
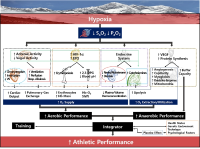
Purpose The purpose of this study is to emphasize the need for the establish and the use of altitude training center via examining exercise training method in natural or artificial altitude environment that is applied to various elite athletes in various advanced countries to maximize exercise performance and its effectiveness. Results Altitude training in natural or artificial altitude environment enhances aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance baesd on the hematological and nonhematological adaptations to hypoxic conditions. These altitude training methods can be classified into living high training high (LHTH), living high training low (LHTL), and living low training high (LLTH). LHTH (i.e., developed since the 1968 Mexico Olympics) and LHTL (i.e., developed in the 1990s by Levine and Stray-Gundersen) improve exercise performance via hematologic changes through erythropoiesis such as increased hemoglobin mass and erythrocyte volume. On the other hand, LLTH (i.e., has been developed variously since the 2000s) is composed continuous hypoxic training (CHT), intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) and repeated sprint training in hypoxia (RSH), and the altitude environment is constructed using a vacuum pump and a nitrogen generator. In general, LLTH method dose not induce hematological change in a short time within 3 hours. However, CHT and IHT enhance aerobic exercise capacity by improved exercise economy, supply and utilization of blood to tissues, capillary and mitochondrial densities, and oxidative enzyme activity through various biochemical and structural changes in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. RSH enhances anaerobic power and repetitive sprint performance by improving glycolytic enzyme, glucose transport, and pH control. In Korea, however, there are almost no facilities for altitude training that is applied to enhance athletic performance in advanced sports countries and recognition of the need for altitude training is also very poor. Conclusions Therefore, it is very urgent to develop altitude training for maximizing athletic performance in Korea and a lot of support and efforts are needed from the government and local governments.



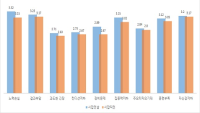
Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide useful information on the improvement of performance by measured the psychological-physiological stresses experienced by elite shooters during a competition. Methods Thirty-eight elite shooters participated in this study (Male = 13, Female = 25). Psychological stress was measured and used for this study based on the stress factors found in the elite target stress study by Park(2015). The cortisol, a physiological stress hormone, was measured using saliva. Results The reliability of the psychological stress sub-factor pre-post analysis results showed no statistically significant. The concentration of cortisol measured on the day before the competition (0.1704 µg/dL) significantly increased immediately before the competition (0.3558 µg/dL). Cortisol immediately before the competition showed negative correlation (r=-.361, p=.036) with the competition score, and the regression variable of cortisol was 13%. Conclusions In this study, physiological stress had a negative effect on elite shooters performance compared to psychological stress.


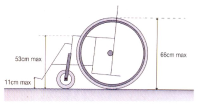
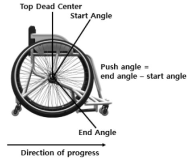
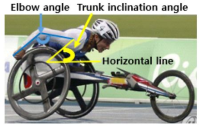
[Purpose] A potential issue for wheelchair sports are the characteristics of wheelchair design. The purpose of this review was to investigate the characteristics of design in wheelchair sports including the height of seat, camber and handrim size for improving the performance. [Results] The optimum height of seat related to trunk, arm length and handrim size. The lower seat showed the push efficient highly, while higher seat increased the energy expenditure. In energy expenditure, the optimum height of seat was 100-120° of elbow angle. Handrim size play the role in gear. The smaller handrim size acts like high gear, it gains disadvantages in acceleration, it gains advantages in maximum velocity. On the contrary, the higher handrim size acts like low gear, it gains disadvantages in maximum speed, it gains advantages in acceleration. The ratio of gear consideration in power and velocity. When increased camber enhanced the lateral stability, easier catch the handrim and easier arm motion. So it improved the energy expenditure and push technique. When increased camber enhanced the mechanical efficiency and stability, but it decreased the power. The racing wheelchair camber using the 8° and 10°. [Conclusion] Athletes, coaches and wheelchair experts are provided with insight in the performance effect of key wheelchair design settings, and they are offered a proven sensitive method to apply in sports practice, in their search for the best wheelchair-athlete combination.



The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of happiness improvement program on psychological variables which were happiness feeling, self-esteem, interpersonal relationship, internal-external locus of control, stress, coping, perceived performance and physiological variables such as cortisol and serotonin of collegiate badminton players. The participants consisted of 10 collegiate badminton players. Happiness improvement program for collegiate badminton players was developed by previous literatures, in-depth-interview, psychological test data, and consultation of happiness improvement experts. The happiness improvement program consisted of 12 intervention program: orientation, rapport development and the understanding happiness, self-esteem enhancement techniques, interpersonal relationship strategies, stress and coping management, peak performance methods, and action plan of happiness improvement program. Each program was applied to participants in about 90-120 minute a session(2-3 times session a week). The instruments of this study were made up of three broad categories: (a) psychological data, b) physiological data, and (c) qualitative data. Firstly, happiness improvement program significantly increased happiness feeling, self-esteem, internal-external locus of control, interpersonal relationship capability, coping skills of collegiate badminton players. Secondly, happiness improvement program significantly decreased stress of collegiate badminton players. Thirdly, participants positively perceived the effects of happiness improvement program on psycho-physiological variables. The limitations of this study and future implications were discussed.
[Purpose] The present study attempted to verify the effectiveness of an early childhood physical health improvement program (subsequently in the present study, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program) developed in Korea by modifying and improving the Mission-X: Train Like an Astronaut program developed by NASA to be suitable for children of ages 4 and 5. [Methods] The subjects in the study were 679 children at 7 facilities in Seongnam city, Osan city, and Yongin city, of which 4 were daycares and 3 were kindergartens. The participant group consisted of 339 children, and the control group consisted of 340 children. The program consisted of total 24 activities 3 times a week over 8 weeks, of which 8 activities were related to nutrition and 16 activities were related to physical activity, and in the 9th and 10th weeks, the 16 physical activities were reconfigured and performed 3 times a week. Physical parameters and related fitness parameters were measured before and after the program, and an ANCOVA analysis was performed in which descriptive statistics and scores before the program were the covariate variables. [Results] The results show that first, growth statuses of participant children were in the upper middle section of the distribution, and second, of the 6 fitness developments, flexibility, balance, and quickness were improved, and in most areas, boys and below-normal-BMI group showed beneficial effects. [Conclusion] Thus, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program is conclusively proven to be effective for early-childhood physical development.
Purpose The purpose of the study was to perform a comparative analysis of the YANG Hak Seon technique carried out by "K" athlete with the kinematical data of "Y" athlete and propose a method to improve the YANG Hak Seon technique of "K" athlete. Method The subject recruited for the study was a male athlete from Korean national team (Age: 21, height: 1.65 m, body weight: 59.6 kg, and career: 11 years). Four high - speed cameras were used to analyze the 3D motion of the YANG Hak Seon technique performed by "K" athlete. The variables selected for analysis were the velocity of COM, displacement of COM, the rotational & torsional angle of the trunk and rotational & torsional angular velocity of the trunk. The results obtained were compared to the preexisting data of the "Y" athlete (data set from the published research). Results Firstly, the horizontal displacement of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the "K" athlete was observed to be shorter along with lower vertical displacement during landing compared to “Y” athlete. In addition, the overall horizontal velocity was low and vertical velocity was not generated which rises during the BC (board contact) phase. Although the rotational angular velocity of the trunk was lower during the BC, HC (horse contact) phase and LD (landing) phase, torsional angular velocity was higher during the LD. Conclusion In order to improve the completeness of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the K player, it is necessary to enter with a fast and low posture on the footplate during the initial phase. In the BC phase, it is essential to raise the COM simultaneously while landing on the footplate and increase the rotational angular velocity of the trunk.

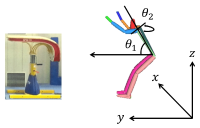

PURPOSE This study compares the effects of video group and metaverse group counseling for student athletes to analyze differences in immersion, sychological skills learning effects, and each approach’s participation experiences. METHODS Twenty-four high school archery students were divided into three groups: a metaverse experimental, a video comparison, and a control group. For the experimental and comparative groups, 10 non-face-to-face psychological skills training sessions were conducted. With the control group, results were compared and analyzed by measuring psychological skills and social presence pre- and post-training. Additionally, analysis of the qualitative effects of psychological skills training was performed. RESULTS The psychological skill test’s quantitative analysis of the video comparison group showed a more significant effect in anxiety control factors than the metaverse experimental and the control groups. Moreover, in the social presence test, both the metaverse and the video groups showed significant differences in social presence and satisfaction; furthermore, Scheff post-verification results showed that the two environments’ satisfaction was significantly higher than that of the control group. Qualitative analysis confirmed that the metaverse and video groups experienced psychological, technical, and relational changes in common. CONCLUSIONS Although the metaverse group using avatars was likely to increase immersion, both the video and the metaverse groups were effective in psychological skills training, suggesting that the training effect may vary depending on the non- face-to-face environment’s stability and participation method. Future studies should examine effects of applying the metaverse platform to sports psychological skills training and various psychological support activities by solving the metaverse environment’s technical limitations.
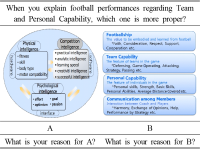
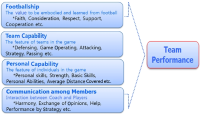
Purpose The following study was conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance, which has previously been considered as the total sum of individual performances. Method The concept of team performance was extracted by a conductive content analysis and an exploratory factor analysis of the data gathered from middle school football players. To verify the validity of the extracted concept, football experts' opinions were collected. Results The idea of team performance, categorized by Footballship, Team Capability, Personal Capability, Communication among Members, has been taken differently from the total sum of individual performances. Footballship is the virtue that should be materialized, and simultaneously earned during the game. Team Capability is a available resource for team's performance, Personal Capability is a available resource for a player's performance, and Communication among Members is the intimacy of communication between coaches and players. The conglomeration of experts' opinions on the concept of team performance and its components shows that team performance is evidently different from the total sum of individual performances. Conclusion The following study has been conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance. Team performance exists, standing distinct from the sum of individual performance, and understanding the concept of team performance will contribute not only to understanding performance, but also to improve the effectiveness of training and managing the team. Interest of the sport society is looked forward to.

Impact of 9-week strength training of racing cyclist candidate during training camp on body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was examined. Two by two (cyclist experience, y/n and strength training (ST) participation, y/n) experiment design was employed. A total of 20 candidates participated and divided evenly into four groups; 1) experienced cyclist participating ST (CST), 2) non-experience cyclist participating ST (nCST), 3) experienced cyclist no participating ST (CnST), and 4) non-experience cyclist no participating ST (nCnST). Two programs were introduced; 1) non ST containing, pre-existing program emphasizing on sprint and acceleration training and 2) new-program containing ST and sprint and acceleration training. CST and nCST participated the latter program. Before and after the 9-week training, body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was tested. After 9 weeks, all groups decreased body weight(p<0.05), body fat content(p<0.05), body mass index, and CST and nCST increased lean body mass(p<0.05). Muscular strength measures such as grip strength, low back strength, 1RM of bench press, 1RM of squat, and anaerobic capacity improved after 9 weeks in all groups(p<0.05). The magnitude of changes was greater in order of CST, nCST, CnST, nCnST. Time trial of 200 meter sprint was faster after 9 weeks in all groups except CnST while 500 meter sprint was improved only in nCnST(p<0.05). After 9 weeks, regardless of previous cyclist experience, those who participated in ST ranked high places at racing cycle competition. Both training programs for the candidates improved body composition and racing cyclist specific fitness. When strength training was added to pre-existing training program emphasized on sprint and acceleration, the racing cycle performance was enhanced. Strength training for racing cyclist is highly recommended to improve their racing performance.
PURPOSE This study seeks to contribute to the enhancement of the performance of domestic wheelchair racers by producing 3D-printed customized gloves and verifying their application effect. METHODS A total of three male wheelchair racers who belong to the T54 and have won gold medals in the National Para Games within the last three years were selected as subjects. Each subject performed three session s of muscle activity and maximum speed measurements before and after applying a 3D-printed glove during the stroke and recovery phases of wheelchair racing, focusing on the pectoralis major (PM), triceps brachii (TB), and erector spinae (ES) muscles. To standardize the muscle activity measurement data, the relative muscle activity level (%) for each section was calculated by maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) for each subject. All maximum speeds of each round of driving were calculated by the average record for comparative analysis. In addition, to verify the effectiveness of applying the 3D-printed glove, the Wilcoxon signed rank test, which is a non-parametric test method, was performed on all measured values using SPSS 24.0. RESULTS This study derived the following results. First, a statistically significant difference was observed in the muscle activity of each major muscle before and after using the 3D-printed glove. In common, an increase in muscle activity of the PM, TB, and ES was confirmed in the stroke section, and an increase in muscle activity of the TB was confirmed in the recovery section. Second, a statistically significant difference was documented in the maximum speed before and after using the 3D-printed glove. When using 3D-printed gloves, the maximum speed increased by 4.57, 3.63, and 1.06km/h for Payer A, and by 5.9, 6.04, and 7.86km/ h for Player B. In the case of Player C, the speed increased by 6.73, 2.27, and 0.83km/h, and all three players improved their maximum speed through the 3D-printed gloves. CONCLUSIONS Our study suggests that the application of 3D-printed customized gloves can have a positive impact on the performance of wheelchair racers. If the application of 3D-printed customized equipment is extended to athletes in a wider range of sports in the future, this could significantly contribute to the improvement of performance in domestic disability sport.