
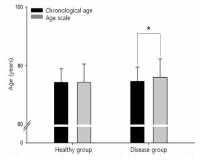
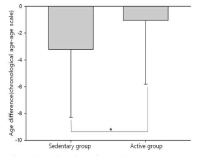
Purpose Evaluating the aging of senior and providing optimal sevices are important things for successful aging. This study identified functional fitness related with heath of aged 65 years or older and developed an age scale (longevity fitness age) for assessing their aging. Methods Participants were 458 older people (166 male, 292 female). They were divided into healthy group and disease group. Healthy group was used for the development of the longevity age equation and disease group was for investigating the validity of the equation. Participants completed 13 function fitness variables. The first principal component obtained from a principal component analysis was used to compute the equation. All variables except for grip strength and carrying beans were correlated with chronological aged. Grip strength and variables related lower functional fitness had differences between healthy group and disease group. Finally, 4 variables were selected for the equation. Results It was the following: longevity fitness age=0.942*X1+2, 185*X2+0.673*X3+0.051*X4+0.588*chronological age+58.401, where X1=standing up from a supine position, sec (s), X2=maximum walking (s), X3=standing up and sitting down a chair (s), X4=one leg balance with eyes open (s). The longevity fitness age of healthy group do not have a difference compared to their chronological age but disease group had a difference significantly. Age difference (chronological age-longevity fitness age) of sedentary group in disease group was significantly bigger than its active group. Longevity fitness age could assess an aging of senior. Conclusion We suggest that it can use as the tool for early detecting senior who need the health care service.

The frailty, characterized by reduced physiological function is closely related to a fall, disability, institutionalization, hospitalization, and mortality in the elderly. A reduced physical fitness is a major phenotype of the frailty. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among pre-frailty, physical activity (PA) and functional fitness in the community dwelling elderly women. The study participants were elderly women (n=338, 70.6±4.2years) aged over 65 who took part in the Korean Healthy Fitness Criteria study for the National Fitness Award Project in 2015. The pre-frailty was defined using the Cardiovascular Health Study frailty criteria. PA was assessed using the International PA Questionnaire (IPAQ). The participants were classified as regular PA participants if they meet the World Health Organization (WHO) PA recommendation for the elderly. Functional fitness was assessed using the composite of the National Fitness Award fitness testing for the elderly. Quality of life was evaluated using EuroQoL visual analogue scale and WHO quality of life assessment. As the results, the pre-frail elderly women were significantly older and obese (body mass index, percent body fat, waist circumference) than the healthy elderly. The pre-frail elderly presented significant decreases in walking, moderate intensity, and total PA compared to the healthy elderly even after adjusted for age and percent body fat. However, no significant difference was found in vigorous-intensity activity between the pre-frail and healthy elderly. Also, the pre-frail elderly women showed the decrease in functional fitness and quality of life compared to the healthy elderly. Regular PA was associated with high levels of muscular endurance and coordination in healthy and pre-frail elderly. In pre-frail elderly, high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance was associated with PA. In conclusion, regular PA is inversely associated with fitness decline in healthy and pre-frail community-dwelling elderly women. Regular PA might attenuate fitness decline in pre-frail elderly women.
PURPOSE This study investigated the perceptions and experiences of collegiate student-athletes with mental health concerns who are receiving sport psychology services. METHODS A total of 196 college student-athletes (98 male, 98 female) were recruited for the quantitative phase, while 14 athletes from 7 sports participated in the qualitative phase. This integrated approach sought to provide a comprehensive perspective on the research subject. The quantitative participants answered scales for depression (CES-D), anxiety (GAD-7), social support (NCAA RSSS), and mental help-seeking attitude (MHSAS), and the qualitative participants underwent in-depth interviews using a semistructured questionnaire based on a socioecological model. Quantitative data were examined using confirmatory factor analysis, reliability measures, independent t-test, and one-way analysis of variance via SPSS 28.0 and AMOS 28.0, and qualitative data were inspected through content analysis and expert meetings. RESULTS First, higher levels of depression, anxiety, and perceived social support were reported by female athletes as opposed to male athletes. Second, athletes in individual sports reported higher levels of social support than those in team sports. Third, athletes who planned to undergo future psychological counseling reported higher anxiety, social support, and helping attitudes than those with no plans to do so. Fourth, athletes who slept for more than seven hours reported lower levels of depression and anxiety and higher levels of perceived social support than those who slept for six hours or less. Fifth, freshman athletes reported higher depression levels than sophomore athletes. Sixth, student-athletes with no scholarships had higher anxiety levels than those with partial scholarships, who then reported higher perceived social support than those with full scholarships. Seventh, a lack of accessibility was the primary barrier to psychological service access for student-athletes. Eighth, engagement in interpersonal relationships was identified as a major stressor among student-athletes. CONCLUSIONS Differences in collegiate student-athletes’ mental health status as well as perceptions of and experiences in sport psychology services depend on various factors. These findings may serve as foundational data for improving sport psychology support services for collegiate student-athletes.
Frailty in older adults is related to an increased risk for poor health outcomes including falls, disability, hospitalization and mortality. The purpose of this study was to determine the thresholds of a functional fitness associated with frailty for community-dwelling woman aged 65 or older. In this study, the National Fitness Award(NFA) items for elderly were utilized as the physical function and fitness testing for korean elderly women. The total of 444 community-dwelling woman completed the testings. Frailty status was classified by the Japan LTCI system ‘Kihon Checklist’ in the study. The prevalence of the frailty was 19.1% in the study. The frail elderly were older and showed higher obesity index such as weight, body mass index (BMI), percent body fat and waist circumference than the normal elderly. After adjusting for age and BMI which was related to frailty, fitness testing items were compared depending on frailty. As the result, the frail elderly showed significantly lower fitness levels in grip strength, 30-second chair stand test, timed up and go, figure-of-8 walk around two cones, and 2-minute step test than the normal elderly. When the fitness cut-off values were analyzed using the ROC curve, also, grip strength: 34.13%, 30-second chair stand test: 14 reps, timed up and go: 7.09 seconds, figure-of-8 walk around two cones: 30.88 seconds, and 2-minute step test: 93 reps. In addition, based on the cut-off values of each fitness item, the group with a low fitness level showed a 1.86 to 3.09 higher odds ratio of frailty than the group with a high fitness level, even after age and BMI were adjusted. In conclusion, these findings indicate that the fitness cut-off values in this study are fitness levels for preventing frailty of Korean elderly women and there will be a need for a large-scale study including subdivided fitness cut-off values for each age group and targets elderly men as well.