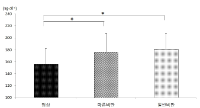
This study was designed to compare physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Sixty women, aged 20-29 yrs, volunteered to participate in the study as subjects. There were three groups, i.e., normal group (BMI < 24 kg·m-2 and %BF < 25%; n = 25), normal weight obese group (BMI < 24 kg·m-2 and 28% < %BF < 40%; n = 22), and obese group (BMI > 26 kg·m-2 and 30% < %BF < 40%; n = 13). Physical fitness, blood lipid profiles, and surrogate indices of insulin resistance were measured and compared among three groups. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) There were significant differences in all variables regarding body composition among three groups. All values were lowest in normal group and highest in obese group. 2) There was significant difference in sit-and-reach among three groups, whereas no significant differences were found in other variables regarding physical fitness among three groups. 3) There were significant differences in all variables regarding blood lipids among three groups. In particular, total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), TC/HDL-C ratio, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were significantly higher in normal weight obese group than normal group. 4) There were significant differences in all variables regarding insulin resistance among three groups. Fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR were lowest in normal group and highest in obese group. It was concluded that there would be abnormal blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance in even normal weight obese individuals as well as general obese individuals in 20s females.


PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of regular moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise on body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile in normal-weight obese women. METHODS The participants in the study were normal-weight obese women in their 20’s, divided into moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE) groups. Aerobic exercise was performed three times a week for 8 weeks. To verify the exercise effect, pre- and post- body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile were analyzed. RESULTS Weight and body fat decreased in both groups, and lean body mass and resting metabolic rate increased in the VIAE group. Blood TC, TG, and LDL-C decreased in both groups and HDL-C increased in the VIAE group. CONCLUSIONS In normal-weight obese women, vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise is more effective than moderate intensity aerobic exercise for improving body composition, resting metabolic rate and blood lipid profile.

Purpose The study examined the effects of a 12-week high intensity circuit training (HICT) on abdominal fat, physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese women. Methods Thirty obese women, aged 32-48 yrs, were recruited and randomly assigned to either HICT group (TR; n = 15) or control group (CON; n = 15). Subjects in the TR group participated in HICT of which resistance exercise and aerobic exercise were performed with a duration of 40 min/session and 3 sessions/wk for 12 weeks, whereas subjects in the CON group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns. Dependent variables included abdominal fat area, body composition, physical fitness, blood lipids profiles, and insulin resistance index. Analysis of variance with repeated measures with Bonferroni corrections was used to compare the outcomes between two groups. Results Main findings of the present study were as follows: 1) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant reductions in overall (i.e., body mass index and percent body fat) and abdominal obesity (i.e., waist circumference, total abdominal fat area, visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area-subcutaneous fat area ratio), 2) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in health-related physical fitness (i.e., muscular strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, balance, and cardiorespiratory endurance), and 3) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in fasting lipids, glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance. Conclusions The current findings of the study suggested that HICT would be an effective exercise intervention to improve metabolic complications associated with obesity and poor physical fitness in obese middle-aged women.



Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.
This study was designed to examine the effects of 12 weeks of resistance exercise training on physique, body composition, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Sixteen females were randomized into one of following two groups: resistance training group (RT group; n=8) and control group (CON group; n=8). Subjects in RT group completed 12 weeks of resistance exercise training for three times/wk, and subjects in CON group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and WHtR decreased significantly in RT group. 2) All variables regarding body composition did not change in both groups; however, fat mass was tended to decrease more in RT group than CON group. 3) Fasting plasma glucose decreased significantly in both groups, whereas other variables regarding insulin resistance did not change significantly in both groups. 4) All variables regarding blood lipids did not change significantly in both groups. Results indicate that 12 weeks of resistance exercise training was beneficial in physique and body composition; however, it was not beneficial in insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Future research including normal weight obese subjects with higher age would be warranted to elucidate more clearly the effects of resistance exercise training on metabolic status.
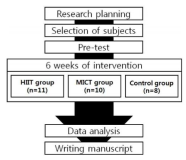
The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 6 weeks of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) under relatively equal energy expenditure on body composition, aerobic capacity, cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s overweight males. Twenty-nine males were randomized into one of the following groups: HIIT group (n=11), MICT group (n=10), and control group(n=8). Subjects in HIIT group completed 6 weeks of training for 25 min/sessions, three times/wk, and subjects in MICT group exercised for 33 min/session to equalize the energy expenditure with HIIT group. Subjects in control group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, fat mass, and WHR decreased significantly in HIIT group. 2) VO2max, VEmax, and time to exhaustion increased significantly in HIT group. 3) SBP decreased significantly in HIIT group and HRrest was tended to decrease in HIIT. 4) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR were tended to decrease in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. 5) HDL-C and TG were tended to improve in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. Results indicate that high intensity intermittent exercise training is more beneficial in aerobic capacity and cardiovascular function. It was also suggested that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise training in either high intensity intermittent or moderate intensity continuous was not sufficient enough to induce changes in body composition, insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles.

PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the associations between accelerometer-measured physical activity and both cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. METHODS We performed a retrospective cohort study with age-sex matched case-control using data from the 2014-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which was administered to South Korean adults (n=320). Individuals were categorized into quartiles based on accelerometer-measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA). Demographic and physical characteristics, waist circumference, visceral adiposity index, blood pressure, lipid profiles, and TG/HDL-C were observed. The associations between MVPA status and cardiometabolic disease risk factors as well as metabolic syndrome were determined using multiple logistic regression. RESULTS For the waist circumference, SBP, DBP, MBP, visceral adiposity, triglyceride, and a surrogate estimate of insulin resistance, the Q1 and Q2 groups had higher means compared with the Q3 and Q4 groups. HDL-C was higher in the Q3 and Q4 groups compared to the Q1 and Q2 groups. Odds ratios for cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome decreased in a curvilinear manner with the increasing quartile of MVPA. CONCLUSIONS Adults with higher MVPA participation were strongly associated with cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome.
Purpose The study was designed to investigate the effects of 12 weeks of circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome. Methods Forty-one menopausal women were randomly assigned to one of three groups. i.e., combined circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation group (CT+T: n=14), L-tryptophan supplementation group (T: n=14), and control group (CON: n=13). The subjects in CT+T exercised three sessions per week and took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in T took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in CON were asked to maintain their life pattern for the same period of intervention. Physical fitness and metabolic syndrome-related variables were measured at pre- and post-test. The data were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) Standing long jump, one leg standing with eyes closed, sit-and-reach, sit-up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in CT+T. 2) Body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, fat mass, and percent body fat decreased significantly in CT+T. 3) Total cholesterol decreased significantly in CT+T. 4) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting plasma insulin, and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in CT+T. FPG and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in T. 5) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and rate pressure product decreased significantly in CT+T. DBP and MAP decreased significantly in T. 6) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in CT+T and T. Conclusion It was concluded that the circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome, and that L-Tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on metabolic syndrome by improving insulin resistance and hypertension in menopausal women.