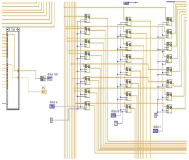
This study was to develop and to apply real-time neurofeedback system for psychological self-regulation of shooters. Neurofeedback system was developed with expert meetings consisting of 8 sport psychology, EEG, and sport engineering experts based on Labview program. Developed neurofeedback system was applied to 4 college shooters for 10 sessions(1 session/week, 30 mins/session). Collected EEG wave data were analyzed by paired sample t-test and independent sample t-test. The results were as follows: Firstly, based on user experience concept neurofeedback system was developed which easily perceived neurofeedback information as traffic lights with minimizing visual search activities. Secondly, after neurofeedback system application right brain activation level of shooters(except one shooter) were increased compared to left brain activation. Based on the results of this study, neurofeedback system can apply various sports and contribute to help athletes’ self-regulation and athletic performance enhancement in sport field.

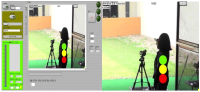

PURPOSE This study was conducted to investigate changes in stress before and after elite shooting athletes participate in a match, and to find out the effect on the match score. METHODS Thirty-wight elite shooting athletes were sampled, questionnaires were distributed to measure psychological stress before and after the match, and saliva was collected before and after the match to measure cortisol. In addition, psychological stress and changes in cortisol before and after the game were investigated, and how psychological stress before and after the game and cortisol affect the score of the game were investigated. Accordingly, a statistical analysis based on data analysis was conducted, and the following research results were obtained. RESULTS The pre-match analysis of psychological stress and cortisol revealed statistically significant changes; both post-match stress and cortisol decreased compared to before the match. Increased psychological stress and cortisol both before and after the match had a negative effect on the match score. CONCLUSIONS These findings confirmed that shooters experience very strong psycho-physiological stress before the match, and the stronger the psychological stress, the lower the game score.
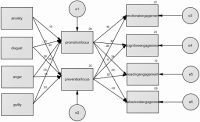
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out the relationship between emotion and control focus and training involvement in games where elite shooters are late. Methods Thus, 228 elite shooters were selected and the research results were derived based on data analysis using discriminatory emotions, control focus, and training attendance scales. Results According to the analysis of the correlation between emotion, control focus, and training involvement, positive emotions of surprise, enjoyment, and interest showed a static relationship with improvement focus and training involvement, while negative emotions such as anger and guilt had a static relationship with prevention focus, but showed an inadequate relationship with training involvement. The multiple regression analysis between emotion and control focus showed that the improvement focus showed the most significant effect of enjoyment emotion, while the prevention focus showed that instability had the most effect on the prevention focus. Overall, the focus of improvement has been shown to be affected by training. Finally, it was found that positive sentiment had a positive effect on improvement focus and training involvement, while negative sentiment affected prevention focus and reduced cognitive involvement. Conclusions Positive sentiment toward the competition has been confirmed to enhance training participation by strengthening the focus of improvement, but negative sentiment has been shown to enhance the focus of prevention, reducing cognitive involvement.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide useful information on the improvement of performance by measured the psychological-physiological stresses experienced by elite shooters during a competition. Methods Thirty-eight elite shooters participated in this study (Male = 13, Female = 25). Psychological stress was measured and used for this study based on the stress factors found in the elite target stress study by Park(2015). The cortisol, a physiological stress hormone, was measured using saliva. Results The reliability of the psychological stress sub-factor pre-post analysis results showed no statistically significant. The concentration of cortisol measured on the day before the competition (0.1704 µg/dL) significantly increased immediately before the competition (0.3558 µg/dL). Cortisol immediately before the competition showed negative correlation (r=-.361, p=.036) with the competition score, and the regression variable of cortisol was 13%. Conclusions In this study, physiological stress had a negative effect on elite shooters performance compared to psychological stress.


The aim of this study is to analyze the correlation between per capita GDP and sports items' demand and to estimate the income elasticities of sports items' demand based on the International Social Survey Programme: Leisure Time and Sports - ISSP 2007 of the GESIS(Leibniz-Institute for the Social Sciences, Germany). The facts found from the analyses are as follows; First, in general, when the correlation coefficient of a particular sports item turns out to be both positive and statistically significant, the item can be interpreted to have a good possibility to be a luxury goods and when the coefficient is ascertained to be both negative and statistically significant, the item can be inferred to have a considerable chance to be an inferior goods. In this study, other team sports(excluding basketball, soccer, volleyball, baseball etc.), squash, walking/trekking/climbing, boat sports, hunting/fishing, horse riding/horse racing, motor sports, shooting, and snow sports were confirmed to show a luxury goods' features and basketball, soccer, volleyball, athletics, and martial arts were identified to have an inferior goods' characteristics. Second, similar to the results of the correlation analysis, in the income elasticities estimation, cockfighting appeared to be an inferior goods and other team sports, squash, walking/trekking/climbing, bowling/curling/bocce, boat sports, darts, hunting/fishing, golf/minigolf, horse riding/horse racing were proved to be a luxury goods.