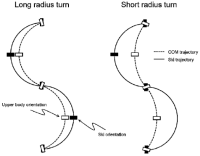
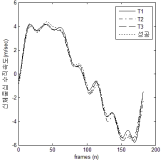
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the three dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip during basic long turn, carving long turn, basic short turn and carving short turn. Methods Fourteen alpine ski instructors from Korea Ski Instructor Association participated in this study. Each skier asked to perform 4-types of turning technique, classified by radius and level. 8 inertial measurement units were used to measure three-dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip joint. Results Significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the mediolateral and vertical axis during long-turn and carving-turn (p<.05). significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the anteroposterior axis in the steering phases 1, 2 and complete phase (p<.05). Conclusions In the Alpine skiing, the short turn requires a complex movement of the lower limb joint compared to the long turn. When performing a long turn, the movement of the ankle joint on the vertical axis are required compared to the short turn. And the carving and short turn need to the movements of the lower limb joint on the mediolateral axis.



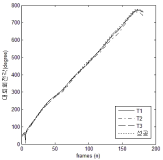
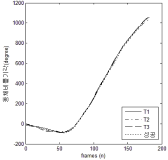
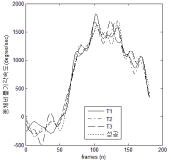
The research was a case study conducted in order to develop a new technique “YANG Hak Seon 2” for YHS athlete. A comparative kinematical three dimensional video analysis was performed with the use of high speed cameras. One successful trial and three of failure trials (T1: Falling backward while landing, T2: sitting reluctantly while landing, T3: Falling of sideways while landing). The result obtained from the study are as follows. Firstly when comparing the successful operation of the technique with failure trials, relatively higher landing angle was secured through increasing the thigh rotation and the body’s rotational velocity. Furthermore, despite increase in rotational velocity at twisting, stable landing was achieved through increasing the moment of inertia by spreading the left shoulder. Secondly, in case of failure trials while taking off the board, the thigh rotational angular velocity was comparatively less which ultimately affected the body position in the next phase of approach to the vault. Thus, due to the affected body position the athlete was not able to utilize the proper momentum of twist in positive direction Hence, it is considered that the velocity of center of mass might have also effected the operation not only the velocity while approaching the board.








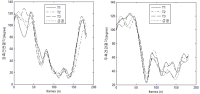



Purpose This study was carried out for the purpose of providing national players of our country by grasping various techniques and difficulty composition of world-level players. Methods For doing so, this research was executed by objecting 9 finalists in parallel bar of 2012 London Olympics and 8 finalists in parallel bar of 2016 Rio Olympics. Collected datum were treated with average, standard deviation, percentage (%) by using SPSS 18.0, and they was analyzed while securing feasibility through expert meeting. Results Research results are same as follows. First, Rio Olympics players appeared higher than London Olympics such like 6,61 points in average D-score of 2012 London Olympics final game and 7.0 points in average D-score of Rio Olympics final game. Second, I group was turned up to prefer Healy technique (34.88%) of D difficulty in two olympics. Third, Ⅱ group carried out Bwd. uprise and salto fwd. p. to sup technique of D difficulty by each 4 players (36.35%) in two olympics, so the technique was displayed as preferred techniques of players. Fourth, Ⅲ group executed at the London Olympics, C difficulty was the most frequently used, but at the Rio Olympics, D difficulty and E difficulty were the most frequent. Fifth, Players in London Olympics and Rio Olympics executed Basket to hdst technique, and it appeared to be most preferred technique by players. Sixth, Ⅴ group executed at the London Olympics, D difficulty was the most frequently used, but at the Rio Olympics, F difficulty was the most frequent. Conclusions These findings will be useful datum to gymnasts and instructors of our country by providing valuable datum in preparing 2020 Tokyo Olympics after grasping preferred techniques and trends of world-excellent players.

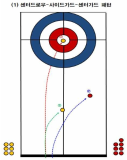
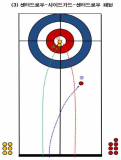
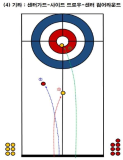
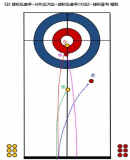
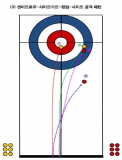
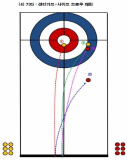
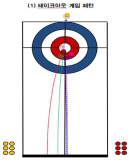
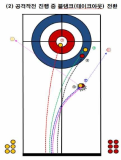
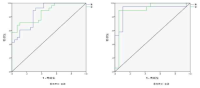
This study has analyzed 33 domestic games and 26 overseas games by targeting women curling teams of home and abroad, and looked into what main performance variables are, how level differences of domestic team appear, and from which variables differences between winning team and defeated team come out in overseas teams. Also, main strategies has been suggested that are used most commonly for kick-off offense and latter offense, blank strategy in order to prepare countermeasures, and digital media DB has been constructed that can utilize proper countermeasures easily and simply, and a model has been proposed for predicting victory/defeat. To accomplish such goal, a variance analysis has been carried out by dividing domestic teams into each level after calculating frequency and ratio with SPSS18.0, and t-test analysis has been carried out by overseas teams. Also, the accuracy of victory/defeat classifications has been suggested by using an artificial neural networks method. As a result, a lot of technical proficiency differences have appeared among Class A(upper rank), Class B(middle rank), and Class C(lower rank) in domestic teams. The ‘Guard’ which is an aggressive variable has turned out to be used more in upper and middle teams than in lower team, and the ‘Tab Back’ has been used more in upper rank than in lower rank. Furthermore, regarding the average comparison on victory/defeat in international games, victory teams have more significant difference(p<.05) than defeated teams in accuracy of shot techniques and strategy accomplishing abilities, and victory teams have been turned out to use less ‘Drew’ and more ‘Take’ than defeated teams significantly in Drew and Take’ technique variable. Finally, the accuracy of a prediction model has been 91.7% for learning and 92.9% for the test result to predict the victory/defeat in international games through the artificial neutral network analysis. The prediction accuracy of domestic games was 81.0% for learning and 71.4% for the test.