PURPOSE Although sport and graffiti often collaborate in various forms and sectors, research on this phenomenon is insufficient. Therefore, this exploratory study analyzed the role of sport in line with the diffusion of graffiti in Korea. METHODS Qualitative research method was applied for data collection and analysis. Specifically, systematic literature review, semi-structured in-depth interviews, and written interviews were used for data collection. Subsequently, content analysis, categorization, and itemization were performed. RESULTS International sporting events had an impact on the diffusion process of graffiti. Additionally, graffiti was used as a promotional content for sporting events and sport brands, and specific sport content were used as the medium for street art works, including graffiti. Furthermore, graffiti was used as a promotional content for marketing activities in collaboration with a professional sports team by general corporations. CONCLUSIONS As graffiti becomes one of the major cultures from a subculture, it is expected to increase public interest in all sports and not just in specific sports through collaboration with graffiti.
[Purpose] It has been known that Korean Olympic Committee (KOC) was recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) on June 20th of 1947, based on the fact that Korea National Olympic Committee (NOC) was recognized by the IOC session held in June of 1947. However, records and archives show that the recognition and the following conditions were somewhat different than what we have known. This study aimed to examine closely and explain how KOC was recognized in 1947, what was the conditions, and what was the role of Avery Brundage related to this agenda. [Methods] This study is a literature review. Brundage Collection, a package of records and letters which Avery Brundage has collected, and the archives of KOC in IOC Olympic Studies Center were examined. [Results] According to the records, Korean NOC was recognized provisionally with a condition of reviewing the situation of an independent nation and responsible for including the North Korean athletes. The unusual recognition appeared to be possible by the role and decision of Avery Brundage who defended the political and military situation of Korean peninsula. [Conclusions] The reviewed documents suggest a need of revision of KOC history as that KOC has been provisionally recognized in 1947 with some conditions. IOC viewed and recognized Korea as a single country and required KOC to include North Korean athletes. The role of Brundage should be revisited.

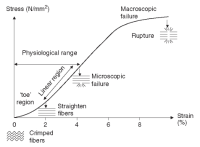
Vertical jumping is one of basic skills in many sports activities. Maximizing vertical jumping performance requires large “power”, which implies that one should generate force against the ground in a short period of time. In order to gain better understandings of how human musculo-skeletal system mechanically functions to achieve maximal power in vertical jumping, the proposed “dynamic catch” mechanism, one of “power amplification” mechanisms through the role of muscle-tendon interaction, was specifically reviewed base on the morphological and mechanical characteristics of lower limb muscle-tendon complex. By understanding basic structural and functional features of human muscle-tendon interaction, this review aims to provide basic scientific information for training and rehabilitation and promote convergence researches in related areas, such as sports biomechanics, mechanical engineering, and sports medicine.


PURPOSE This study aimed to: 1) compare the differences in static lower-extremity alignment (SLEA) between female ballet dancers (BD) and non-ballet dancers (NBD); 2) investigate the differences among gesture leg (GL) and supporting leg (SL) in BD and dominant leg (DL) in NBD; and 3) compare limb asymmetry between groups. METHODS Twenty-nine female BD and 20 NBD were recruited for this study. The quadriceps, tibiofemoral, rearfoot, and genu-recurvatum angles, tibial torsion and varum, and navicular drop height were measured. An independent t-test was conducted to compare SLEA and limb asymmetry between groups. One-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post-hoc tests were performed to determine the differences among the GL, SL and DL. RESULTS BD showed lower quadriceps and rearfoot angles, less tibial varum and navicular drop, and greater tibiofemoral angle (p<.005) than NBD. BD showed less quadriceps angle asymmetry but greater tibial torsion asymmetry (p<.01) than NBD. GL and SL in BD showed differences in quadriceps, tibiofemoral, rearfoot angle, tibial torsion and navicular drop compared to NBD. CONCLUSIONS Repetitive dance movements can transfer varying forces to the GL and SL, potentially contributing to SLEA asymmetry. An intervention strategy that can reduce SLEA asymmetry in BD is needed, as is the identification of elements of ballet training that contribute to maintaining a normal SLEA.
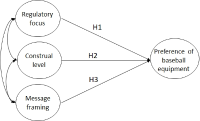
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the propensity to consume the consumer of the baseball equipments who have difference of the product preference by regulatory focus, and who have construal level and suitable message framing. Methods Populations are consumers who have purchased the baseball equipments before, and the sampling groups, five different society baseball group’ league from Seoul and Kyeongi-do, were distributed, 318 copies, by convenience sampling. The questionnaire proceeded by three-way completely randomized design with stimulated sentences of four different advertisement compartmentalized by the regulatory focus, construal level and message framing. The analysis utilized SPSS 21.0 to perform the frequency analysis, manipulation check, independent t-test, two-way ANOVA, and Scheffe was used to post-hoc. Therefore, the result of this study is as below. Results First, after analyzing the distinction of the regulatory focus of the consumers of baseball equipments, the preference of the consumer who has improving focus was higher than that of consumer who has the prevention focus. Second, preference differentiation analyzed by construal level and the message framing of the consumer of the improving focus, the preference was higher when the message framing was positive, and the construal level was in short time. Third, preference differentiation analyzed by construal level and the message framing of the consumer of the prevetnion focus, there was no difference of the preference of the equipments followed by the construal level and message frame for prevention focus consumers.


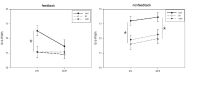
[Purpose] Perception plays an important role in understanding the environment or related objects in order for humans to perform physical movements more effectively. Sometimes they create different movements with different perceptions. Especially, visual perception errors that occur in sports situations can have a considerable effect on performance. Accurate knowledge of the environment in this process of perception is important in performing movements or actions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of learning formation on perception using Muller-Liar illusion diagrams. To measure this, we compared the feedback group that induced knowledge learning and the control group that did not provide knowledge To see if there is a difference. Therefore, in this study, we have provided a visual feedback that can establish the cognitive awareness of the actual stimuli length to subjects, and investigated the changes in their matching action responses. [Methods] A total of 32 young and healthy subjects were randomly divided into two groups (Feedback and Non-Feedback groups). Subjects were asked to match the stimulus size with their index fingers and thumbs. Initially (pre-test), three different visual stimuli (inward, outward, and no arrows) were randomly presented 60 times (20 times each) and the grip sizes were recorded using the Liberty Motion Analysis System (Polhemus Co., America). Then, video clips of two lines merging each other were presented as feedbacks. Post-test protocol was identical to the pre-test protocol. The data were analyzed using the 3-way ANOVA with one RM factor (2 x 3 x 2). [Results] Results showed a significant 2-way interaction effect. Post-hoc results showed significant interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests only in the experimental group. There was a significant decrease in the grip size after feedback in the OUT condition of experimental group. However, in the control group, there was no interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests. [Conclusion] Overall, current results indicates that, while visual illusion can affect the action, the provision of visual feedback can establish the awareness of actual stimulus size and suppress the influence of illusion on action.

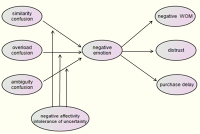
Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify how the three variables of consumer confusion proneness affect consumers' negative emotion, word of mouth, trust and decision postponement during the process of purchasing golf club. Futhermore, this study looked through the moderating effect of the personal characteristics in the relation between consumer confusion proneness and negative emotion. Method A total of 850 questionnaires were used for data analyses(i.e., frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling) with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. Results First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer's negative emotion. Second, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on negative WOM. Third, consumer's negative emotion had no significant effect on distrust. Fourth, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on decision postponement. Fifth, the moderating role of negative effectivity partially had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Sixth, the moderating role of intolerance of uncertainty had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Conclusion The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on over all golf industry as in service providing point of view as well as development and application relate to it.

PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.
PURPOSE The United Nations (UN) has proposed 17 Sustainable Development Goals and has been extending its efforts to achieve them. Sport can be linked closely to the third goal, which is related to health and well-being. Therefore, this study aimed to explore and to analyze individual's changed sport activities during the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on ways to achieve health and well-being related goals through sport. METHODS A qualitative research method was employed, and in-depth interview methods were used for data collection. For data analysis, categorization and itemization were used along with content analysis. RESULTS Looking at the derived results, in the context of an infectious disease such COVID-19, sport activity patterns have changed due to reasons such as stadiums or facilities, interpersonal reasons, fear, inconvenience, staying healthy, increase in leisure time, and individual preferences. CONCLUSIONS Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the indicators of health and well-being related SDGs are exhibiting a downward trend. At this point, it is necessary to find a way to achieve the goal through sport that can participate voluntarily for the purpose of pursuing pleasure.
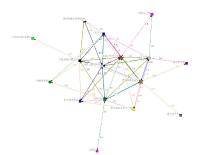
The purpose of this study was to investigate structural characteristics and participants` roles & functions of sport policy network in Korea, by social network analysis on structural characteristics of sport policy network and AHP analysis on participants` roles and functions. For that, 21 executive officers from 19 organizations and agencies related to sports policy were selected as study subjects, and, the materials collected from whole twice surveys on them were analysed by Ucinet 6 and Expert Choice 2000 program. As the results, the governmental organizations like the Blue House and Ministry of CultureㆍSports and Tourism composed the central position group of sport policy network of Korea, and took the main functions of planing and arrangement within their main roles of policy agenda formation and policy decision, so, sport policy network of Korea could be called centralized network by government. And, in cases of private agencies, Korea Sports Council composed the central position group only in policy network of professional sport, Korea Council of Sport for All of sport for all, and Korea Sports Association for the Disabled of disability sport, and, each of them took the main roles and functions of policy execution in their fields, so, it was obvious that the private agencies were divided into their own sport policy areas.