PURPOSE This study aimed to prove the mediator effect of skill level on participation frequency and injury level of leisure sports players with the highest injury rate. METHODS Raw data of the “2019 Sports Safety accident data” conducted by the Korea Sports Safety Foundation were used for this study. We analyzed 857 leisure sports players participating in events with the top four highest injury rates (Basketball, Soccer, Baseball/Softball, Foot Volleyball). Frequency, descriptive statistics, and correlation analyses using SPSS version 27.0 and Process macro model 4 were employed for analysis. RESULTS The results regarding participation frequency, injury severity, and skill level among recreational athletes are as follows. First, a positive correlation was established between the participation frequency of recreational athletes and their skill levels. Second, the correlation between participation frequency and injury severity was observed only in soccer and basketball. Third, skill level plays a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. The results indicate that as the participation frequency among leisure sports players who participate in ball sports with a high injury rate increases, this affects the degree of injury. CONCLUSIONS Skill level appears to play a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. Based on the results, we recommend safety education not only on the relationship between participation frequency and injury level, but also the intermediary role of skill level.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.







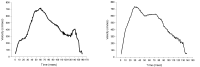

The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of running economy and energy return in lower extremities according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes, furthermore to investigate the relationship between running economy and energy return for the improvement of sports performance. Subjects employed for this study were 10 healthy male college students who have not had the experiences in lower extremities injuries. Four different kinds of shoes in bending stiffness as with 0.56 N/mm, 0.74 N/mm, 0.96 N/mm, 1.21N/mm were used respectively. 3-D cinematography and pulmonary gas analyzer were utilized for energy return and energy consumption data during running according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes to obtain the following results. As the bending stiffness of running shoes increased, the statistical significance were not founded, however, the tendency of decrease in max. flexion moment and power, increase in max. extension moment and power in lower extremity joint were showed. Joints energy showed no statistical significance in phase 1, however, the tendency of lesser absorbtion as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased were showed. More energy were generated as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased in phase 2 with no statistical significance. Energy economy increased according to the increase of bending stiffness of running shoes. Negative correlation were showed between flexion moment of hip joint and energy consumption(p<0.05). Slightly higher degree of correlation between max. flexion power of hip and ankle joint and energy consumption were showed without statistical significance. Negative correlation were showed between joints energy and energy consumption for ankle joint in phase 1(p<0.05).

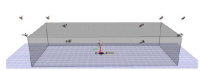

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the lower limb muscle activity based on direction prediction presence or absence and gender during side cutting in healthy college students. METHODS The study participants included 14 healthy males and females (8 males; 6 females). All participants ran at full speed for a distance of 12m, and side-cutting was carried out at 45 degrees in a randomly indicated direction and in a fixed direction. Simultaneously, data regarding vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris muscle activity of the dominant leg were collected using an electromyography sensor, and data regarding vertical acceleration were collected using an inertial sensor attached to the pelvis. A sync webcam was used for obtaining the initial contact of side cutting and the stance period time. During the 10 milliseconds (pre-activation) prior to the initial contact and 50% of the stance phase (loading phase), vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris average muscle activity and hamstring to quadriceps ratio included as variables. RESULTS During the pre-activation and loading phase, the vastus medialis muscle activity of the male group was higher in the unexpected condition than in the expected condition. Furthermore, hamstring to quadriceps ratio was confirmed to be lower under unexpected condition compared to under expected condition during on loading phase. CONCLUSIONS The study results suggest that the risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury may increase with side cutting under unpredictable conditions. It is expected to provide useful information for identifying factors related to knee injury in the general population.