Purpose The purpose of the study was to investigate the effect of vibratory stimulus on the static postural control of 8 healty senior adults. Methods To achieve this goal, all subjects participated in two different kinds of static postural control tasks. Task 1 was a static postural control task, where both-legs stand on the ground. Second task was an unstable static postural control task using only single leg stance. As they maintain their balance, 6 different vibratory stimulus were provided on the sole of their feet(personal threshold 0%, 80%, 90%, 100%, 110%, 120%). Results The results of the study were as follows: First, there was no significant differences in postural control ability according to different types of vibrator intensity. Second, there was a significant difference in single-leg postural control ability according to vibrator intensity. Third, there was a significant difference in anterio-posterior stability according to the different types of vibrator intensity. Conclusion Stochastic resonance using vibratory stimulus was more effective in the single leg stance task, rather than the double leg stance task. Moreover, sub-threshold vibratory stimulus(80%, 90%) intensity were more effective than higher vibratory stimulus(100%, 110%, 120%).




This study was designed to investigate the effects of combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise on musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Thirty patients volunteered to participate in the study as subjects, and they were divided into one of three groups, i.e., chiropractic group (n=10), PNF exercise group (n=10), and combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise group (C+P group; n=10). Subjects in three groups went through each program for 25 min/session, three times/wk for eight weeks. Cervical alignment, cervical muscular strength and endurance, and cervical range of motion were measured and compared among groups and between pre- and post-test utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables regarding cervical alignment increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. 2) All variables regarding cervical muscular strength and endurance increased significantly in all three groups. 3) All variables regarding cervical range of motion increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in ROM regarding flexion and extension in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. It was concluded that all three treatments applied in this study would be effective for functional recovery of the musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Especially, combination of chiropractic and PNF pattern exercise would be the most effective intervention for the patients.


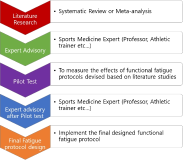
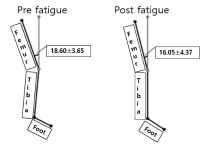
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a functional fatigue protocol on lower extremity dynamic and static postural control. Methods A total of 20 physically active collegiate students participated in this study (ten males, ten females; age 22.5±2.7 years; mass 67.0±13.0 kg; height 168.0±8.9 cm). A unilateral stance with eyes closed for 10 seconds was performed to test static postural control using a balance force plate and single-leg drop landing on 30cm box was performed as a dynamic postural control test and captured using VICON motion analysis system. Results The results of this study showed an average heart rate of 176.3 beats/minute, an 18 rating on the perceived exertion scale, significant differences in blood lactate, and a static postural control deficit after fatigue as compared with before fatigue(p<.05). Dynamic postural control after fatigue changed landing strategy in the form of stiff landing. Knee flexion was decreased at initial contact and at peak vertical ground reaction force, also, both decreased valgus and internal rotation of knee joint. Conclusions This protocol may use for enhancing fatigue-endurance training as well as for inducing fatigue. Further, to ascertain a landing strategy, it is recommended to increase landing height to clearly observe changes in landing strategy.








The purpose of this study was to examine the influence 12 weeks of Hatha yoga exercise has upon changes in postural control ability of high school girls. The research subjects were 27 high school girls (yoga group: 15, control group: 12). Changes that took place after yoga exercise were comparatively analyzed after having them train Hatha yoga for 12 weeks. The research variables that were measured were the moving range of COP in static postural balance, Rambling & Trembling in the moving range of COP, and postural change in the sagittal plane. The mean and the standard deviation(SD) were calculated on each measurement item by using the SPSS Ver 21.0 statistical program. To verify difference in pre-value between groups, an independent t-test was carried out. The verification of change according to time within the group after 12 weeks of yoga exercise was conducted in a paired t-test. To inspect interaction by time and group before and after yoga exercise, two-way repeated measures ANOVA was implemented. As a result, the moving distance of the pre and post direction in the moving range of COP was reduced. Rambling and Trembling in the pre-and-post direction significantly decreased. And in postural change of the sagittal plane, there was significant interaction between two groups in the neck and thigh parts. It was thought that the 12 weeks hatha yoga exercise has positive influence upon improving the postural control mechanism in female high school students and has an effect even on change in the postural control ability of an individual.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to compare the dynamic postural control of youth athletes with and without a history of lateral ankle sprains. METHODS Twenty-eight youth athletes (14 lateral ankle sprain, 14 healthy control) participated in this study. All participants answered the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure questionnaire and were subject to the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) for dynamic postural control evaluation to collect the joint angles of the lower extremity, a center of pressure (COP) path, and COP velocity. Independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test were performed to analyze the difference between the groups. RESULTS The lateral ankle sprain group (LAS) was found to have a long experience in participating in sports, and low Foot and Ankle Ability Measure scores were identified when compared to the healthy control (CON; p<0.05). LAS was observed with a short reach distance, less hip flexion, and dorsiflexion angles during the anterior direction of SEBT when compared to CON (p<0.05). Furthermore, LAS showed a slower anteroposterior and mediolateral center of pressure velocities in the posteromedial aspect of SEBT and a slower anteroposterior COP velocity in the posterolateral aspect of SEBT when compared to that of CON (p<0.05). There were no differences between the groups with respect to the other variables (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, decreased anterior reach distance of SEBT may be affected by changing the dynamic posture control strategy of the lower extremity joint on the sagittal plane in LAS.

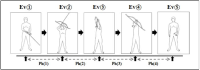
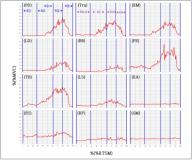
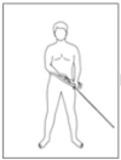
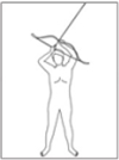
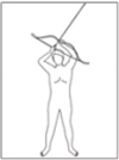
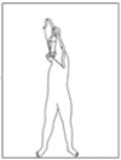
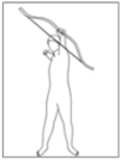
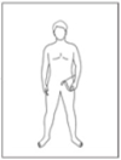
The past few decades has seen increasing kinematic studies using surface electoromyography (EMG) in archery, however there has been no such specific study in Korean traditional archery. The purpose of this study was to evaluate EMGs during archery shooting motion in Korean traditional archers. Ten men Korean traditional archers were participated, and divided into two groups according to the shooting stance; parallel stance group(PSG, n=5) and oblique stance group(OSG, n=5). The surface EMGs were measured 12 muscles during shooting motion of five events including Junbi(Set), Geogung(Set up), Manjak(Full draw), Balsi(Release), Machigi(Ending). At the result, muscle activity of posterior deltoid, trapezius, rhomboid major, latissimus dorsi, biceps brachii, forearm extensor bundle, triceps brachii, levator scapulae significantly increased at event of full draw and release, then significantly decreased again at event of ending, respectively(p<.01, p<.001). The muscle activity of erector spinae(ES) was also significantly increased at event of full draw and release(p<.01, p<.001), while no significant changes in muscles of rectus abdominis, rectus femoris(RF), gluteus maximus. As a result of comparing PSG and OSG, muscle activity of RF in OSG was higher than PSG at event of release(p<.05), it remained until event of ending(p<.05). On the other hand, the higher the tension of the bow, the higher the muscle activity of the draw arm at event of release(p<.05). These results suggest that when Korean traditional archery shooting, both side arm and back muscles are more activated than the abdomen, leg and hip muscles. The parallel stance might suppress the muscle activity of the lower extremities to twist the upper body. And the higher bowstring tension needs to increase of muscle strength in BB of draw arm.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of trunk stabilization exercise (TSE) with abdominal expansion maneuver (AEM) that lasted for 8 weeks on postural stability and functional movement in college athletes. METHODS Twenty college athletes participated in the program (AEM=9, Control=11) and were subjected to 8-week TSE. The AEM group performed exercise by applying AEM techniques during TSE, and control group performed TSE without breathing-related instructions. Both groups measured postural stability with lower-quarter Y-balance test (LQYBT) and functional movement with functional movement screen (FMS) before and after applying TSE to verify the interaction before and after this study with the two groups. Two-way repeated analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the differences between groups and time for an absolute value of LQYBT and FMS, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests for post-hoc analysis. RESULTS As a result of the left and right LQYBT, there was a significant difference between the time x group (p=.041, p=.033), and post-hoc analysis indicated that there was a significant difference between the AEM and control groups (p=.000, p=,000). Furthermore, the FMS total score indicated that there was a significant difference between the time × group (p=.039), and the post-hoc analysis showed the AEM group had significant results (p=.001), while there were no significant results in the control group (p=.255). CONCLUSIONS Application of AEM during TSE seems to be effective with regard to postural stability and functional movement in college athletes.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect of push-up plus exercise(PUPE) on stabilization of the scapula and to use it as basic data for shoulder rehabilitation program. Methods In this study, research papers were collected using Research Information Sharing Service(RISS) and Pub-Med Central.(PMC) as a search term for scapular stabilization, push - up plus, shoulder joint injury rehabilitation and scapular stabilization exercise. Also, it was used as basic data of literature analysis. The collected data were classified into the structure and movement of the scapula and shoulder, kinesiologic relation of the scapula and the mechanism of injury, and the effect of push-up plus Results Serratus anterior is a typical stabilizing muscle, and it forms a force couple with the upper and lower trapezius to control the movement of the scapula. The PUPE is an effective exercise method to selectively strengthen serratus anterior, which are the stabilizing muscles of the scapula, and is an exercise method that is also useful for correcting the wrong postures and movements because of hypertonus upper trapezius. In addition, various conditions such as application posture, arm position, and ground instability were suggested during PUPE. Conclusion The results of this study confirmed that PUPE is an effective program for scapula stabilization in the rehabilitation of shoulder injuries and injured patients and athletes. The PUPE will be used as a rehabilitation exercise program for patients and athletes who need rehabilitation of the shoulder joint.
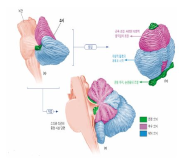
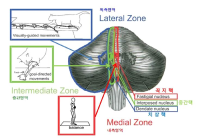
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).




The purpose of this study was to identify the characteristics through technical analysis of dismount to perform the successful landing. The subjects in this study were male gymnastic players of the national team, hish-speed cameras were used to record the salto backward dismount on the parallel bars of the subjects and to study the qualitative and quantitative analysis. The evaluations including feedback of each subjects’problem were as follow: KHH showed early release timing compared to other players. It could be one of factors which can not decelerating the rotational speed, so the correction of posture is needed. NYI didn’t slide to the left at the release phase, and showed big rotation of body compared to other players so the center of mass moved to the rear. The correction of the hand position at flight phase is necessary to perform the V-shaped position. RSD landed in a state where the rotation is insufficient, so the training using elasticity of parallel bars at phase 2, and the correction of hand position are in need. PMS’s rotation angular velocity of body increased consistently, so showed instable land. Therefore the training to ensure the height of flight is required. PEJ showed high vertical position of CM at the release phase which is help for height of flight. He performed ideal V-shaped position, and took a relatively stable landing position. BGR also showed high vertical position of CM and performed ideal V-shaped position, so he landed in a posture in which the most stable. YHS should push vertically rather than horizontally at the moment of release. Especially, the hand position is not on the hamstring but on the back of the knee to perform the ideal V-shaped position. CJY showed little hip angle at the release phase, so he can’t take a position for vertical rise. Also he showed the lowest knee angle and performed rotation and landing in a state that cannot extend the knee. If such problems are corrected, it will be helpful to landing position not only in parallel bars but also in other events.