analysis among studies to date. The study was reclassified by specialty, composed of professors of physical education and doctors of exercise physiology. The final selected study analyzed the subject and the trend of studies in terms of comprehensive perspectives. In detail, it analyzed hormonal and enzymatic changes in criteria such as leptin, 5-HT, ACTH(adrenocorticotropic hormone), cortisol, testosterone, GH(growth hormone), LDH(lactate dehydrogenase), CPK(creatine phosphokinase), antioxidants in blood samples and protein, and enzymatic and morphologic changes in for CRP, VEGF(vascular endothelial growth factor), PAI-1(plasminogen activator inhibitor-1), MAD(malondialdehyde), carnosin, and SDH(succinate dehydrogenase), the area of muscle fibers, ratio of type Ⅰ/Ⅱ muscle fiber and capillary proportion per muscle fiber in the extracted muscle by biopsy, for example. Finally, urine samples, and hormonal changes (like cortisol), were analyzed. The results of the analysis of domestic and overseas studies according to combined training has shown that this training has more varied effects than single training and lower improvement by interference effect or magnifying the effect of one type of training amongst the combined training types appears, rather than higher improvement through combined trainings. Therefore, it should be investigated in view of performance improvements relating to the characteristic of sports.

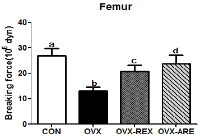
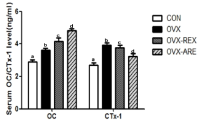
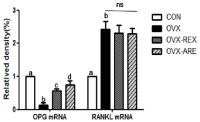
Purpose Osteoporosis is a systemic metabolic bone disease characterized by gradual decrease of bone mass and damage of the bone microstructure. In particular, postmenopausal osteoporosis is the most common type in women after menopause. This study aims to investigate the effects of combined exercise training on bone mineral density (BMD) and OPG/RANKL mRNA levels in ovariectomized rats. Methods A total of 40 Sprague-Dawley female rats were randomly divided into four groups: (1) CON (sham-operation, n=10), (2) OVX (ovariectomy, n=10), (3) OVX-REX (ovariectomy-resistance exercise, n=10), and (4) OVX-ARE (ovariectomy-combined aerobic and resistance exercise, n=10). Combined exercise training was performed on a treadmill and ladder adapted to rats in alternate days (4 days/wk, for 12 wk). Results Compared to the OVX group, all exercise treatments increased BMD and bone breaking force(p<0.05). In the bone turnover markers, serum C-terminal telopeptides of type-1 collagen (CTX-1) was significantly decreased in the exercise groups compared with OVX group and osteocalcin (OC) level was increased in the exercise groups (p<0.05). Additionally, in the exercise groups, expression of OPG mRNA was significantly increased compared with OVX group (p<0.05), and RANKL mRNA was slightly decreased but no significant between groups. Furthermore, OVX-ARE group showed more effects than OVX-REX group. Conclusions These results suggest that combined exercise may be a more effective therapeutic strategy to prevent and delay postmenopausal osteoporosis than resistance-only training.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 16 weeks’ combined exercise training on insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods Twenty-eight participants were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., exercise training group (EX: n=14) and control group (CON: n=14). Subjects in EX participated in 3 sessions of 60 min-combined exercise for 16 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same period. The variables regarding insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre-post test utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR tended to decrease in EX, whereas increased significantly in CON. 2) IL-6, TNF-α, hs-CRP decreased in EX, but the changes were not statistically significant. 3) MDA increased significantly and GPx decreased significantly in both EX and CON. 4) Leukocyte telomere length increased significantly in EX. 5) Fat-free mass increased in EX, whereas fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in EX. 6) Arm curl, chair stand, sit & reach, tandem test, 10m walking speed, and up & go improved significantly in EX. Conclusion It was concluded that the combined exercise for 16 weeks had a positive effect on improving insulin resistance, increasing leukocyte telomere length, as well as enhancing body composition and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes.
This study was designed to investigate the effects of combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise on musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Thirty patients volunteered to participate in the study as subjects, and they were divided into one of three groups, i.e., chiropractic group (n=10), PNF exercise group (n=10), and combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise group (C+P group; n=10). Subjects in three groups went through each program for 25 min/session, three times/wk for eight weeks. Cervical alignment, cervical muscular strength and endurance, and cervical range of motion were measured and compared among groups and between pre- and post-test utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables regarding cervical alignment increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. 2) All variables regarding cervical muscular strength and endurance increased significantly in all three groups. 3) All variables regarding cervical range of motion increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in ROM regarding flexion and extension in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. It was concluded that all three treatments applied in this study would be effective for functional recovery of the musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Especially, combination of chiropractic and PNF pattern exercise would be the most effective intervention for the patients.


The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of National Fitness Award program group exercise classes on daily fitness and balance-confidence among the elderly participants(n=496, 80.2% women). This study investigated body composition, daily fitness, and balance-confidence, and quality of life among the subjects who participated in the combined exercise program of improving physical fitness class for 8-week in the 10 national physical fitness certification centers by the demonstration project for the elderly of 2013 Korean National Fitness 100 project. Body composition and physical fitness for daily living were defined by Korean National Fitness 100 project for elderly, also the balance-confidence and health-related questionnaires were added. The following results were obtained by comparing the pre-test and post-test. In body composition body weight (p<.05), body mass index (p<.05), fat mass (p<.01), and percent body fat (p<.05) were significantly decreased, but muscle mass was not. Except for walking-around-two-cones-in-a-figure 8, all other daily fitness items such as relative grip strength (p<.001), chair sit to stand, two minutes place to walk, and sit-and-reach significantly increased (p<.01), and timed up and go were significantly decreased (p<.01). In balance confidence rating ABC tests (p<.001) were shown significantly increased. Although, quality of life measured by EQ-5D was not significantly improved, self-health status measured by EQ-VAS (p<.001) showed significant increase. Therefore, the group exercises of National Fitness Award program improved body composition, daily fitness and balance confidence in Korean elderly participants.
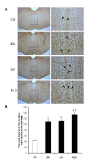
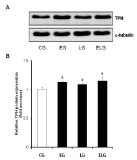
The main purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise and bright light exposure on serotonin expression in rat brain. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n=9 in each group), specifically, control group (CG), exercise group (EG), light group (LG), and exercise+light group (ELG). Rats in EG were subjected to treadmill exercise (5 days/week, 30 min/day), LG rats exposed (5 days/week, 30 min/day, 10,000 Lux), ELG rats subjected to treadmill exercise in combination with exposure, and CG rats remained sedentary over a four-week period. We observed a significant increase in serotonin expression in the raphe obscurus nucleu and the midbrain of rats in EG, LG, and ELG, compared to CG. Interestingly, serotonin expression was significantly increased in ELG, compared to EG and LG in the raphe obscurus nucleu via immunohistochemistry. In the western blot, it showed a increased pattern in ELG, compared to EG and LG. The overall results showed that treadmill exercise and/or bright light had positive effects on serotonin expression in the brain. Therefore, we suggest that moderate exercise or exposure to bright light during a growth child may be beneficial in brain action.

Purpose The valuable impacts of exercise-intervention in diverse type of cancer patients were rationally well-prescribed, though many experimental and review researches already performed in this fields. Generally, cancer-related fatigue and pain remains one of the most prevalent problems for cancer populations. Therefore, exercise has become increasingly significant in cancer prevention and progression. The purpose of this recent study was to analyze the combined exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, pain, quality of life and cancer prognosis in diverse type of cancer patients. This study analyses the safety and feasibility of exercise intervention in diverse stages of cancer patients such as early stage, advanced stage and even metastatic periods in cancer populations. we also wanted to know the impacts of dose-response trial of aerobic and resistance exercise on quality of life in cancer survivors. Methods we conducted a comprehensive PubMed/MEDILINE electronic database from Jan 2015 to August 2020. The reference lists of eligible experimental research articles and relevant systemic review articles were checked. Inclusion criteria were adult cancer survivors from randomized controlled trials performing well-tailored exercise intervention programs to diverse type of cancer patients, Using predefined search items ‘exercise-intervention, cancer & immunology’. Based on reference search, more than 100 articles were identified whereas 30 research papers met the inclusion criteria and were well connected with exercise-intervention and cancer progression. we analyzed the connections between physical exercise and cancer intervention in the main text. Results Moderate to vigorous exercise (aerobic and resistance exercise) revealed to decreased level of cancer-related fatigue, pain, and cancer-related symptoms, however increased level of sleep quality, activities of daily living, exercise performance and health- related quality of life. Exercise intervention reduced pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress as well as insomnia, fatigue, pain symptoms whereas it enhanced the antioxidant systems and immune functions. In addition, home-based aerobic physical exercise might enhance muscular strength and quality of life in many types of cancer survivors. Psychological intervention also effective for reducing cancer-related fatigue and pain during and after cancer treatment. they might be the much better intervention than available pharmaceutical options. we believe that it is the related mechanisms of immune cell mobilization and activation such as NK cells which is induced by the activation of sympathetic system during and after physical exercise. Conclusion According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that implementation of exercise intervention appear to be the best non-pharmaceutical interventions for cancer populations, and also revealed to be safe and feasible in early and advanced stages, although not in the metastatic periods. Sometimes, psychological intervention such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) might be useful in reducing anxiety, depression, fatigue, pain and enhancing quality of life, quality of sleep for cancer populations. we can conclude, exercise-intervention might not just be prevention effect but might be therapeutics, however more studies are urgently needed to confirm the exercise intervention on the NK-receptors activation and immune connection of cancer populations.

Purpose This study was designed to investigate the effects of weight-bearing exercise and CareRing treatment on cardiovascular responses, popliteal vein functions, and vascular elasticity of 30-40s women who had worked longer than eight hours a day in a standing position. Methods Thirteen subjects participated in 30 min of standing up treatment (STAND), weight-bearing exercise treatment (EX), and weight-bearing exercise with CareRing treatment (EX+RING). Each subject took part in the three trials repeatedly in a counter-balanced order and proceeded with a wash-out period of at least one week between the respective trials. Results The main results were as follows: 1) Significant reduction in EDV, no change in the diameter of popliteal vein, trend of reduction in blood flow of popliteal vein, and increased baPWV, indicating reduction of vascular elasticity of whole body, were shown in the STAND. 2) CO and EF increased significantly, and TPR decreased significantly in the EX. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of popliteal vein increased significantly, and baPWV decreased significantly from immediately after the treatment throughout the recovery phase in the EX. 3) HR, CO, and EF increased significantly in the EX+RING. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume increased significantly in the EX+RING. Diameter of popliteal vein increased significantly immediately after the treatment and decreased significantly at 40 minutes of recovery. TPR and baPWV decreased significantly immediately after treatment compared to the STAND. Conclusions It was concluded that weight-bearing exercises would be effective in preventing venous or cardiovascular diseases occurred due to long-standing in 30-40s women, who are at high risk for such diseases. Furthermore, it would be more effective to combine pressure treatment with CareRing during weight-bearing exercises.

Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of a single corrective exercise (CEX) and corrective kinesio taping (CKT) on gait patterns, plantar pressure, balance, and pain in 20~30s female patients with moderate hallux valgus. Methods Twenty-one participants (age: 30.1±5.1 yrs; height: 164.1±4.8 cm; body weight: 56.7±6.8 kg; body mass index: 21.2±5.7 kg·m-2; hallux valgus angle: 27.2±6.1°) with hallux valgus was recruited and participated in three trials, i.e., CEX trial, CKT trial, and combined CEX and CKT (CEX+CKT) trial, repeatedly in a counter-balanced order. One week of wash-out period was placed between the trials to minimize the effect of the previous treatment on the next treatment. Variables related to gait pattern, plantar pressure, balance, and pain were measured during each treatment. We carried out repeated two way ANOVA on measured variables. Results 1) Regarding gait patterns, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant increases in the length of patients strides, the single support line during the stance phase, and significant reduction of the cadence. 2) Regarding gait cycle, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant reductions in the contact times of forefoot, midfoot, and heel. There was a significant reduction of double stance phase in CEX treatment. 3) Regarding foot pressure on gait, CEX+CKT treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of midfoot and heel. CEX treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of forefoot. 4) Regarding balance, CEX treatment and CKT treatments significantly increased one leg standing with eyes closed. 5) Pain was significantly reduced in CKT treatment and CEX+CKT treatments. Conclusions According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that a single CKT treatment was effective in reducing pain when walking and that plantar pressure, gait pattern, gait cycle, and balance were improved through a single bout of CEX treatments. Therefore, treatments by stage, starting with CKT treatments to reduce the pain, and then treating CEX to improve the gait pattern, gait cycle, foot pressure when walking, and balance ability, would be effective. Future research is warranted to identify the effects of long-term treatments.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on a body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate. Fifty-one elderly women were randomly assigned to aerobic training group (EX: n=12), resveratrol supplementation group (R: n=13), combined aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation group (EX+R: n=12), and control group (CON: n=14). The subjects in EX group exercised three sessions per week, 40 minutes per session for 8 weeks, the subjects in R group took 500 mg of resveratrol per day for 8 weeks, and the subjects in EX+R group received both treatments. The subjects in CON group were asked to maintain normal daily life pattern without any treatment for the same period of intervention. Body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured at pre- and post-test and the data were compared among groups and between tests by utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Physique and body composition did not change significantly in all groups. 2) Muscular endurance increased significantly in EX+R group, whereas the other physical fitness-related variables showed no significant changes in all groups. 3) Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c tended to be improved in EX+R group. 4) AST, ALT, and γ·GT showed no significant changes in all groups. 5) Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure increased significantly in CON group. Heart rate tended to be decreased in EX+R group and EX group. It was concluded that the 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation had positive effects on muscular endurance, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in T2DM elderly women. Research investigating the effects of a longer period of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on the same variables would be warranted in the future.