Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of aerobic exercise intensity on body composition, health related fitness, and quality of life in elderly women. Methods 48 elderly women over 65 years of age without physical and mental problems were assigned to four groups: control group, low intensity, moderate intensity, and high intensity aerobic training group. The aerobic exercise group applied a heart rate reserve (HRR) to low-intensity group (HRR 40-55%), moderate intensity group (HRR 55-70%), high intensity group (HRR> 70%) for 12 weeks, 3 times a week for 20 minutes a day. Subjects of the control group were to maintain their usual lifestyles during the same intervention period. Body composition, health related fitness, and quality of life were measured and analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA. Results The main results obtained in this study are as follows. 1) There was a significant decrease in sitting forward bending in the low intensity group and a significant increase in EQ-VAS. 2) There was a significant decrease in body weight, BMI, and 6 minutes walking in the moderate intensity group, and a significant increase in grip strength and EQ-VAS. 3) The high intensity group showed a significant decrease in weight, BMI, waist circumference, sitting forward bending, and 6 minutes walking, and a significant increase in grip strength, sit and stand, functional reach, and VO2max. On the other hand, there was no significant change in all variables in the control group. Conclusions In conclusion, aerobic training was found to be effective for body composition, health related fitness and quality of life in elderly women. In particular, it can be concluded that high intensity aerobic training is effective for health related fitness, and low and moderate intensity aerobic exercise is effective for improving quality of life.

Purpose This study was designed to investigate the effects of weight-bearing exercise and CareRing treatment on cardiovascular responses, popliteal vein functions, and vascular elasticity of 30-40s women who had worked longer than eight hours a day in a standing position. Methods Thirteen subjects participated in 30 min of standing up treatment (STAND), weight-bearing exercise treatment (EX), and weight-bearing exercise with CareRing treatment (EX+RING). Each subject took part in the three trials repeatedly in a counter-balanced order and proceeded with a wash-out period of at least one week between the respective trials. Results The main results were as follows: 1) Significant reduction in EDV, no change in the diameter of popliteal vein, trend of reduction in blood flow of popliteal vein, and increased baPWV, indicating reduction of vascular elasticity of whole body, were shown in the STAND. 2) CO and EF increased significantly, and TPR decreased significantly in the EX. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of popliteal vein increased significantly, and baPWV decreased significantly from immediately after the treatment throughout the recovery phase in the EX. 3) HR, CO, and EF increased significantly in the EX+RING. Blood flow velocity and blood flow volume increased significantly in the EX+RING. Diameter of popliteal vein increased significantly immediately after the treatment and decreased significantly at 40 minutes of recovery. TPR and baPWV decreased significantly immediately after treatment compared to the STAND. Conclusions It was concluded that weight-bearing exercises would be effective in preventing venous or cardiovascular diseases occurred due to long-standing in 30-40s women, who are at high risk for such diseases. Furthermore, it would be more effective to combine pressure treatment with CareRing during weight-bearing exercises.

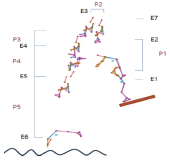
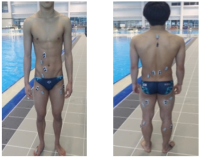
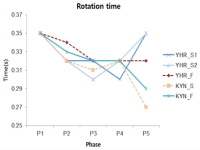
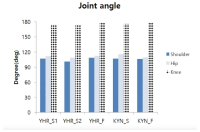
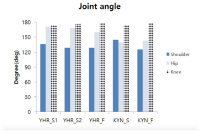
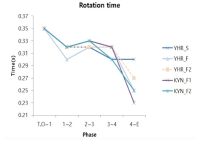
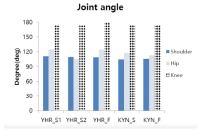
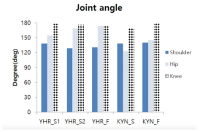
Purpose The purpose of this study is to overcome the shortcomings of 109C(Forward 4 ½ somersault) skill(Level 3.7) for two members of the men’s national diving team(YHR, KYN). Methods For qualitative analysis of the performed skill, three high-speed cameras and water-attached EMGs consisting of a total of ten placements were used. We instructed the two players to perform single-leg jump and double-leg jumps a total of three times each. Results The results of this study indicate that YHR and KYN appeared to increase their time or maintain the same time compared to the previous phase and displacement appeared higher when skill success occurred after the double-leg jump. The Shoulder & hip joints of YHR, KYN appeared larger in E2 and the hip joint of KYN appeared to increase in E1. Single-leg jump appeared similar or decreased the performed time of the previous phase in the last P5. YHR appeared larger only at a hip joint angle and KYN appeared smaller at the hip joint. The muscle activity(iEMG) of the two players appeared greater during skill failure than most of the muscles. Conclusions When perfectly performing 109C skills, the acquisition of medals in international competitions is possible. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to study all of the variables that pertain to 109C.




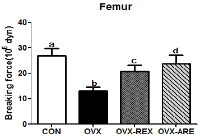
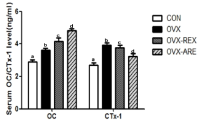
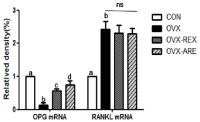
Purpose Osteoporosis is a systemic metabolic bone disease characterized by gradual decrease of bone mass and damage of the bone microstructure. In particular, postmenopausal osteoporosis is the most common type in women after menopause. This study aims to investigate the effects of combined exercise training on bone mineral density (BMD) and OPG/RANKL mRNA levels in ovariectomized rats. Methods A total of 40 Sprague-Dawley female rats were randomly divided into four groups: (1) CON (sham-operation, n=10), (2) OVX (ovariectomy, n=10), (3) OVX-REX (ovariectomy-resistance exercise, n=10), and (4) OVX-ARE (ovariectomy-combined aerobic and resistance exercise, n=10). Combined exercise training was performed on a treadmill and ladder adapted to rats in alternate days (4 days/wk, for 12 wk). Results Compared to the OVX group, all exercise treatments increased BMD and bone breaking force(p<0.05). In the bone turnover markers, serum C-terminal telopeptides of type-1 collagen (CTX-1) was significantly decreased in the exercise groups compared with OVX group and osteocalcin (OC) level was increased in the exercise groups (p<0.05). Additionally, in the exercise groups, expression of OPG mRNA was significantly increased compared with OVX group (p<0.05), and RANKL mRNA was slightly decreased but no significant between groups. Furthermore, OVX-ARE group showed more effects than OVX-REX group. Conclusions These results suggest that combined exercise may be a more effective therapeutic strategy to prevent and delay postmenopausal osteoporosis than resistance-only training.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate differences among perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression in contact and non-contact sports and verify the structural relationship model of perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression in the field of sports. Methods Male college athletes (N=299) participated in the study and perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression questionnaires were utilized after their verification of validity and reliability were conducted. The descriptive statistical analysis, the multivariate analysis, the correlation analysis, the structural equation analysis, and the multi-group analysis were conducted. Results The results are as follows: First, the level of perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression were significantly different between contact and non-contact sports (F=4.316, p<.001). Additionally, subfactors of aggression such as hostility, physical aggression, and verbal aggression factors in contact sports showed a higher average than non-contact sports. Second, perfectionism positively affected anxiety (t=6.936, p<.001) and anxiety positively affected aggression (t=3.380, p<.001). Moreover, the complete mediation effect of anxiety was found in the path from perfectionism to aggression (β=.152, p<.01). Finally, we compared path coefficients between contact and non-contact sports. As a result, positive causal relationships was indicated in the path from anxiety to aggression (β=.511, p<.001) in contact sports. However, it was not discovered in non-contact sports (β=.149, p>.05). Conclusions In conclusion, perfectionism causes anxiety and anxiety is a mediator leading to aggression in sports. Such effect is more predictable and observable in contact sports in which aggression is more favorable and encouraged. Implications and suggestions for future research are discussed.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the performance contents of men's floor exercise and to provide basic materials for achieving excellent results at world competitions. Methods Teams ranked 1 - 12 who participated in the World Championships' floor movement group competition selected a total of 59 players by the convenience sampling method and carried out technical statistics, frequency analysis, member variable variance analysis, and post hoc analysis. Results First, as a result of frequency analysis of the difficulty of each group, all the teams ranked 1 to 12 liked the most difficulty of C and found that they do not like the F difficulty the most. Secondly, there was a difference in average for each group's start score, ranking 1st to 4th> 5th to 8th> 9th to 12th place. Thirdly, there was a difference in average of difficulty levels for each group B, C, E, and it became very significant with E difficulty.Results of post hoc analysis B difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th, 5th to 8th), C difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th), E difficulty (1st to 4th> 5th to 8th ·9th to 12th). Conclusion These results show that in floor exercise, the art of more than C difficulty and the connection technology of A, B, C, difficulty, E and F, difficult difficulty such as difficulty, creative and dynamic performance composition is excellent It clearly states that it is a condition for getting results.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.








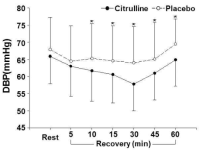
It has well known that post-exercise hypotension (PEH) after a bout of aerobic exercise was a major mechanism to reduce blood pressure though exercise training, and that citrulline supplementation reduced blood pressure by increasing nitric oxide in vivo. However, the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH have not been fully elucidated yet. This study was designed to examine the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH after a bout of aerobic exercise in prehypertensive and normotensive 20s males. The effects of a four-day citrulline or placebo treatment on blood pressure, cardiovascular function, and blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during recovery phase after a bout of exercise performed for 30 min at 70% VO2max were compared and analyzed. All subjects participated in a citrulline trial and a placebo trial repeatedly according to a counter-balanced order. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial pressure measured at 10-60 min of recovery phase in citrulline trial were significantly lower than placebo trial. Rate-pressure product measured at 30 min and 45 min of the recovery phase in citrulline trial was significantly lower than placebo trial. 2) No significant differences were found in heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), and total peripheral resistance (TPR) measured during the recovery phase between two trials. There were significant differences in HR, stroke volume, CO, and TPR among times within a trial. 3) No significant difference was found in blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during the recovery phase between two trials. The results would be summarized that the PEH was augmented by the citrulline supplementation, and that burden to cardiac muscle as well as cardiovascular function were not affected by the citrulline supplementation. It was concluded that the short-term citrulline supplementation would be very effective to augment the PEH. A research investigating the effects of citrulline supplementation on the PEH in pre-hypertensive and/or hypertensive individuals would be warranted. In addition, a study examining the effects of citrulline supplementation during long-term exercise training on the blood pressure in hypertensive patients also would be warranted in near future.

The purpose of this study was to examine whether the difference between ingestion of nutrition supplements for 8 weeks can regulate physical activities and fatigue recovery. Fifty one middle-aged women participated in this study and were divided into placebo, ingestion of 20g energy supplement and ingestion of 40g energy supplement groups. Energy supplement mainly consists of carbohydrates and proteins. All subjects take in this supplement one time per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity and fatigue recovery were measured before and after ingestion of energy supplement for 8 weeks by using the Wingate anaerobic and a blood tests. In the Wingate anaerobic test, the peak power(p<.01) and average power(p<.05) were significantly increased in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group. Although concentrations of lactate and growth hormone in the blood didn’t show a significant differences among groups, blood concentrations of cortisol and ammonia were further enhanced in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group(p<.001). The results of present study provide evidence that energy supplement mixed with carbohydrates and proteins may be effective to increase physical activity as well as to reduce blood concentration of fatigue-related factors after exercise.
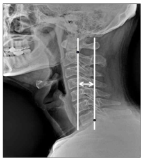
This study was designed to investigate the effects of combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise on musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Thirty patients volunteered to participate in the study as subjects, and they were divided into one of three groups, i.e., chiropractic group (n=10), PNF exercise group (n=10), and combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise group (C+P group; n=10). Subjects in three groups went through each program for 25 min/session, three times/wk for eight weeks. Cervical alignment, cervical muscular strength and endurance, and cervical range of motion were measured and compared among groups and between pre- and post-test utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables regarding cervical alignment increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. 2) All variables regarding cervical muscular strength and endurance increased significantly in all three groups. 3) All variables regarding cervical range of motion increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in ROM regarding flexion and extension in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. It was concluded that all three treatments applied in this study would be effective for functional recovery of the musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Especially, combination of chiropractic and PNF pattern exercise would be the most effective intervention for the patients.

