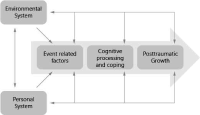
[Purpose] This study attempted to provide a literature review of the research on posttraumatic growth and to propose a revised model which mainly explain the relationships among serious leisure, posttraumatic growth, health, and happiness. The concept of psychological growth following a traumatic life event is most commonly referred to as posttraumatic growth in the literature and was first coined by Tedeschi and Calhoun (1995). It can be postulated that such experiences can lead to a richer appreciation for life, more compassion for others, closer relationships with others, better understanding of one's potentials and possibilities, and stronger religious faith. [Methods] The purposes of this study were achieved by (1) reviewing the posttraumatic growth and its relationship to serious leisure; (2) analyzing recent posttraumatic growth related models; and (3) proposing a revised posttraumatic growth model and a research agenda to further progress posttraumatic growth research. [Conclusions] Although there is an abundance of evidence for the existence of posttraumatic growth, its nature as well as benefits in relation to participation in serious leisure remain very partially understood. This study proposes a revised model for understanding the process of porsttraumatic growth in which serious leisure and cognitive processing play a significant role. Important implications of the relationships between serious leisure and posttraumatic growth are mainly discussed, alongside recommendations for future research.



PURPOSE This study aims to provide policy recommendations for the development of women’s football and the enhancement of the Women’s University Football League (WUFL) by examining participant satisfaction and meaningfulness of football. METHODS To achieve this goal, we distributed survey questionnaires, including 5-point Likert scale and open-ended questions, and subsequently analyzed 153 responses using qualitative data analysis software, N-vivo. RESULTS Our findings reveal that female students actively engaged in the WUFL express high overall satisfaction. Furthermore, participants perceive football as a source of happiness, an energy booster, and a platform for new experiences. Their involvement in football goes beyond typical leisure; it is regarded as a form of serious leisure. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, we propose actions such as fostering and elevating amateur women’s competitions, promoting female students’ participation in football, and developing a comprehensive strategy for increasing women’s enjoyment of playing football.