PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of regular moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise on body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile in normal-weight obese women. METHODS The participants in the study were normal-weight obese women in their 20’s, divided into moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE) groups. Aerobic exercise was performed three times a week for 8 weeks. To verify the exercise effect, pre- and post- body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile were analyzed. RESULTS Weight and body fat decreased in both groups, and lean body mass and resting metabolic rate increased in the VIAE group. Blood TC, TG, and LDL-C decreased in both groups and HDL-C increased in the VIAE group. CONCLUSIONS In normal-weight obese women, vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise is more effective than moderate intensity aerobic exercise for improving body composition, resting metabolic rate and blood lipid profile.
This study was designed to examine the effects of 12 weeks of resistance exercise training on physique, body composition, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Sixteen females were randomized into one of following two groups: resistance training group (RT group; n=8) and control group (CON group; n=8). Subjects in RT group completed 12 weeks of resistance exercise training for three times/wk, and subjects in CON group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and WHtR decreased significantly in RT group. 2) All variables regarding body composition did not change in both groups; however, fat mass was tended to decrease more in RT group than CON group. 3) Fasting plasma glucose decreased significantly in both groups, whereas other variables regarding insulin resistance did not change significantly in both groups. 4) All variables regarding blood lipids did not change significantly in both groups. Results indicate that 12 weeks of resistance exercise training was beneficial in physique and body composition; however, it was not beneficial in insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Future research including normal weight obese subjects with higher age would be warranted to elucidate more clearly the effects of resistance exercise training on metabolic status.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to review the governance of the 2018 Pyeong Chang Winter Olympic Organizing Committee (POCOG), and to suggest potential governance models for the next mega sport event organizing committee. Methods For this study, In-depth Interview was conducted on 5 subjects who were involved in the process of organizing Pyeong Chang Olympic Games internally and also externally. Throughout the interviews, the subjects were asked to answer questions about the leadership of POCOG management, working relationships among the staff members, and improvement plans for the next mega event. Results The results of the study are as follows: First, POCOG sat up a governmental system and then tried to blend government officials and people from private sector to run the committee; Second, POCOG leadership was not an effective to run an Olympic Organizing Committee; Third, there were not effective working relationships among the staff members in the committee; Lastly, the subjects proposed the future organizing committee to hire more experts, to establish some kind of system that can prevent the turnover, and to go for privatization with the limited involvement from the government. Conclusions Therefore, this study suggests that the future mega sport event organizing committee should implement effective governance in bring more experts, and keeping them from the beginning to the end of the event. Also the organizing committee should consider implementing corporate governance to run the committee with entrepreneurial mindset, and to create cooperative working environment among the committee members.
Purpose The present study compared physical fitness, metabolic syndrome risk factors, and resting metabolic rate (RMR) according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Methods Fifty-one women in their 20s were recruited and assigned into three groups, i.e., normal group (n=18), normal weight obesity (NWO) group (n=18), and obesity group (n=15) according to BMI and %BF. Physical fitness, metabolic syndrome risk factors, and RMR were measured and compared among three groups. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Physical fitness were not significantly different among three groups. 2) Regarding 1-RM, arm curl and leg extension were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group. Leg press was significantly lower in normal group than obesity group. 3) Regarding metabolic syndrome risk factors, there were significant differences in waist circumference, ordering from low to high such as normal, NWO, and obesity groups. Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group, while HDL-C was significantly higher in normal group than NWO group and obesity group. 4) Regarding RMR, absolute values of RMR such as VO2(㎖·min-1), RMR (Kcal·min-1), RMR (KJ·min-1), and RMR (Kcal·day-1) were significantly lower in normal group and NWO group than obesity group. On the other hand, relative value of RMR such as RMR (KJ·kg-1FW·h-1) was significantly higher in normal group than NWO group and obesity group. Conclusions It was concluded that obese women showed increased risk of metabolic syndrome and low relative RMR level, and NWO had similar problems. Active health management through physical activity and dietary control should be committed to NWO individuals because the NWO has possibility of high risk of metabolic syndrome and reduction of metabolic rate from 20s even though there was no problem in their external appearance.
The primary purpose of the study was to compare cardiovascular function, mental health indices, stress-related variables according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Sixty-eight women, aged 20-29 yrs, participated in the study as subjects. There were three groups, i.e., normal group (BMI<24 kg·m-2 and %BF<25%; n=25), normal weight obese group (BMI<24 kg·m-2 and 28%<%BF<40%; n=19), and obese group (BMI>26 kg·m-2 and 28%<%BF<40%; n=24). Cardiovascular function, mental health indices, stress-related blood variables were measured and compared among three groups. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) SBP, DBP, mean arterial pressure, and RPP were significantly higher in obese group than normal group. 2) There were no significant differences in mental health indices among three groups. 3) Fasting plasma insulin, fasting plasma glucose, and CRP were significantly higher in obese group than normal weight obese group and normal group. It was concluded that there would be abnormal cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and inflammation in general obese individuals in 20s females, not normal weight obese and normal individuals.
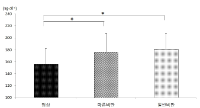
This study was designed to compare physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Sixty women, aged 20-29 yrs, volunteered to participate in the study as subjects. There were three groups, i.e., normal group (BMI < 24 kg·m-2 and %BF < 25%; n = 25), normal weight obese group (BMI < 24 kg·m-2 and 28% < %BF < 40%; n = 22), and obese group (BMI > 26 kg·m-2 and 30% < %BF < 40%; n = 13). Physical fitness, blood lipid profiles, and surrogate indices of insulin resistance were measured and compared among three groups. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) There were significant differences in all variables regarding body composition among three groups. All values were lowest in normal group and highest in obese group. 2) There was significant difference in sit-and-reach among three groups, whereas no significant differences were found in other variables regarding physical fitness among three groups. 3) There were significant differences in all variables regarding blood lipids among three groups. In particular, total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), TC/HDL-C ratio, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were significantly higher in normal weight obese group than normal group. 4) There were significant differences in all variables regarding insulin resistance among three groups. Fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR were lowest in normal group and highest in obese group. It was concluded that there would be abnormal blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance in even normal weight obese individuals as well as general obese individuals in 20s females.

