
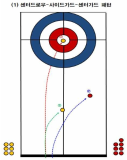
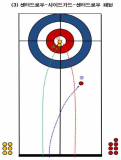
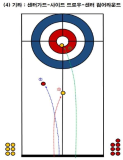
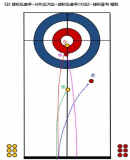
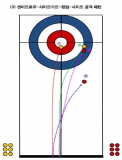
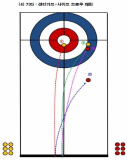
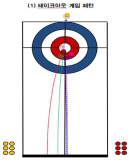
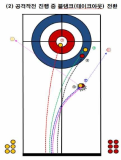
This study has analyzed 33 domestic games and 26 overseas games by targeting women curling teams of home and abroad, and looked into what main performance variables are, how level differences of domestic team appear, and from which variables differences between winning team and defeated team come out in overseas teams. Also, main strategies has been suggested that are used most commonly for kick-off offense and latter offense, blank strategy in order to prepare countermeasures, and digital media DB has been constructed that can utilize proper countermeasures easily and simply, and a model has been proposed for predicting victory/defeat. To accomplish such goal, a variance analysis has been carried out by dividing domestic teams into each level after calculating frequency and ratio with SPSS18.0, and t-test analysis has been carried out by overseas teams. Also, the accuracy of victory/defeat classifications has been suggested by using an artificial neural networks method. As a result, a lot of technical proficiency differences have appeared among Class A(upper rank), Class B(middle rank), and Class C(lower rank) in domestic teams. The ‘Guard’ which is an aggressive variable has turned out to be used more in upper and middle teams than in lower team, and the ‘Tab Back’ has been used more in upper rank than in lower rank. Furthermore, regarding the average comparison on victory/defeat in international games, victory teams have more significant difference(p<.05) than defeated teams in accuracy of shot techniques and strategy accomplishing abilities, and victory teams have been turned out to use less ‘Drew’ and more ‘Take’ than defeated teams significantly in Drew and Take’ technique variable. Finally, the accuracy of a prediction model has been 91.7% for learning and 92.9% for the test result to predict the victory/defeat in international games through the artificial neutral network analysis. The prediction accuracy of domestic games was 81.0% for learning and 71.4% for the test.





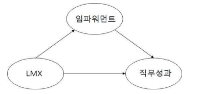
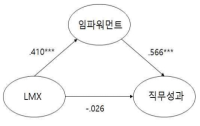
The current study aimed to investigate the relationships between leader-member exchange (LMX) quality, empowerment, and job performance of fitness center instructors. Data were mainly analyzed using a structural equation modeling technique with the AMOS program. The results, based on a paper-and-pencil survey with 263 respondents from 15 fitness centers, reported that LMX quality positively influences the level of empowerment perceived by subordinates while employee empowerment has a positive effect on job performance. However, LMX quality does not statistically influence self-rated job performance. Employee empowerment mediates the relationship between LMX quality and job performance.

Impact of 9-week strength training of racing cyclist candidate during training camp on body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was examined. Two by two (cyclist experience, y/n and strength training (ST) participation, y/n) experiment design was employed. A total of 20 candidates participated and divided evenly into four groups; 1) experienced cyclist participating ST (CST), 2) non-experience cyclist participating ST (nCST), 3) experienced cyclist no participating ST (CnST), and 4) non-experience cyclist no participating ST (nCnST). Two programs were introduced; 1) non ST containing, pre-existing program emphasizing on sprint and acceleration training and 2) new-program containing ST and sprint and acceleration training. CST and nCST participated the latter program. Before and after the 9-week training, body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was tested. After 9 weeks, all groups decreased body weight(p<0.05), body fat content(p<0.05), body mass index, and CST and nCST increased lean body mass(p<0.05). Muscular strength measures such as grip strength, low back strength, 1RM of bench press, 1RM of squat, and anaerobic capacity improved after 9 weeks in all groups(p<0.05). The magnitude of changes was greater in order of CST, nCST, CnST, nCnST. Time trial of 200 meter sprint was faster after 9 weeks in all groups except CnST while 500 meter sprint was improved only in nCnST(p<0.05). After 9 weeks, regardless of previous cyclist experience, those who participated in ST ranked high places at racing cycle competition. Both training programs for the candidates improved body composition and racing cyclist specific fitness. When strength training was added to pre-existing training program emphasized on sprint and acceleration, the racing cycle performance was enhanced. Strength training for racing cyclist is highly recommended to improve their racing performance.
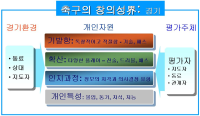
The purpose of this study was to explore a framework of understanding football performance. Researcher review was conducted to organize perspectives for football performance and drew implications as well as drift of football performance based on intelligence approach. Discussions for intelligence had been proceeded in concepts of learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence. Discussions of football performance approaches fitness, skill, and strategies in traditional intelligence aspects. The multiple intelligence perception discusses perspective, mentality, body, and analysis. The successful intelligence perspective deals with creativity, practical intelligence, and football talents. However, specific discussions for moral intelligence have not been progressed yet. FIFA’s social responsibility project and UEFA’s RESPECT campaign reflect that the discussions of football performance develops in a way of the moral intelligence. In European football, issues regarding value, such as RESPECT and against Racism, are currently emerging. Considering the change in the European football, the global football leagues will share the issues related to value in the near future. Given the fact that discussion for intelligence had been proceeded learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence, the moral intelligence will be a main concern in the further football performance discussion. The moral intelligence will be incorporated into football performance evaluations soon. Furthermore, teams and players will strive to place efforts in order for pursuing value and reputation as factors of performance.




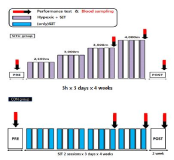
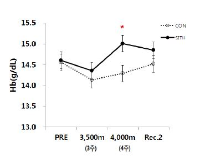
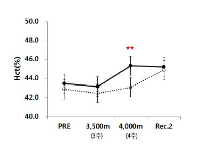
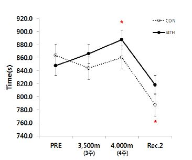
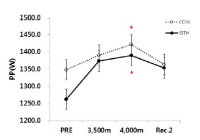
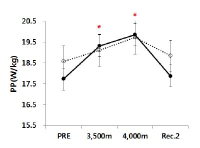
In this study, hypoxic exposure and training with regard to the current progress during the various models 'live and/or sleep high: train high' by way of 4 weeks in elite level tennis players. The experimental group which SITH(SIT with hypoxic) a 2,500m-4,000m to the graded elevation every 500m increased by the week five times a day, two times four weeks treated to a SIT (sprint interval training) and three hours of exposure in hypoxic chamber(simulated normobaric hypoxic). The CON(control) was conducted same period and methods without exposure to hypoxia that a SIT at sea level. As a results, the haematological variables were Hb and Hct compared Pre with the treatment at the end of 4,000 m(at 4 weeks) has been shown to significantly increased in both groups respectively(p<.05, p<.01; vs. Pre). Aerobic exercise capacity related variables that Time was SITH has been shown to significantly increased at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre). Also, VO2max was SITH has been showed increased in the same period a tendency(p=.072). Anaerobic exercise capacity related variables that PP(W) was both groups increased significantly at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre), and PP(W/kg) was CON group has been showed increased in the same altitude a tendency, whereas SITH group has been showed increased at 3,500m and 4,000m respectively(p<.05; vs. Pre). Therefore, this study was unlike previous studies with similar positive results as a follow-up study will be contribute to the attainment of a higher value.

This study was to explore the factors influencing Olympic performance positively and negatively. In order to achieve this purpose, 60 athletes, who participated in 2012 London Olympic games, responded on open-ended questionnaire. In addition, 10 athletes, who won medals in London Olympic, responded on in-depth interview. Collected data were analyzed by deductive content analysis. The results of this study were as follows: firstly, the factors influencing Olympic performance positively were psychological preparation, strengthening training, physical conditioning, support from significant others, material support, cheering of Korean people, self respect as a Korean national athlete, different game environment, team cohesion, sharing Olympic experience, and support of sports science. Secondly, the factors influencing Olympic performance negatively were psychological pressure, excessive expectation, negative interpersonal relationship, condition decline, overtraining, unstable environment, insufficient facilitation, decrease in performance level, and especially ineffective village room placement and media management during Olympic period. Thirdly, the differences between Olympic games and other world competitions , perceived by athletes were competition scale, psychological attitude, training support, systematic preparation, and benefits from winning medals. The results of this study will give fundamental information in developing a scale which can measure Olympic preparation level and in developing Olympic preparation guideline. Therefore, it will help athletes ,who participate Olympic for the first time or athletes who did not perform well in pre-participated Olympic games, to understand and apply in training the factors influencing Olympic performance and help them to perform better in Olympic games.
PURPOSE This study theoretically explains the relationship between Keirin players’ core competencies and their performances. It also analyzes the impact of interaction between objectively identifiable core competencies and players’ efficiency toward their results, that is, the ability to convert their resources into performance. METHODS Using Python 3.11.1, 20,185 race records were collected of cyclists who competed at Gwangmyeong Velodrome in 2022 and 2023, and player efficiency was estimated using the R 4.3.1 package. Subsequently, the impact of players’ physical abilities (200 m records) on performance and player efficiency’s influence on the relationship between physical ability and performance were analyzed using Model 1 of PROCESS 4.1 Macro installed in SPSS 26.0. RESULTS First, players’ physical ability had a statistically significant impact on their performance. Specifically, the 200 m record significantly influenced the likelihood of finishing in the top 1 (coef = –.68 , p<.01 ), top 2 (coef = –.56, p<.01), and top 3 (coef = –.46, p<.01). Second, player efficiency moderated the relationship between players’ 200 m record and the likelihood of finishing within the top ranks. Specifically, the interaction term’s influence was empirically demonstrated between 200 m records and player efficiency on the likelihood of finishing within the top 1 (coef = –.47, p<.05), top 2 (coef = –.28, p<.05), and top 3 (coef = –.28, p<.05) for players with similar speeds, in that it significantly increased. CONCLUSIONS This study pioneers research that explains the relationship between players’ key competencies and performance based on resource-based theory, and it empirically demonstrates that player efficiency serves as a moderating variable in the relationship between key competencies and performance.
PURPOSE This study sought to investigate the effects of passive warm-up on flexibility, exercise performance, and lactate oxidation rate in track and field athletes. METHODS A total of eight male athletes with more than three years of athlete experience were recruited as participants, and passive warm-up (PW) and active warm-up (AW) treatments were conducted in a single-group crossover study design. The participants performed thermal stimulation at 40°C for 20 minutes as a PW and performed a 60-70% HRmax cycle as an AW. Flexibility and exercise performance were measured after each treatment. Anaerobic power was measured using the Wingate test, and lactic acid concentration was measured. RESULTS Body temperature significantly increased in both PW and AW, and no significant difference was observed in exercise performance between treatments. Flexibility and lactic acid oxidation rate were significantly higher in PW than in AW. CONCLUSIONS In track and field sprinters, PW did not exhibit any significant difference in anaerobic power and exercise performance compared to AW even though no physical exercise was performed, and PW was effective in body temperature, lactic acid oxidation rate, and flexibility. PW suggests the possibility of replacing AW.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of field and on-ice performances of ice-hockey players and the relationship of performance with subjective joint pain and dysfunction. METHODS A total of 25 male college icehockey players were evaluated for 19 items of performance. Pain and dysfunctions in the lower extremities and lower back were confirmed through the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score, Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, Hip Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score, and Osweatry Disability Index questionnaire. Players with similar performance characteristics were classified through a cluster analysis, and differences in performance and patient-reported outcomes between clusters were analyzed with a one-way analysis of variance. RESULTS The ice-hockey players were classified into “lower muscular strength and performance (cluster 1),” “lower cardiorespiratory endurance (cluster 2),” and “high muscular strength and performance (cluster 3).” Players in cluster 1 had more frequent ankle and knee joint dysfunctions and pain compared to those in cluster 3. Several performance test items affected the subjective joint score, and the related performance items were more in the proximal joint than in the distal joint. CONCLUSIONS Ice hockey players should perform training to supplement their individual lack of on-ice and field performance. Since performance may be limited because of joint dysfunction and pain, a joint-specific intervention strategy should be applied to improve physical and athletic performances.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of perceived organizational support of high school football players on innovative performance. Of particular note, we focused on examining the mediation effect of self-management between perceived organizational support and innovative performance. METHODS A total of surveys returned was 137 and the data used for the final analysis was 130. The data was processed using SPSS 21.0 statistical program and Lisrel 9.2 for confirmatory factor analysis. RESULTS The results of the analysis were as follows: first, perceived organizational support of high school football players had a positive effect on players’ self-management. Second, players’ self-management had a positive effect on players’ innovative performance. Third, players’ self-management fully mediated between perceived organizational support and players’ innovative performance. CONCLUSIONS The study concluded that maximizing both perceived organizational support and self-management of the high school football players are necessary in order for the organization to achieve high level of innovative performance.