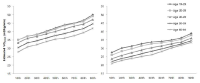
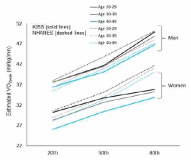
To provide the distribution of cardiorespiratory fitness including Bruce treadmill exercise time and estimated peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and investigate association with cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic syndrome, sedentary lifestyle, or education level among Korean adults. Analysis of data on 2,006 adults (19-64 yr) who had completed a maximal grade treadmill exercise test, from the Sports Institute of Sports Science Fitness Standards (KISS FitS) project 2014-2015. The mean maximal exercise time was 11’26’‘, 11’18’‘, 11’06’‘, 10’03’‘ and 8’51’‘ (minutes and seconds) for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, for women, it was 9’49’‘, 9’09’‘, 8’42’‘, 8’01’‘ and 7’33’‘ for the corresponding age groups. The mean peak oxygen uptake was estimated as 42.3, 41.8, 41.2, 37.6 and 33.6 ml/kg/minute for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, For women, it was 34.0, 31.8, 30.3, 28.0 and 26.4 ml/kg/minute for the corresponding age groups. A positive association between cardiorespiratory fitness level and education level was observed for both men and women. Furthermore, participants with sedentary lifestyle had a significantly lower cardiorespiratory fitness than participants with activity lifestyle. Finally, Men with moderate and high fitness level had 50% and 87% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, and women had 48% and 50% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, respectively, than the ones with low fitness level after adjustment for age, smoking, alcohol intake, and sedentary lifestyle. These results can be used to track future Korean assessments and to evaluated interventions. The differences in fitness status by education level, sedentary lifestyle or metabolic syndrome can also be used to develop health policies, program and educational services.

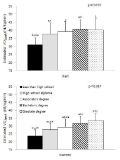
Frailty in older adults is related to an increased risk for poor health outcomes including falls, disability, hospitalization and mortality. The purpose of this study was to determine the thresholds of a functional fitness associated with frailty for community-dwelling woman aged 65 or older. In this study, the National Fitness Award(NFA) items for elderly were utilized as the physical function and fitness testing for korean elderly women. The total of 444 community-dwelling woman completed the testings. Frailty status was classified by the Japan LTCI system ‘Kihon Checklist’ in the study. The prevalence of the frailty was 19.1% in the study. The frail elderly were older and showed higher obesity index such as weight, body mass index (BMI), percent body fat and waist circumference than the normal elderly. After adjusting for age and BMI which was related to frailty, fitness testing items were compared depending on frailty. As the result, the frail elderly showed significantly lower fitness levels in grip strength, 30-second chair stand test, timed up and go, figure-of-8 walk around two cones, and 2-minute step test than the normal elderly. When the fitness cut-off values were analyzed using the ROC curve, also, grip strength: 34.13%, 30-second chair stand test: 14 reps, timed up and go: 7.09 seconds, figure-of-8 walk around two cones: 30.88 seconds, and 2-minute step test: 93 reps. In addition, based on the cut-off values of each fitness item, the group with a low fitness level showed a 1.86 to 3.09 higher odds ratio of frailty than the group with a high fitness level, even after age and BMI were adjusted. In conclusion, these findings indicate that the fitness cut-off values in this study are fitness levels for preventing frailty of Korean elderly women and there will be a need for a large-scale study including subdivided fitness cut-off values for each age group and targets elderly men as well.
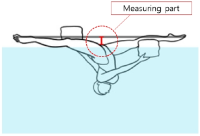
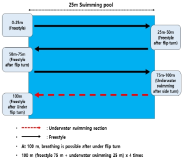
Purpose The purpose of this study is to compare the physical fitness levels among artistic swimmers in artistic swimmer national team trials. It is aimed to strengthen the physical fitness evaluation criteria of the national team and construct a physical fitness evaluation item suitable for an artistic swimming event. Methods A total of twenty two female elite artistic swimmers participated in this national team selection trial. Measurement list was performed body composition (Height, Weight, Body fat(%), Skeletal muscle mass, Lean body mass, BMI, Shoulder width, Arm span), Basic physical fitness (Push-up, Sit-up, Chin-up, Endurance of trunk backward extension and Sargent jump), Flexibility (Trunk backward extension, Shoulder flexibility, Frog position and Underwater split R, L) and Swimming test (100 m freestyle, 400 m freestyle). Data were analyzed by Independent t-test using SPSS Statistics ver 25.0. Results Age and skeletal muscle mass were significant difference between the two groups (p<.05). Also, 400 m swimming test was significantly different (p<.001). However, there were no significant differences in basic physical fitness and flexibility. Conclusions These results suggest that selected athletes are excellent not only in acting but also in physical fitness. Based on these results, it is necessary to construct a physical fitness items for the preliminary artistic swimming and to classify the physical fitness evaluation criteria according to the characteristics of the artistic swimmers.


Purpose This study confirmed the historical significance of the First World War US Combat Strength Training Fitness System for contributing in the ROK military sports development. Methods This research method is literature analysis to be focused by the previous US Army Field Manuals. Results Concretely, The meaning of US Army fitness training was divided into four stages. First, this study confirmed the actual condition of the US Army fitness before First World War. Since 1916, US Army has developed a group physical training program applied the items suitable for the war and has systematically reflected the program in the recruitment training. Second, this study confirmed the process of operating military fitness program during the First World War. US Army physical fitness program provided an effective method to suit soldier fitness for war. Third, this study observed the fitness training changes of US Army after the First World War. At that time, US Army focused on maintaining health and basic physical strength for civilians and reserve forces, but US Army ran parallel with basal physical fitness and combat physical fitness after the Korean War. Fourth, this study compared military strength training between First World War and current US Army. Since First World War, the training of US Army has been developed around doctrine and manuals to be maintained the consistency of the system. In conclusion, US Army physical training system of First World War meant to be provided the basis of current military physical education and physical training. In other words, current fitness training is not dogmatic but has evolved, and it accommodated the basics of soldier physical training course from the past.







The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of National Fitness Award program group exercise classes on daily fitness and balance-confidence among the elderly participants(n=496, 80.2% women). This study investigated body composition, daily fitness, and balance-confidence, and quality of life among the subjects who participated in the combined exercise program of improving physical fitness class for 8-week in the 10 national physical fitness certification centers by the demonstration project for the elderly of 2013 Korean National Fitness 100 project. Body composition and physical fitness for daily living were defined by Korean National Fitness 100 project for elderly, also the balance-confidence and health-related questionnaires were added. The following results were obtained by comparing the pre-test and post-test. In body composition body weight (p<.05), body mass index (p<.05), fat mass (p<.01), and percent body fat (p<.05) were significantly decreased, but muscle mass was not. Except for walking-around-two-cones-in-a-figure 8, all other daily fitness items such as relative grip strength (p<.001), chair sit to stand, two minutes place to walk, and sit-and-reach significantly increased (p<.01), and timed up and go were significantly decreased (p<.01). In balance confidence rating ABC tests (p<.001) were shown significantly increased. Although, quality of life measured by EQ-5D was not significantly improved, self-health status measured by EQ-VAS (p<.001) showed significant increase. Therefore, the group exercises of National Fitness Award program improved body composition, daily fitness and balance confidence in Korean elderly participants.
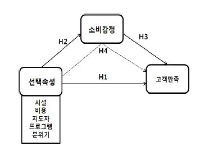
The purpose of the study was to provide managers and owners of fitness center with new marketing strategies for distinction strategies of quite competitive Korean fitness industry with analysis of mediating effects of consumption emotion within the relationship of fitness selection attribute and customer satisfaction. This paper chose fitness center customers as population of this study who registered in each 5 fitness centers in Seoul and Gyeonggi using convenience sampling. For this study, 400 questionnaires were given fitness center customer. For the analysis of data, 376 questionnaires were used using SPSS 15.0 Windows and Amos 7.0. To examine respondents demographics traits, frequency analysis was processed and reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis and correlation analysis for relationship among the variables were conducted. For the verification of model suitability and research hypotheses, the mediating effects were tested by using Bootrapping method and Aroian-test through structure equation modeling. The significance level was set at α=.05, and the results are as follows. First, Among fitness selection attribute variables, structural strategy, cost, a trainer and program had significant influence on customer satisfaction, but, atmosphere and facilities had not significant on customer satisfaction. Second, Among fitness selection attribute variables, structural strategy, cost, a trainer and atmosphere had significant influence on consumption emotion, but, facilities and program had not significant on consumption emotion. Third, consumption emotion had significant influence on customer satisfaction. Fourth, consumption emotion fully mediated in the relationship between fitness selection attribute and customer satisfaction.



Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between the track records and physical abilities in elite cyclists(keirin). Methods Twenty three elite cyclists were measured height, weight, lower body circumference(thigh, calf, and ankle), basal physical abilities(grip/back muscle strength, 25m sprint, Sargent jump test, Burpee test, shuttle run test), one-repetition maximum(1RM) strength(back squat, bench press, leg curl, power clean, dead-lift, leg press), aerobic capacity(V̇O2max, METs, HRmax), and track records(200m and 500m). Stepwise multiple regression analyses were performed to investigate which physical abilities related to track records. Results A statistically significant relationship was found between 200m track records and 2 variables which were the thigh circumference and 1RM leg press(p<.05). Also, the thigh circumference and 1RM leg press were significantly related to 500m track records(p<.05). Conclusions The results showed that the thigh circumference and maximal strength were associated with the track records in elite cyclists(keirin).



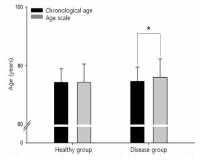
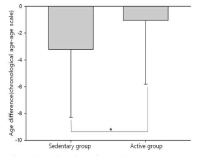
Purpose Evaluating the aging of senior and providing optimal sevices are important things for successful aging. This study identified functional fitness related with heath of aged 65 years or older and developed an age scale (longevity fitness age) for assessing their aging. Methods Participants were 458 older people (166 male, 292 female). They were divided into healthy group and disease group. Healthy group was used for the development of the longevity age equation and disease group was for investigating the validity of the equation. Participants completed 13 function fitness variables. The first principal component obtained from a principal component analysis was used to compute the equation. All variables except for grip strength and carrying beans were correlated with chronological aged. Grip strength and variables related lower functional fitness had differences between healthy group and disease group. Finally, 4 variables were selected for the equation. Results It was the following: longevity fitness age=0.942*X1+2, 185*X2+0.673*X3+0.051*X4+0.588*chronological age+58.401, where X1=standing up from a supine position, sec (s), X2=maximum walking (s), X3=standing up and sitting down a chair (s), X4=one leg balance with eyes open (s). The longevity fitness age of healthy group do not have a difference compared to their chronological age but disease group had a difference significantly. Age difference (chronological age-longevity fitness age) of sedentary group in disease group was significantly bigger than its active group. Longevity fitness age could assess an aging of senior. Conclusion We suggest that it can use as the tool for early detecting senior who need the health care service.

PURPOSE This study investigated the correlation between anaerobic power and maximum muscle strength in relation to core muscle strength among Korean national golfers. METHODS A total of 96 national golfers (53 females and 43 males) participated in the study. Body composition was assessed using multi-frequency impedance devices, while core and lower extremity muscle strength (extension, flexion, flex/ex ratio) was measured using isokinetic strength tests. Anaerobic power was evaluated through peak power, average power, and power drop rate tests conducted on bicycle ergometers, along with one-repetition maximum (1RM) tests for squats and bench presses. Mean and standard deviation values were calculated for all variables, and linear regression analysis was performed to verify correlations, with statistical significance set at α=.05. RESULTS The comparison of physical characteristics between male and female national golfers revealed significant differences in age, height, body fat percentage, lean body mass, and weight. There was a strong correlation between core muscle strength and isokinetic lower extremity muscle strength. Additionally, a strong correlation was observed between core muscle strength and anaerobic power and between peak power and average power. Furthermore, there was a high correlation between core muscle strength and bench press and squat maximum muscle strength. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights the correlation between various professional physical fitness variables of Korean national golfers over the past decade. The findings are expected to provide valuable insights for coaches and players in developing future training programs.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the factors affecting job stress in fitness instructors, and to elucidate the mediating effects of mindset on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress. METHODS Using convenience sampling, a survey was conducted with 217 male and female fitness instructors nationwide. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0 for descriptive statistics, frequency analysis, and reliability analysis, and AMOS 22.0 for confirmatory factor analysis to validate the measurement tools. SPSS PROCESS Macro v4.0 (Model 4) was utilized to verify the mediating effects of the research model. RESULTS Self-reflection among fitness instructors was found to significantly reduce job stress. A growth mindset was found to have a partial mediating effect on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress among fitness instructors, whereas a fixed mindset did not have a significant impact . CONCLUSIONS The results confirm that self-reflection and having a growth mindset significantly influence the reduction of job stress in fitness instructors.