PURPOSE The main purpose of this study was to examine the difference in visual search strategies based on the skill level in success and failure cases in badminton short serves. METHODS To this end, six badminton experts (experience: more than 10 years) and six novices (less than 1 years) participated. The participants’ eye movement was recorded during each trial, and mean fixation duration, mean saccade amplitude, percentage of viewing time on each fixation location, final fixation duration, and gaze entropy were analyzed. RESULTS First, the mean fixation duration did not differ significantly, but the mean saccade amplitude increased when expert players failed to perform the serve successfully. Second, the percentage of viewing time on each location results showed that the overall viewing time was lower when the performance was unsuccessful, and the expert players fixated longer time viewing the net and space when they made a successful serve. Third, expert players showed longer QE than novice players when they made a successful serve. Finally, the gaze entropy results showed that expert players showed greater gaze entropy during successful performance, indicating that the gaze pattern was randomly distributed across trials. CONCLUSIONS When learning a badminton serve, we should fully recognize and explore the receiver’s location and external environment, and subsequently, before initiating serve movement, focus on the net or space between the receiver’s racquet and shoulders to make a more successful performance. In addition, we should make various patterns of the visual search strategy, rather than the fixed or consistent search strategy, to deceive receivers.
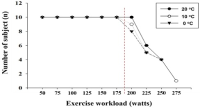
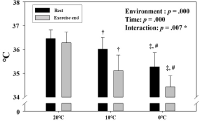
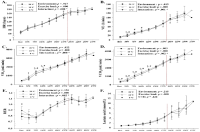
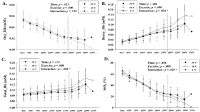
Purpose This study aimed to investigate the effects of acute cold stress (10℃, 0℃) compared with ordinary temperature (20℃) on exercise performance and physiological response at rest and during exercise. Methods A total of 10 healthy men (21.55 ± 2.16) were selected. In each environmental condition (20℃, 10℃, 0℃), the three testing order was randomly selected at crossover, and there was a week interval between the graded exercise test (GXT). On the testing day, they remained resting for 30 min in each environmental condition. Dependent variables (body temperature, energy metabolism parameters, skeletal muscle oxygenation profiles, and exercise performance parameters) were measured at rest and during GXT. Results In body temperature, at each environmental condition, there was a significant decrease (p<.05) at 10℃ and 0℃ compared with 20℃ after exercise, and in the difference depending on the environment at rest. After exercise, the body temperature significantly decreased (p<.05) in proportion to the decrease in temperature. There was no difference in heart rate and blood lactate level in energy metabolism, and the respiratory exchange ratio was significantly higher (p<.05) at 0℃ than 20℃. Minute ventilation (VE), oxygen uptake (VO2), and carbon dioxide excretion (VCO2) were significantly lower (p<.05) at 0℃ than 20℃ and 10℃ at various exercise load. All skeletal muscle oxygenation profiles did not show significant changes at rest and during exercise. In exercise performance, maximal oxygen uptake was significantly lower (p<.05) at 0℃ than 20℃, and exercise time to exhaustion was also significantly lower (p<.05) at 0℃ than 20℃ and 10℃. Conclusion Acute cold stress induces deterioration of exercise performance via a decreased body temperature and an increase in VE, VO2, and VCO2 during the same exercise load. In addition it was confirmed that this phenomenon was more prominent at 0°C than at 10°C when compared to 20°C.


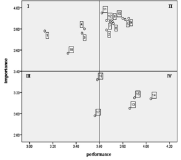
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out what young amateur golfers consider the most when purchasing golf apparel and to find out the Importance-Performance attributes when choosing golf apparel. Methods Amateur golfers in their 20s through 40s who have purchased golf clothing directly were selected as the subject. A total of 350 questionnaires were distributed using the purposive sampling method, and 331 copies as a final validity sample. For data analysis exploratory factor analysis Cronbach’α, frequency analysis, and Importance-Performance analysis by using SPSS 21.0. Results First, except for ‘fancy design’, ‘water-proof function’, ‘elasticity comfort’, ‘brand name’ there were significant differences between importance and satisfaction of selection attribute. Second, ‘harmonic colors’, ‘has its own characteristics’, ‘expressing beauty’, ‘elasticity comfort’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅰ. Third, ‘fancy design’, ‘water-proof function’, ‘temperature maintenance function’, ‘elasticity and durability’, ‘brand name’, ‘high-priced yet popular brand’, ‘popular brand’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅱ. Fourth, ‘comfortable to wear’, ‘convenient for physical activity’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅲ. Fifth, ‘can be also worn for outdoor wear’, ‘wear for gathering’, ‘wear as daily attire’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅳ. Conclusions The results will be the basis for effective target marketing on young amateur golfers who are rapidly emerging and will be able to grasp the characteristics of golf apparel that they really want.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide basic data for spectators group of Taekwondo performance efficient marketing activities through market segmentation from characteristics, perceived values of the Taekwondo performance spectators. Methods The subjects of this research were Kukkiwon, Taekwondowon and 1,021 questionnaires were finally used for the analysis. The results of this research were drawn by frequency analysis, CFA(confirmatory factor analysis), reliability analysis, cluster analysis (hierarchical and K-means), cross-tabulation analysis and One-way ANOVA were used for data processing through SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0. Results As results of the analysis, It was subdivided into three clusters (such as group of male college students, man group of low perceived value and high degreed women group of low pragmatism). Conclusions The significant differences of the characteristics and perceived value appeared from each cluster. Cluster 1: A group of male college students, and the highest perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 2: A group of male, and a low perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 3: A group of high degreed women and a low pragmatism of perceived value. Therefore, a practical marketing strategy was needed for each groups.

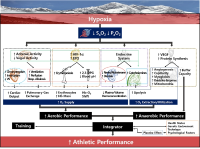
Purpose The purpose of this study is to emphasize the need for the establish and the use of altitude training center via examining exercise training method in natural or artificial altitude environment that is applied to various elite athletes in various advanced countries to maximize exercise performance and its effectiveness. Results Altitude training in natural or artificial altitude environment enhances aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance baesd on the hematological and nonhematological adaptations to hypoxic conditions. These altitude training methods can be classified into living high training high (LHTH), living high training low (LHTL), and living low training high (LLTH). LHTH (i.e., developed since the 1968 Mexico Olympics) and LHTL (i.e., developed in the 1990s by Levine and Stray-Gundersen) improve exercise performance via hematologic changes through erythropoiesis such as increased hemoglobin mass and erythrocyte volume. On the other hand, LLTH (i.e., has been developed variously since the 2000s) is composed continuous hypoxic training (CHT), intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) and repeated sprint training in hypoxia (RSH), and the altitude environment is constructed using a vacuum pump and a nitrogen generator. In general, LLTH method dose not induce hematological change in a short time within 3 hours. However, CHT and IHT enhance aerobic exercise capacity by improved exercise economy, supply and utilization of blood to tissues, capillary and mitochondrial densities, and oxidative enzyme activity through various biochemical and structural changes in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. RSH enhances anaerobic power and repetitive sprint performance by improving glycolytic enzyme, glucose transport, and pH control. In Korea, however, there are almost no facilities for altitude training that is applied to enhance athletic performance in advanced sports countries and recognition of the need for altitude training is also very poor. Conclusions Therefore, it is very urgent to develop altitude training for maximizing athletic performance in Korea and a lot of support and efforts are needed from the government and local governments.


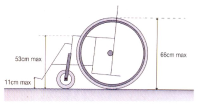
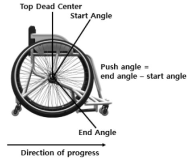
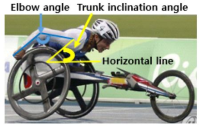
[Purpose] A potential issue for wheelchair sports are the characteristics of wheelchair design. The purpose of this review was to investigate the characteristics of design in wheelchair sports including the height of seat, camber and handrim size for improving the performance. [Results] The optimum height of seat related to trunk, arm length and handrim size. The lower seat showed the push efficient highly, while higher seat increased the energy expenditure. In energy expenditure, the optimum height of seat was 100-120° of elbow angle. Handrim size play the role in gear. The smaller handrim size acts like high gear, it gains disadvantages in acceleration, it gains advantages in maximum velocity. On the contrary, the higher handrim size acts like low gear, it gains disadvantages in maximum speed, it gains advantages in acceleration. The ratio of gear consideration in power and velocity. When increased camber enhanced the lateral stability, easier catch the handrim and easier arm motion. So it improved the energy expenditure and push technique. When increased camber enhanced the mechanical efficiency and stability, but it decreased the power. The racing wheelchair camber using the 8° and 10°. [Conclusion] Athletes, coaches and wheelchair experts are provided with insight in the performance effect of key wheelchair design settings, and they are offered a proven sensitive method to apply in sports practice, in their search for the best wheelchair-athlete combination.




Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the changes of gait patterns and muscle activations according to dual tasks during stair ascending. Methods Twelve sedentary young male adults(Age: 27.0±1.8 yrs, Weight: 65.8±9.9 kg) without any lower extremity injuries participated in the study. Participants performed stair walking up 7 floors and their ascending motion on each floor was analyzed according to dual tasks. A wireless electromyography (EMG) were attached on the Rectus Femoris(RF), Biceps Femoris(BF), Gastrocnemius(GN), Tibialis Anterior(TA) muscle to calculate integrated EMG(iEMG) and co-contraction index(CI). Chest and left heel accelerometer signal were recorded by wireless accelerometer and those were used to calculate approximate entropy(ApEn) for analyzing gait pattern. All analyses were performed with SPSS 21.0 and for repeated measured ANOVA and Post-hoc was LSD. Results The results of this study indicated that dual task appeared to increase their time, CI and there were a statistically significant difference in most muscle on each floors compared to the non dual tasks. Also, ApEn were a statistically significant difference in only left and right direction than non dual task. Subjects showed more irregular pattern and instability muscle activation response during dual tasks. Conclusion Because there are many dangers often use of stairs in everyday life, in the future, we have to make a lot of efforts to prevent fall.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between performance factors and physical fitness in secondary school female biathlon athletes. Participants in this study were 14 female biathlon athletes. Methods All factors such as aerobic capacity(VO2max, %AT), wingate test(peak power, average power, fatigue index), isokinetic test(trunk, knee, hip, ankle), 1RM test(leg press, chest press, lat pull down), physical fitness(grip, knee and back muscle strength, sit & reach, power, agility) were tested. In order to analyze collected data, pearson product moment and multiple regression analysis were utilized. The results were summarized as follows : First, there was a significant correlation between aerobic. Results The results were summarized as follows : First, there was a significant correlation between aerobic capacity and three factors(standing broad jump, isokinetic test 60° right knee extension)(p<.01). There was a significant correlation between wingate test and four factors(isokinetic test 30° left ankle ever, 30° right ankle ever, 120° left ankle inver, leg press)(p<.10). Conclusion These results suggested new evidence that ankle strength is necessary for performance in female biathlon athletes.


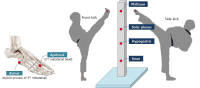
Purpose The aim of this study was to assess accuracy, consistency and performance time of the kick(front kick, side kick) of elite Poomsae players who accustomed excessive high kick. Methods Accuracy, consistency and performance time were measured by 3D motion capture system. Twelve elite Poomsae players(age: 28.83±1.80 yrs, height: 171.75±4.29 cm, weight: 67.58±3.6 kg) performed Poomsae kick according to the four target(philtrum, solar plexus, hypogastric, knee) and target or non-target. Results 1) Both of Front kick and Side kick were evaluated highest accuracy and consistency at philtrum. 2) Both of Front kick and Side kick were tend to increase on accuracy and consistency as the target height increasing. 3) The accuracy of Front kick and Side kick was decreased when the target is not provided at hypogastric and solar plexus. 4) There were statistically significant differences in performance time according to the height of four targets on Side kick but no differences on Front kick in performance time. Conclusion Overall elite Poomsae players who are familiar with kicking in high target were assessed poor kicking performance on lower target.




Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the causal relationship between competitive strategy, absorption capacity and business performance of commercial fitness center and to confirm the control effect of absorption capacity between competitive strategy and business performance. Methods 330 fitness center managers and administrators were selected for the study. Out of 330, 308 questionnaires were collected and used for data analysis. The questionnaire consisted of confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and structural equation model analysis. Finally, Ping 's two - step approach was used to verify the moderate effect of absorptive capacity. Results The results of the study are as follows. First, competition strategy of fitness center has a positive effect on absorptive capacity. Second, the competition strategy of fitness center has a significant effect on business performance. Third, the absorptive capacity did not effect the management performance. Fourth, the absorptive capacity was found to be moderate effect between the competition strategy and the management performance of the fitness center. Conclusion Based on the results, the fitness center managers and administrators of fitness center should set up competitive strategy internally and increase absorptive capacity to utilize external information by internalizing it.

