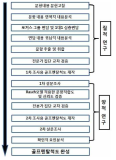
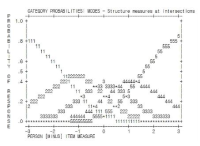
The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

Purpose The purpose of this research is to provide implications for the study of the physical education curriculum in Korea and China by comparatively analyzing the revised high school physical education curriculum in the two countries. Methods Using Bereday(1964)’s four steps of comparison model in education, this study focuses on the format and content of the general high school physical education curricula of Korea and China, each curriculum having been revised respectively in 2015 and 2017. Results First, in terms of format, both countries consider PE a necessity and share similarities in regard to course structure, credit allocation and document format. Nevertheless, though both countries are oriented toward competency-centered education, there are some differences with respect to official education curriculum documents, numbers of subjects and hours of study based on the reality and situation of each country. Second, in terms of content, both countries present various teaching methods and evaluation principles for the sake of acquiring core competence. However, the Korean curriculum prefers to advocate learning of the value of physical activity to achieve core competencies, while the Chinese curriculum prefers to focus on acquiring athletic skills and health knowledge for achieving core competencies. Conclusions After comparing physical education curriculum in both countries, two implications could be obtained. One is that the consistency problem in Korea should be solved between the core competency, the teaching and learning methods and evaluation standards. The other is that, in China, integrated value of physical education should be paid more attention and core competency as well as teaching and learning methods should be considered.

Purpose This research analyzed the Korean and Japanese cycle racing businesses by comparing each country’s total profits and total audience from 1996 to 2016. Methods In this process, it used total profits data and total audience data from 1966 to 2016. The data showed an economic correlation between Korean and Japanese cycle racing businesses by using each county’s economic variables. Results According to regression analysis, the income and audiences of Korean cycle racing industry has been increased as their income level has been increased. However, Japanese cycle racing generally has negative effects between income level and other variables except audiences. Moreover, aging population affects negatively to Korean cycle racing industry. In contrast, aging population is less affects to Japanese cycle racing industry. Furthermore, improvement of employment and unemployment rate affects negatively to Korean cycle racing industry. As a result, Korean cycle racing industry looks like a gambling. On the other hands, Japanese cycle racing industry becoming one of leisure sports industry. Conclusions Korean cycle racing industry has to examine closely Japanese’s restructuring method & result. Also, they have to analyze closely Japanese’s sociocultural variables which explain decreasing profits and increasing audiences. In other words, Korea cycle racing industry needs to various methods to becoming leisure sports industry.