The aim of this study was to evaluate gender differences of expert and non-expert in match playing time, moving distance, energy consumption and heart rate (average, maximal) during 16 simulated badminton matches in male (n = 16) and female (n = 16) national elite players. The players had perform three sets on same day, and this time observed the playing time, moving distance, energy consumption and heart rate (resting, average, maximal) level during badminton match. Analyses of variance with repeated measures were used to test any significant time×group interaction effects on the measured variables. Statistical significances were tested at p = 0.05 with spss-pc (version 18.0). As a result, male's player had significantly difference between expert and non-expert in moving distance (p=.012), energy consumption (p=.003), average heart rate (p=.002) and maximum heart rate (p=.002). Female's players showed significant difference between expert and non-expert in moving distance (p=.001) and energy consumption (p=.012). In conclusion, there seemed to be an increased playing intensity (i.e., moving distance, energy consumption, average heart rate and maximum heart rate) from expert than non-expert in gender differences. These results suggest that men male's players with expert performed the game at a higher intensity than compared to non-expert, on the other hand female's player with non-expert showed that more activity and energy consumption was unclear during the game

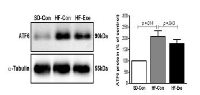
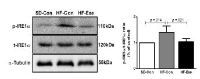
This study was to performed to the effect of 8-week endurance exercise influences on body weight, glucose tolerance and ER-stress in soleus of 16weeks Rats fed High-Fat diet. Rats were randomly assigned to 3 group; (1)Sprague-Dawley Control diet (SD-Con/n=4), (2)High-Fat diet Control (HF-Con/n=4), (3)High-Fat diet Exercise (HF-Exe/n=4). Exercise group ran on the treadmill for 30min/day at the level of 21m/min for 5days/week during 8weeks. Results showed that body weight and glucose tolerance of the HF-Con group was remarkably increased(p<.05) compared to other groups. However, HF-Exe group significantly decreased body weight and glucose tolerance compared to HF-Con group. Moreover, level of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺, which are main proteins of ER-stress were significantly increased in HF-Con group higher than other group, whereas HF-Exe group significantly decreased the expression of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺. Taken together, these finding suggested that the reduction of the body weight, glucose tolerance and unfolded protein response by treadmill exercise may represent a positive adaptation protecting against high-fat diet-induced ER stress.




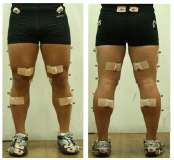
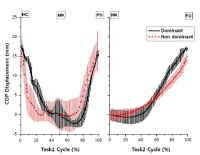
The purpose of this research is to investigate the factors affecting the performance capability of lunge movements by performing lunge movements which are commonly used as a method of instant physical movement in sports with a kinetic analysis including an EMG analysis. This research targeted 14 skilled fencers and made the subjects perform kick-lunges which allow them to go farthest from their positions and performed an analysis on such, applying a 3D motion analysis system and an EMG system. The subjects performed kick-lunges in two movements; one with a preliminary movement and the other without it and those are performed with both dominant leg and non-dominant leg. The result of this research is as follows. The lunges with a preliminary movement showed higher performance capability than those without it. Furthermore, as the level of skills gets higher, the length of lunges gets longer, and it seemed that a tactical mechanism shortening exercise performance times was used as a mechanism to control the impulse coming from such lengthened lunges. In addition, a difference appeared in mechanical factors such as moment and power in a dominant leg movement and it seemed to result from a difference in an functional capability using muscles.




The purpose of this study was to examine the effect on Electro-chemical screen and anaerobic exercise capacity caused by short-term weight loss in amateur boxing players. Subjects of this study were 10 male university boxing player who conducted to weight loss methods. In 1st weight loss, boxing players took rapid weight loss during 5-7days, In 2nd weight loss, boxing players took weight loss 3kg during 2 weeks. The change of ECS and anaerobic exercise capacity were measured before and after weight loss period. Anaerobic exercise capacity was measured by 1RM of bench press and squat. In addition, using the wing-gate test muscle power and power endurance was evaluated. To find out the changes in ECS, urine and saliva was collected after waking up were analyzed. The results were as follow. First, 1RM of squat(p=.003), peak power(p=.023) and mean power(p=.015) showed significant decrease after 1st weight loss method. However in 2nd weight loss method, no factor of ECS and anaerobic exercise capacity were significantly decreased. Second, total urea(p=.015), urine rH2(p=.017), urine conductivity(p=.003), and utilization of vitamin(p=.005) showed significant decrease after 1st weight loss method. However in 2nd weight loss method, urine conductivity(p=.038) and saliva rH2(p=.028) showed significant increase after weight loss. In conclusion, amateur boxing players need a systematic weight loss to maintain optimal conditioning.
PURPOSE This study investigated the effects of moderate-intensity continuous exercise (MICE) and high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE), performed postprandially, on blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels in men aged 40–50 with prediabetes and prehypertension. METHODS Twelve men with prediabetes and prehypertension were selected. After consuming a liquid meal, the participants participated in three trials: MICE, HIIE, and a non-exercise condition, with a one-week washout period between each trial. The trials were conducted in a counter-balanced manner to ensure equal energy expenditure across conditions. The intensity of the MICE trial was set at 70% of the heart rate reserve (HRR), whereas the HIIE trial alternated between 50% and 90% of HRR for 30 minutes. Blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels were measured at various time points during each trial, and a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA was used for analysis. RESULTS 1) In the MICE trial, significant reductions were observed in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), systolic blood pressure (SBP) (at 50 minutes post-exercise), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (at 20, 40, 50, and 60 minutes post-exercise). 2) In the HIIE trial, significant reductions in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), SBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise), and DBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise) were observed. Blood lactate levels significantly increased. 3) When comparing the two exercise trials, blood glucose in the HIIE trials showed a recovery trend post-exercise, and blood lactate levels increased to a greater extent. CONCLUSIONS These findings suggest that both MICE and HIIE effectively lower blood glucose during exercise, but HIIE causes a more rapid post-exercise increase in blood glucose compared to MICE. In addition, MICE results in a smaller rise in blood lactate. Therefore, MICE is recommended for improving prediabetes and prehypertension. Future research should compare these effects in healthy individuals and examine long-term adaptations to repeated exercise.
PURPOSE This study examined levels of safety knowledge and practice among recreational sports participants, focusing particularly on impacts of gender, age, injury experience, and exercise-level profile. In sports environments, understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted strategies to promote safe behaviors. METHODS Survey data from 7725 participants engaged in regular recreational sports activities were analyzed. Latent Profile Analysis was employed to categorize participants based on their injury experience and exercise levels, resulting in two profiles: Group 1 (moderate or severe injury experience with intermediate exercise levels) and Group 2 (mild injury experience with beginner exercise levels). Three-way ANOVA was then used to evaluate relationships between these profiles and safety knowledge and practice levels. RESULTS Results revealed significant differences across sex, age, and profile groups. Compared with women, men demonstrated higher levels of safety knowledge and practice, which were likely influenced by greater exposure to high-intensity sports and risk-taking tendencies. Adolescents exhibited the highest levels of safety knowledge and practice linked to structured safety education, but these levels declined in early adulthood and then increased again in middle age due to growing health awareness and preventive motivations. Furthermore, participants in Group 1 consistently showed higher levels of safety knowledge and practice than those in Group 2, highlighting injury experience’s role in shaping safety behaviors. CONCLUSIONS These findings underscore the importance of developing gender-specific safety education programs, age-appropriate interventions, and training initiatives tailored to beginning participants. Future research should evaluate these strategies’ long-term impact on safety practices and injury prevention in diverse sports settings.
PURPOSE This study compared the spatiotemporal gait parameters and kinetic variables of lower extremity joints during gait between normal and presarcopenia groups of middle-aged women. METHODS Middle-aged women participants (n=24) were divided into two groups based on the Appendicular Lean Mass Index (ALMI): a normal group (n=12) and a presarcopenia group (n=12). During walking by each group, spatio-temporal gait variables and the maximum moments and net joint power of the ankle, knee, and hip joints in different directions were calculated and compared using independent samples t-tests with IBM SPSS 27.0 software. RESULTS The normal group and the presarcopenia group showed no statistically significant differences in spatiotemporal gait variables. However, during the shock absorption phase of gait, the presarcopenia group showed significantly higher maximum knee abduction, maximum knee internal rotation, and maximum hip external rotation moments than the normal group. Additionally, the presarcopenia group exhibited significantly higher maximum net knee power during the shock absorption phase. Conversely, during the propulsion phase of gait, the normal group exhibited significantly higher maximum net ankle power than the presarcopenia group. CONCLUSIONS Middle-aged women with presarcopenia experienced higher knee joint loading and lower ankle joint propulsion during walking, indicating the need for training to improve lower limb strength.
PURPOSE This study sought to investigate the effects of passive warm-up on flexibility, exercise performance, and lactate oxidation rate in track and field athletes. METHODS A total of eight male athletes with more than three years of athlete experience were recruited as participants, and passive warm-up (PW) and active warm-up (AW) treatments were conducted in a single-group crossover study design. The participants performed thermal stimulation at 40°C for 20 minutes as a PW and performed a 60-70% HRmax cycle as an AW. Flexibility and exercise performance were measured after each treatment. Anaerobic power was measured using the Wingate test, and lactic acid concentration was measured. RESULTS Body temperature significantly increased in both PW and AW, and no significant difference was observed in exercise performance between treatments. Flexibility and lactic acid oxidation rate were significantly higher in PW than in AW. CONCLUSIONS In track and field sprinters, PW did not exhibit any significant difference in anaerobic power and exercise performance compared to AW even though no physical exercise was performed, and PW was effective in body temperature, lactic acid oxidation rate, and flexibility. PW suggests the possibility of replacing AW.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of an 8-week gluteus medius strengthening exercise on back pain, balance, and strength in female office workers with low back pain. METHODS The participants of this study were female office workers aged 30 to 48 years old who reported low back pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS) ranging from 3 to 7. Twenty-six participants were randomly assigned to the exercise (n=13) and control (n=13) groups. The study applied a gluteus medius strengthening program to the exercise group for 8 weeks, three times a week, and 60 minutes per session. The participants in the control group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns during the period of intervention. Data collected from the test were analyzed through repeated two-way ANOVA, paired t-test, and independent t-test. RESULTS First, there has been a significant decrease in the pain level, as evidenced by VAS and Korean oswestry disability index (KODI) scores. Second, there was a statistically significant improvement in both static and dynamic balance capabilities. Last, back strength also significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Application of the gluteus medius strengthening exercise appears to be effective for low back pain, static and dynamic balance capabilities, and back strength.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.