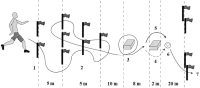
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effect of acute tart cherry juice intake on recovery after intermittent exercise in female field hockey athletes. METHODS Sixteen university female field hockey athletes were studied for a total of 3 days. The cohort was divided into 2 groups, placebo group (n=8, PLA) and the tart cherry juice group (n=8, TCJ), Each supplement was consumed 5 times over 48 hours. On the first day of the study, venous blood was collected before the test, and physical fitness variables (20m sprint, 5-0-5 agility, and Countermovement jump) were performed twice before and after the Yo-Yo Intermediate recovery test 1 to determine the degree of muscle damage and recovery of physical fitness factors. After all tests on Day 1, supplements (PLA, TCJ) were taken. After 24 hours, venous blood collection was performed, and after 48 hours, venous blood collection and physical element variables were measured to verify the effectiveness of tart cherry juice. RESULTS In the TCJ group, a significant effect was found over time in the 5-0-5 ability among the fitness variable items (p<.001) In Countermovement jump (CMJ), there was a significant effect over group and time (p<.001). Second, significant effects over group and time were shown in Interlukin-6 (IL-6) among variable items related to muscle damage and inflammation through venous blood collection (p<.05) and LDH (p<.001), and CK (p<.01) showed a tendency to decrease with time. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that acute tart cherry juice intake after intermittent exercise tends to reduce muscle damage and inflammation-related variables in female field hockey players, which could help them recover quickly, especially after hectic game schedules.
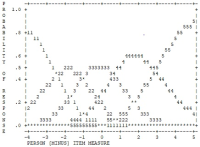
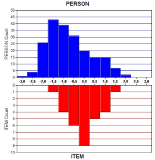
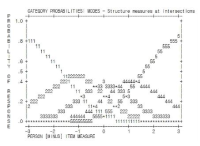
Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine item goodness-of-fit and the optimal categorization of an instrument measuring Korean elite young soccer player’s self-esteem using a two-facets Rasch model (item parameters and person parameters). Methods 10-item Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES) with five response categories was administered to 366 elite young soccer players from the Korea football association. The Rasch analysis was conducted by WINSTEPS 3.65. Results First, the model fit the data well. Second, 5-category rating scale did function well. Third, a item-person map illustrated the distribution of RSES items and person’s level of self-esteem. Fourth, the separation reliability of the items and person was shown to be an acceptable degree of confidence, respectively. Lastly, there was statistically significant difference in self-esteem between starting players and bench players, which supported the known-difference evidence of validity. Conclusion These findings provided additional support for the suitability of the RSES in assessing self-esteem of Korean elite young soccer players.


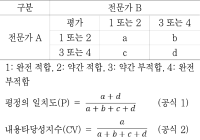
Purpose Common content knowledge(CCK) is composed of rules, techniques, and tactics. Such knowledge is a requirement for effective teaching of physical education (PE). There are, however, few validated tests of CCK. Thus, the purpose of this study was to develop a CCK test of soccer and evaluate the validity and reliability of the test using Rasch modeling (Rasch, 1980). Methods We developed thirty item common content knowledge test for soccer. Then, we used Rasch modeling to evaluate the validity and reliability of a test of soccer. Pre-service teachers (N=92) majoring in physical education and non-PE major (N=111) participated in this study. Results Thirty questions demonstrated good item-model fit. Moderately high internal consistency for person-ability and high internal consistency for item-difficulty are reported. Both Infit and Outfit statistics showed a good fit between the data and the Rasch model. Conclusions The analysis provides evidence to support the validity and reliability of this instrument as a CCK test of soccer. Limitations of the study were discussed and suggestions were provided to improve the test.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of an 8-week unstable surface Pilates training on physical fitness, abdominal muscle thickness, lumbar isokinetic muscle function, and pain in women aged 30–40 who are living a sedentary lifestyle and experiencing nonspecific low back pain. METHODS The training group (TR, n = 15) performed Pilates using small apparatuses on an unstable surface for 50 min/session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas the control group (n = 13) maintained their usual living pattern during the same intervention period. RESULTS 1) The body weight, body mass index, percent body fat, and fat mass decreased significantly in the TR, 2) whereas the hand grip strength, trunk extension, sit-andreach, and modified Schober test scores improved significantly. 3) The thickness of the external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis increased significantly in the TR. 4) Lumbar isokinetic flexor strength per body weight increased significantly in the TR. The endurance and endurance per body weight of the lumbar isokinetic extensor and lumbar isokinetic flexor also significantly increased in the TR. 5) The Korean Oswestry disability index (KODI) and the visual analog scale (VAS) score decreased significantly in the TR. 6) Significant negative correlations were found between the change rates in the KODI and nondominant hand grip strength, external oblique thickness, transversus abdominis thickness, and lumbar isokinetic extensor endurance. A significant negative correlation was found between the change rates in the VAS score and external oblique thickness. CONCLUSIONS The results revealed that the 8-week unstable surface Pilates training was beneficial in improving physical fitness, abdominal muscle thickness, lumbar isokinetic muscle function, disabilityindex, and pain levels in women aged 30–40 years who were having a sedentary lifestyle and experiencing nonspecific low back pain.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8-week aerobic exercise and polyphenol intake on body composition, cardiovascular response, vascular endothelial function, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in prehypertensive men. METHODS The study included twenty-eight males in their 20-30 years of age with prehypertension. Participants in the aerobic exercise + polyphenol intake group (EX + PP; n = 14) performed aerobic exercise three sessions/week, 30 min/session, at 65% of the heart rate reserve, and consumed polyphenol (grape seed extract 300 mg) for 8 weeks. Participants in the aerobic exercise + placebo intake group (EX + PL; n = 14) performed the same aerobic exercise; however, they consumed placebo instead of polyphenol. All independent variables were measured at pre-test and post-test, and the data were analyzed. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) SBP and MAP at rest decreased significantly in EX + PP, while MAP decreased significantly in EX + PL group. 2) In the EX + PP group, CO increased significantly, whereas DBP, MAP, and TPR decreased significantly during the hand grip exercise. In contrast, CO decreased significantly, while DBP and TPR increased significantly in the EX + PL group during the hand grip exercise. 3) Regarding vascular endothelial function, % FMD increased significantly in EX + PP group. 4) Sit-up increased significantly in both EX + PP and EX + PL groups; however, sit-and-reach in EX + PP group was significantly higher than that in EX + PL group at post-test. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study showed that the 8-week aerobic exercise would have positive effects on body composition, cardiovascular response, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in hypertensive men. Additionally, polyphenol intake would contribute more towards reduction of blood pressure at rest and during exercise and improvement of vascular endothelial function.
Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.

[Purpose] This study aimed to examine the effects of complex physical training on exercise and football performances in youth football players. [Methods] The subjects (n=16) were randomly assigned to either a complex physical training group (CPG, n=8) or a control group (CON, n=8). CPG was performed the complex physical training for 50 minute per day, and 2∼3 times per week, for 8 weeks. Exercise performance (health related physical fitness, skill related physical fitness, Y-balance and functional movement screen; FMS) and football performance (juggling, speed dribbling, shot passing, long kick and triple hop) were measured before and after 8 weeks complex physical training. [Results] Sit-up (p=0.002), sit and reach (p=0.040), 50-m run (p=0.031), side step (p=0.005), single-leg standing with eyes closed (p=0.040), plank (p=0.023), dominant composite score (p=0.002) and non-dominant composite score (p=0.005), deep squat (p=0.009), inline lunge (p=0.042), active straight leg-raise (p=0.015), rotary stability (p=0.049), total score(p=0.001), speed dribbling (p=0.030), dominant triple hop (p=0.001) and non-dominant triple hop (p=0.032) were statistical significant interactions between group and time. [Conclusion] Our findings indicate that complex physical training has beneficial effects on performance improvement of exercise and football in youth football players.

The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

PURPOSE This study aims to analyze elective courses in overseas physical education curricula and explore directions to improve the national physical education curriculum. METHODS Physical education curricula from the Ontario Ministry of Education and New South Wales Department of Education, and an administrative announcement book of the 2022 Revised Physical Education Curriculum were collected and analyzed. RESULTS The Ontario physical education curriculum offers a range of elective subjects that fit students’ need to enter universities and colleges. It also has a systematic curriculum flowchart within elective courses. The NSW physical education places importance on learning life skills and offers content-endorsed courses that comprises core studies and optional modules. CONCLUSIONS This study clarified the differences between the learning content of elective subjects and suggested the necessity of developing plans to provide students with effective course path.
PURPOSE The ethical leadership of Taekwondo instructors plays a crucial role in enhancing the value of Taekwondo. Therefore, this study explores the elements of ethical leadership among Taekwondo instructors by drawing on the insights from Lao Tzu's Tao Te Ching. METHODS Through the Tao Te Ching, an oriental classic containing the ideas of Lao Tzu, we have extracted and discussed the elements of ethical leadership that Lao Tzu conveys to Taekwondo leaders in this era. RESULTS The ethical leadership of taekwondo leaders in the Tao Te Ching was presented as the virtues of inaction and humility as behavioral norms. Inaction as a code of conduct was discussed about a leader who practices inaction in a changing world through subjective thought rather than a meaningful Taekwondo leader who leads Taekwondo with an existing pattern and looks at ethics. A Taekwondo instructor must possess the virtue of humility. A Taekwondo instructor with humility must be glazed, soft, and humble as water. CONCLUSIONS In a Taekwondo culture that follows the Confucian ideology of extreme austerity, Lao Tzu's ethic of non-action and the virtue of humility can be like wearing an ill-fitting robe. However, standing on the edge, outside the frame of reference of the ideologies and values we have come to believe in and follow, and seeing the world as it is, not as it should be, according to the laws of nature, provides a new discourse for Taekwondo philosophy.