
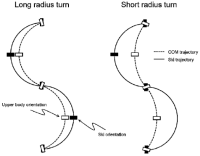
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the three dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip during basic long turn, carving long turn, basic short turn and carving short turn. Methods Fourteen alpine ski instructors from Korea Ski Instructor Association participated in this study. Each skier asked to perform 4-types of turning technique, classified by radius and level. 8 inertial measurement units were used to measure three-dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip joint. Results Significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the mediolateral and vertical axis during long-turn and carving-turn (p<.05). significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the anteroposterior axis in the steering phases 1, 2 and complete phase (p<.05). Conclusions In the Alpine skiing, the short turn requires a complex movement of the lower limb joint compared to the long turn. When performing a long turn, the movement of the ankle joint on the vertical axis are required compared to the short turn. And the carving and short turn need to the movements of the lower limb joint on the mediolateral axis.


PURPOSE This study aimed to explore ways to utilize augmented reality (AR) in school sports and leisure by examining the case of an elementary school sports club using augmented reality-based e-sports. METHODS A self-study approach and Eisner's(1995) educational criticism were utilized. Data including photos, videos, literature, and memory boxes related to the elementary school AR sports club were collected weekly during the school semesters from March 2023 to January 2024, spanning a total of 30 weeks. The data were analyzed following the stages of analysis by Elo & Kyngäs(2007). RESULTS Augmented reality can act as a personalized exercise coach by visualizing physical activity information. Through posture and movement analysis, education on physical strength and expression can be provided that is linked to home; it can also expand the range of sports experiences and create a new sports culture. In order to effectively utilize AR, edtech field experts must be trained, and content must be developed through cooperation between companies and schools. The educational effectiveness of the content must be verified and the management system must be inspected, and public facilities utilizing edtech must be expanded. CONCLUSIONS AR has endless development potential in school sports and leisure, but these will require active interest and support from educational authorities.
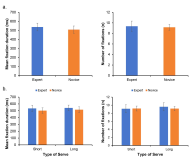
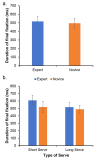
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the differences in visual search strategies between expert and novice badminton players while performing badminton serve. [Method] To this end, expert (more than 10 years experience) and novice (less than 6 months experience) badminton players performed 15 trials of two types of serve (i.e., short-serve and long-serve), in total 30 trials. All the participants’ eye movement was recorded during each trial, and mean fixation duration, fixation distribution, final fixation duration and location, and gaze entropy were analyzed. [Results] The results showed that there was no difference in mean fixation duration between expert and novice players. The analysis of mean fixation duration on each location showed that participants fixated more on the net while doing short serve whereas fixated more on the space when they did long serve. In particular, expert players fixated more on the space while doing long serve than novice players, and fixated more on the net and racquet for the short serve. However, novice players fixated more on the location of shuttle would be landed. The final fixation duration was not different between expert and novice players. Further, expert players showed higher gaze entropy than novice players. [Conclusion] The findings indicate that expert players fixated more on the net for the short serve, and the space for the long serve, and visual search strategies of experts were more varied than novice players.


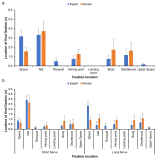

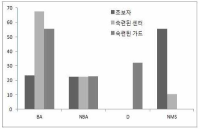
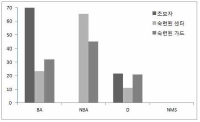
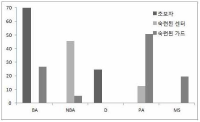
The purpose of this research was to investigate the difference in decision making and perceived eye-focus location on peripheral vision and attacker's expertise in basketball tactical game. A total of twenty four subjects who were expert guard players (n=8), expert basketball center players (n=8), and novices (n=8), participated in this experiment. All subjects participated two tasks. The first task was to anticipate the attack direction after viewing a sequence of basketball tactic film. These films simulated three situations including offensive patterns. The three situations were consist of 3, 6, 9 degree peripheral vision. The second task was to express the level of confidence on their anticipation and to verbalize the perceived visual cues immediately after responding. For this research, an Eyelink eye movement system, an equipment for measuring anticipating, basketball tactic film were used. The variables on anticipation of attack direction were speed, accuracy, and the level of confidence. The acquiring process of advanced visual cues was examined through analyzing visual search strategies and perceived eye-focus location. In order to examine the difference in visual search, in decision making, and in perceived eye-focus locations as a function of expertise, data were analyzed through descriptive statistics, two-way ANOVA, and two-way MANOVA. This research had the following results. First, there was a significant difference on the search rate among the three groups. But, on the other hand, expert guard and center exhibited more fixations of shorter duration than the novices in the 6 and 9 degree condition. Second, results from the ratio of fixation time allotted to areas in the 3 degree condition revealed that experts spent more time fixating the ball-attacker(BA) than novices. The results from the ratio of fixation time allotted to areas in the 6 and 9 degree condition revealed that expert guard and center spent more time fixating the non-ball attacker(NBA) than novices. Expert guard also fixated longer on the pass attacker(PA) and meaning space(MS) than novices. Finally, experts paid attention to two or three locations simultaneously, whereas novices did to only one location such as the ball, attacker, defender, non-meaning space in all condition.





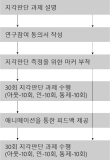
PURPOSE The quiet eye (QE) is defined as the final fixation time that is a specific target prior to initiating movement. This study aimed to identify the cause of QE in golf putting and to present an efficient practice method for improving putting skills. METHODS Thirty participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups. Each group practiced golf putting in different ways for two days. RESULTS The QE group showed a significant difference in putting scores, which was higher than that of the control group. The visual-occlusion group showed no difference compared to the other groups in terms of putting scores. The QE group showed a significant difference in terms of QE in the retention and competition tests compared to the pretest. The control group tended to have a slightly longer QE in competition tests compared to the pretest. The visualocclusion group showed no statistically significant difference in QE based on the period. All three groups had significantly longer swing times over the selected period. There was no significant difference in terms of the alpha power of the occipital lobe based on group and period. CONCLUSIONS The position of the visual-occlusion group became stable. However, the QE did not lengthen. The QE group had a longer QE. Furthermore, the control group that practiced with their eyes open tended to have longer QE. Therefore, QE may be related to visual-based cognitive processing rather than posturalkinematics. Finally, this study proved that QE practice is a more efficient method for novices in golf putting.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect of push-up plus exercise(PUPE) on stabilization of the scapula and to use it as basic data for shoulder rehabilitation program. Methods In this study, research papers were collected using Research Information Sharing Service(RISS) and Pub-Med Central.(PMC) as a search term for scapular stabilization, push - up plus, shoulder joint injury rehabilitation and scapular stabilization exercise. Also, it was used as basic data of literature analysis. The collected data were classified into the structure and movement of the scapula and shoulder, kinesiologic relation of the scapula and the mechanism of injury, and the effect of push-up plus Results Serratus anterior is a typical stabilizing muscle, and it forms a force couple with the upper and lower trapezius to control the movement of the scapula. The PUPE is an effective exercise method to selectively strengthen serratus anterior, which are the stabilizing muscles of the scapula, and is an exercise method that is also useful for correcting the wrong postures and movements because of hypertonus upper trapezius. In addition, various conditions such as application posture, arm position, and ground instability were suggested during PUPE. Conclusion The results of this study confirmed that PUPE is an effective program for scapula stabilization in the rehabilitation of shoulder injuries and injured patients and athletes. The PUPE will be used as a rehabilitation exercise program for patients and athletes who need rehabilitation of the shoulder joint.

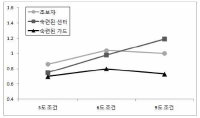
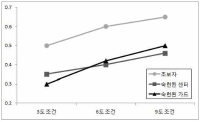
[Purpose] Perception plays an important role in understanding the environment or related objects in order for humans to perform physical movements more effectively. Sometimes they create different movements with different perceptions. Especially, visual perception errors that occur in sports situations can have a considerable effect on performance. Accurate knowledge of the environment in this process of perception is important in performing movements or actions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of learning formation on perception using Muller-Liar illusion diagrams. To measure this, we compared the feedback group that induced knowledge learning and the control group that did not provide knowledge To see if there is a difference. Therefore, in this study, we have provided a visual feedback that can establish the cognitive awareness of the actual stimuli length to subjects, and investigated the changes in their matching action responses. [Methods] A total of 32 young and healthy subjects were randomly divided into two groups (Feedback and Non-Feedback groups). Subjects were asked to match the stimulus size with their index fingers and thumbs. Initially (pre-test), three different visual stimuli (inward, outward, and no arrows) were randomly presented 60 times (20 times each) and the grip sizes were recorded using the Liberty Motion Analysis System (Polhemus Co., America). Then, video clips of two lines merging each other were presented as feedbacks. Post-test protocol was identical to the pre-test protocol. The data were analyzed using the 3-way ANOVA with one RM factor (2 x 3 x 2). [Results] Results showed a significant 2-way interaction effect. Post-hoc results showed significant interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests only in the experimental group. There was a significant decrease in the grip size after feedback in the OUT condition of experimental group. However, in the control group, there was no interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests. [Conclusion] Overall, current results indicates that, while visual illusion can affect the action, the provision of visual feedback can establish the awareness of actual stimulus size and suppress the influence of illusion on action.

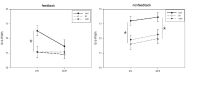
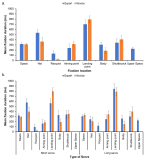
PURPOSE The main purpose of this study was to examine the difference in visual search strategies based on the skill level in success and failure cases in badminton short serves. METHODS To this end, six badminton experts (experience: more than 10 years) and six novices (less than 1 years) participated. The participants’ eye movement was recorded during each trial, and mean fixation duration, mean saccade amplitude, percentage of viewing time on each fixation location, final fixation duration, and gaze entropy were analyzed. RESULTS First, the mean fixation duration did not differ significantly, but the mean saccade amplitude increased when expert players failed to perform the serve successfully. Second, the percentage of viewing time on each location results showed that the overall viewing time was lower when the performance was unsuccessful, and the expert players fixated longer time viewing the net and space when they made a successful serve. Third, expert players showed longer QE than novice players when they made a successful serve. Finally, the gaze entropy results showed that expert players showed greater gaze entropy during successful performance, indicating that the gaze pattern was randomly distributed across trials. CONCLUSIONS When learning a badminton serve, we should fully recognize and explore the receiver’s location and external environment, and subsequently, before initiating serve movement, focus on the net or space between the receiver’s racquet and shoulders to make a more successful performance. In addition, we should make various patterns of the visual search strategy, rather than the fixed or consistent search strategy, to deceive receivers.