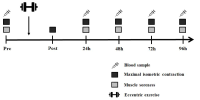
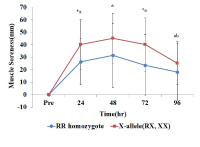
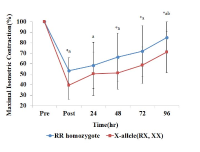
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the change of muscle damage markers after maximal eccentric exercise and to verify the difference of recovery according to ACTN3 gene polymorphism. [Methods] Fifty healthy males participated in this study. Subjects performed 25 times/1 set (total 2 set) maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexor muscles on a modified preacher curl machine with a between-sets rest time of 5 min. Maximal isometric contraction (MIC) was measured 6 times (pre, post, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Muscle soreness (SOR) was measured 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Blood samples were collected 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). ACTN3 gene polymorphisms were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Data were analyzed using a 2-way repeated measure ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test. [Results] Analysis of ACTN3 gene polymorphism revealed the following distribution: 22% RR (n=11), 50% RX (n=25), and 28% XX (n=14). Individuals were classified into the RR homozygote group (n=11) and the X-allele group (n=39). MIC showed a significant difference between groups and interaction (p<.05). The groups differed significantly in MIC at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after exercise and the X-allele group decreased more than the RR homozygote group. The groups differed significantly in muscle soreness and interaction (p<.05). SOR in the X-allele group was significantly higher than in the RR homozygote group at 24 h after exercise. Although blood CK activity was lower in the RR homozygote group than in the X-allele group, but there was no significant difference between the groups (p>.05). [Conclusion] The RR homozygote group showed lower muscle strength reduction rate, muscle soreness and blood CK activity than the X-allele group. This indicates that RR individuals have a lower risk of exercise-induced muscle damage than those with an X-allele.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to analyze the biomechanical variables involved in ballet dancers’ ankle muscle imbalance when performing relevé movements. METHODS The subjects of this study (n=14, age: 22.29±1.73 years old, height: 161.4±5.06cm, weight: 51.88±7.51kg) were 14 ballet dancers with 9 years of experience. Based on the reciprocal muscle strength ratio, the dancers were divided into the following groups: Close to the normal value (RMIS) and far from the normal value (RMIB) using the maximum values of plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the ankle joint using an isokinetic measurement equipment (60°/sec). RMIB). The biomechanical variables, namely the ankle joint movement and ground reaction force, were subsequently measured. SPSS 26.0 was used for data analysis and independent t-test was used for statistical verification. RESULTS The ground reaction force in the Z (vertical) direction based on the ankle joint muscle strength imbalance of ballet dancers was significantly lower in the RMIB group. In addition, although it was not a statistically significant difference, the plantar flexion movement was lower in the RMIB group, and there was a significant difference in the generation of ankle joint movement in the Z direction. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, in order for a ballet dancer to efficiently utilize the force generated from the supporting leg when performing a movement, ankle imbalance must be taken into consideration when training.
Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of a single corrective exercise (CEX) and corrective kinesio taping (CKT) on gait patterns, plantar pressure, balance, and pain in 20~30s female patients with moderate hallux valgus. Methods Twenty-one participants (age: 30.1±5.1 yrs; height: 164.1±4.8 cm; body weight: 56.7±6.8 kg; body mass index: 21.2±5.7 kg·m-2; hallux valgus angle: 27.2±6.1°) with hallux valgus was recruited and participated in three trials, i.e., CEX trial, CKT trial, and combined CEX and CKT (CEX+CKT) trial, repeatedly in a counter-balanced order. One week of wash-out period was placed between the trials to minimize the effect of the previous treatment on the next treatment. Variables related to gait pattern, plantar pressure, balance, and pain were measured during each treatment. We carried out repeated two way ANOVA on measured variables. Results 1) Regarding gait patterns, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant increases in the length of patients strides, the single support line during the stance phase, and significant reduction of the cadence. 2) Regarding gait cycle, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant reductions in the contact times of forefoot, midfoot, and heel. There was a significant reduction of double stance phase in CEX treatment. 3) Regarding foot pressure on gait, CEX+CKT treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of midfoot and heel. CEX treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of forefoot. 4) Regarding balance, CEX treatment and CKT treatments significantly increased one leg standing with eyes closed. 5) Pain was significantly reduced in CKT treatment and CEX+CKT treatments. Conclusions According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that a single CKT treatment was effective in reducing pain when walking and that plantar pressure, gait pattern, gait cycle, and balance were improved through a single bout of CEX treatments. Therefore, treatments by stage, starting with CKT treatments to reduce the pain, and then treating CEX to improve the gait pattern, gait cycle, foot pressure when walking, and balance ability, would be effective. Future research is warranted to identify the effects of long-term treatments.
PURPOSE This study investigated the effect of non-linear periodization strength training on basic and professional fitness of national cross-country skiers. METHODS The body composition (height, weight, BMI, body fat %), basic physical strength (grip strength, lung capacity), anaerobic power (peak power, average power), graded exercise test (maximum heart rate, running time, VO2max, lactic acid), isokinetic strength (trunk strength), and 1RM (bench press, dead-lift, squat, shoulder press, leg curl, bicep curl, cable triceps extension) of nine national cross-country skiers (male: 5, female: 4) were measured. All analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0, Kruskal-Wallis H tests were applied to observe the changes by training methods. Mann-Whitney U tests were used as Post Hoc. RESULTS The results indicated that running time and VO2max post-test improved compared to that for the pre-test for graded exercise test. The lumbar extension strength of the post-test was higher than that for pre-test. There was no significant difference in other variables. CONCLUSIONS It is suggested that nonlinear periodization strength training can be expected to improve running time, VO2max, and trunk strength for cross-country athletes; however, it does not affect the overall changes.
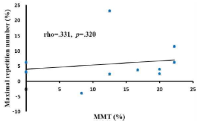
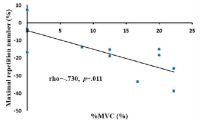
The purpose of this study was to determine whether maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance. Eleven healthy, resistance-trained males were tested for one repetition maximum (1-RM) the chest-press exercise, and than manual muscle testing (MMT), two-arm at 80% of 1-RM and one-arm at 40% of 1-RM in the pectoralis major were measured for the maximum voluntary contraction (%MVC) and maximum number of repetitions during the chest press exercise. Exercise velocity was constantly 4 seconds (concentric: 2-s, eccentric: 2-s) per repetition. The changes in %MVC were significantly higher in non-dominant limb (NDL) compared with dominant limb (DL) pectoralis major during two-arm chest press (p < 0.01) and one-arm chest press exercise (p < 0.05). In contrast, the changes in MMT (p < 0.05) and maximum repetition number (p < 0.01) were significantly higher in DL compared with NDL during one-arm chest press exercise. There was no correlation between maximum repetition number and MMT (rho = 0.331, p = 0.320). However, maximum repetition number was significantly negative correlated with %MVC in two-arm chest press (rho = -0.730, p = 0.011). It is possible that maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance.

PURPOSE This study analyzed the difference in lower extremity joint angle and shock absorption patterns at the point of maximum ground reaction force during single-leg drop landing with or without anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR). METHODS Forty adult males were recruited for this study, with 19 in the ACLR group (age: 20.52±1.43years, height: 179.26±5.18cm, weight: 74.91±6.29kg) and 21 in the control group (age: 21.42±1.61years, height: 174.97±6.83cm, weight: 69.27±7.56kg). Participants performed single-leg landings on a 30cm tall box. An independent sample t-test was used to analyze the difference in kinetics variables at the point of maximum ground reaction force upon landing, with significance set at p=0.05. RESULTS The lower limb joint angle showed significant differences in hip flexion, hip abduction, knee flexion, and knee valgus (p<0.05) between groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the results of kinetics variables during single-leg landing (maximum ground reaction force, lower extremity stiffness, and shock absorption time). CONCLUSIONS The ACLR group showed a clear difference in kinematics compared to the control group, but no significant difference in kinetic results was found. The two groups compensated for the same impact with different movements, though movements in the ACLR group may increase the risk of ACL re-injury. Those with ACLR should strive to reduce the risk of re-injury by training to use correct movements.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effect of an ankle strap on kinetic variables of the lower limb during forward jump landing. METHODS Twelve healthy adult men (mean age, 23.58±2.22 years; mean height, 177.83±5.37 cm; mean weight, 75.00±7.72 kg) participated. The participants stood barefoot on both legs at a horizontal distance of 40% of their body height from the center of the force plate, then jumped forward and landed on the force plate with their dominant or non-dominant leg over a 30-cm hurdle while wearing or not wearing an ankle strap. Joint angle, peak vertical force, loading rate, and leg stiffness were calculated. Paired t-test and repeated-measures two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni’s post hoc tests were used to compare the characteristics of both lower limbs and the effect of wearing an ankle strap. The significance level was α < .05 RESULTS Our results showed significant differences in kinematic variables between the dominant and non-dominant legs without the ankle strap. With the ankle strap, the inversion angles at the ankle joints of both lower extremities were significantly decreased, and an interaction effect between both legs and the ankle strap occurred in the internal rotation angle of the ankle joint. Kinetic variables did not differ significantly. CONCLUSIONS The ankle strap did not completely compensate for ankle instability in the non-dominant leg, but it significantly reduced the angle of internal rotation at the ankle joint. Thus, we recommend that correct wearing of the ankle strap in sports since it reduces the possibility of lateral ankle sprains to some extent.
PURPOSE This study aimed to characterize the kinematic variables of stair climbing in adult women by analyzing the effects of varying heel heights on their climbing behavior. METHODS A total of 24 adult women (age: 22.08±1.28years; height: 160.43±4.30cm; weight: 54.10±6.39kg) participated in this study. All subjects wore the same type of high heels with heights of 1cm, 5cm, and 7cm while performing stair climbing on stairs measuring 18cm in height. Ten infrared cameras (200Hz) and ground reaction force sensors (1000Hz) were set up on the stairs, along with an 8-channel electromyography system (1000Hz) to analyze the maximum moments at each joint and the muscle activation during stair climbing. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM., USA). All variables underwent the Shapiro–Wilk normality test, with repeated measure analysis of variance or the Friedman test applied based on the results. Post hoc tests were conducted using the LSD test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test. RESULTS Our study found four key findings. First, a significant decrease in maximum dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, and adduction moments of the ankle joint was observed with increasing heel height. Second, the maximum extension, adduction, and external rotation moments of the knee joint significantly decreased as heel height increased, while the maximum abduction and internal rotation moments significantly increased. Third, the maximum flexion, extension, and abduction moments of the hip joint significantly increased with higher heel heights. Fourth, muscle activity of the rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and gastrocnemius decreased with increasing heel height compared to walking; however, muscle activity in the tensor fasciae latae increased. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that as heel height increases, the risk of injury may rise due to limited ankle use and increased moments in the knee and hip joints, potentially leading to muscle strength imbalances in adult women, particularly through the overuse of specific muscles.
Purpose This study was conducted to analyze the differences of physical characteristics focused on the physique, strength, and power for cycling national athletes (Sprint cyclists and Road race cyclists). Methods We measured various factors (e.g., height, weight, body fat ratio, thigh circumference, waist circumference, anaerobic power, isokinetic muscular strength, muscle power, squat jump by 1RM intensity, and so on) for a total 11 male cycling national athletes (5 Sprint cyclists and 6 Road race cyclists). Results First, the body composition showed the significant differences only in weight (p=0.31) and BMI (p=.001) for Sprint cyclists. Second, the values of the anaerobic power for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists only at peak power (p=0.28), whereas there was no significant difference in average power, isokinetic muscular strength, and muscle power between the two groups. Third, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle (p = .016) for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists. Fourth, the significant difference in Time to Peak Torque was not found between two groups. Fifth, the values for the Sprint cyclists showed the significant difference in all 5 intensity groups (0%, 30%, 50%, 60%, and 80%) (p=.001) of the squat jump. Also, there was a statistically significant difference only in 0% velocity between the two groups, except for exercise intensity. Conclusions From the various measures between two groups, the Sprint cyclists relatively showed the high weight, BMI (muscle mass), and maximum power. Additionally, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle and the squat jump were higher in the Sprint cyclists than the Road race cyclists. These data may be used as basic data to improve the physical fitness factors related to the athletic performance of the athletes by reflecting them in the effective training plan and evaluation of the athletes.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of an 8-week online yoga training on body composition, muscle activity, flexibility, and balance in males (n=7) and females (n=15). METHODS Twenty-two participants were recruited and divided into two groups (Exercise group, n=11 and control group, n=11). All participants had two visits. During the visits, body composition, muscle activity for forward and back-bending poses, flexibility for sitting-forward and back-bending poses, and balance for one-leg standing were determined. After 8-week yoga training, all measurements were re-performed. An independent t-test was performed to determine the difference between the exercise and control groups. A two-way repeated measures of ANOVA was used to assess the interaction effects (group*time). All values were represented as mean ± standard deviation. An α level was set at 0.05 for all analyses. RESULTS First, the height significantly increased (F=16.573, p=0.001) and body fat mass (F=7.109, p=0.015) and body fat percent (F=7.667, p=0.012) were significantly decreased after the 8-week online yoga training. Second, the muscle activity for vatus lateralis doing a back-bending pose (F=6.140, p=0.022) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Third, the flexibility on sitting-forward bending pose (F=4.661, p=0.043) and back-bending pose (F=11.650, p=0.003) were statistically increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Lastly, balance on the Center Of Pressure (COP) X (F=5.769, p=0.026) and the Center Of Pressure (COP) Y (F=4.365, p=0.05) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. CONCLUSIONS This study will provide scientific evidence on improving exercise programs using online yoga training on physical activity.