The purpose of this study was a investigate the endothelial function of prehypertensive during dynamic exercise. Hypothesis of this study was to impair the endothelial function in prehypertensive compared to normtensive during dynamic handgrip exercise. Eleven healthy prehypertension (24±2 yrs) and ten healthy normotensive (25 ± 2 yrs) were recruited in this study. Participants were performed dynamic handgrip exercise in one contraction per second at 30% of maximum voluntary contraction for three minutes. Vascular (blood vessel diameter, blood flow) and cardiar response (stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output) were measured at rest and during exercise. Flow mediated dilation (FMD) was decrease significantly in prehypertensive less than normotensive (p<0.05) at rest, and vasodilation of prehypertensive was reduced significantly less than normitensive during exercise (p<0.05). All the cardiovascular responses were aot significantly different at rest and during exercise between prehypertensive and normotensive. These results suggest that endothelial function is impaired in prehypertensive compared to in normotensive


The objective of this study was to reveal the characteristics of lower extremity motions of middle-aged women in accordance with their walking speed, and also to suggest elements of improving functions of walking-shoe for the improvement of gait stability. Total 30 healthy middle-aged women were asked to walk in their preferred speed and also speed 20% faster than that. Using the 3D motion capture system and the plantar pressure measuring system, the characteristics of lower extremity motions were measured. For the analysis on differences in motions between preferred and faster speeds, the paired t-test was performed. At this time, the significance level was set up as α=.05. The walking in faster speed showed the greater ground contact angle than walking in preferred speed while its gait stability was low. Also, the faster walking showed the bigger plantar pressure, and especially, the pressure on the great toe was high. It would be necessary to improve functions of shoes for the gait stability and dispersion of pressure on feet while fast walking.

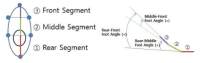

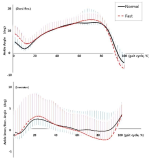

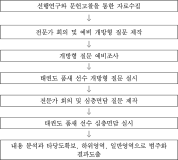
The purpose of this study was to develop and validity Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete(CSATF). The participants were composed of the 48 Taekwondo Form athlete to explore sub-factors of Competitive State Anxiety for Taekwondo Form athlete. The data were collected by an open-ended questionnaire and interview. The participants were composed of 257 national Taekwondo Form athlete to develop Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete. This 157 athlete data were used for items analysis, reliability analysis and exploratory factor analysis. And 100 athlete data were utilized for confirmatory analysis. Also convergent validity, discriminant validity, predictive validity latent mean analysis of CSATF were performed The results of this study were as follows. Firstly, the results revealed that the four general dimensions were identified such as cognitive anxiety, somatic anxiety, state of confidence, environmental anxiety. Secondly, CSATF comprised cognitive anxiety(5 item), somatic anxiety(5 item), state of confidence(5 item) and environmental anxiety(6 item). Thirdly, convergent validity, discriminant validity and predictive validity, the multi-group analysis according to gender examined validity of CSATF.


Sportscasting in Physical Education (Lee, 2011) is a class activity that students simulate sports broadcasting (e.g., students report, analyze, and comment on game play). It encourages problem solving (PS) learning for students. Scaffolding is the support with the intention of helping the student achieves his/her learning goals and contributes to problem solving. However, limited studies have examined if sportscasting with scaffolding is effective instructional strategies for PS. The purpose of this study was to examine effects of sportscasting with scaffolding on PS abilities, and on academic achievement. Participants were 46 college students. The static-group comparison design was used: an experiment group (N=26) with supportive scaffoldings (e.g., conceptual explanation, terminology dictionary, visual materials) and a control group (N=20) with reflective scaffoldings (e.g., organizing the environment, using appropriate cues to guide behaviors, and modeling). The results revealed that students in reflective scaffoldings had higher PS abilities than students in supportive scaffoldings. However, two groups were not statistically different in academic achievement. Sportscasting with instructional scaffolding promote a deeper level of cognitive skills and male students performed better than female students. The effective scaffolding types (Lewis, 2010) for sportscasting were discussed to help students to foster PS skills.


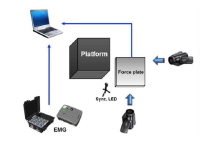
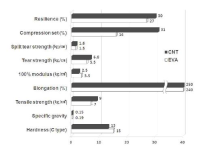
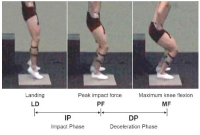
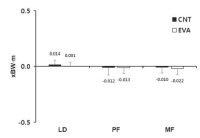
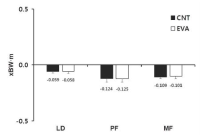
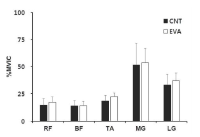
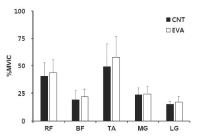
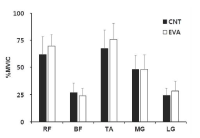
The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of carbon nanotube-based insole on the resultant joint moment and muscle activity of the lower extremity during drop landing. Ten males with no known musculoskeltal disorders were recruited as the subjects. Two digital camcorders and one force plate were used to obtain 3-D kinematics and kinetics of the lower extremity. To assess the myoelectric activities of selected muscles, five surface electrodes were attached to the right side of the lower extremity. For each dependent variable, paired t-test was performed to test if significant difference existed between with carbon nanotube-based insole(CNT) and ethylene vinyl acetate-based insole(EVA) conditions(p<.05). The results showed that average and peak IEMG values from RF, TA, MG, and LG in CNT were lower than corresponding values in EVA. Although no significant difference in resultant joint moment was found between two conditions, a decrease in the knee extension moment was found with CNT. This indicates that wearing carbon nanotube-based insole may help to decrease impact force and to control excessive flexion movement of the knee joint during landing.







The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.




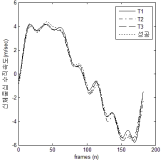
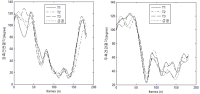
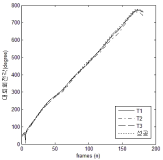
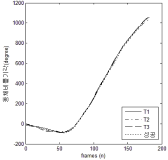
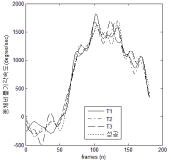
The research was a case study conducted in order to develop a new technique “YANG Hak Seon 2” for YHS athlete. A comparative kinematical three dimensional video analysis was performed with the use of high speed cameras. One successful trial and three of failure trials (T1: Falling backward while landing, T2: sitting reluctantly while landing, T3: Falling of sideways while landing). The result obtained from the study are as follows. Firstly when comparing the successful operation of the technique with failure trials, relatively higher landing angle was secured through increasing the thigh rotation and the body’s rotational velocity. Furthermore, despite increase in rotational velocity at twisting, stable landing was achieved through increasing the moment of inertia by spreading the left shoulder. Secondly, in case of failure trials while taking off the board, the thigh rotational angular velocity was comparatively less which ultimately affected the body position in the next phase of approach to the vault. Thus, due to the affected body position the athlete was not able to utilize the proper momentum of twist in positive direction Hence, it is considered that the velocity of center of mass might have also effected the operation not only the velocity while approaching the board.












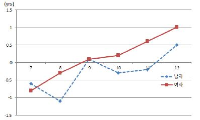
This study classified and analyzed groups of spectators of professional baseball through market segmentation and predicted the sports consumer behavior by using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model. The results of hierarchical cluster analysis, K-means cluster analysis, cross-tabulation analysis and one-way ANOVA using PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 suggest five clusters of consumer segments and by using Modeler 14.1, artificial neural networks model was made to predict the data. By using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model, hit ratio was grasped about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. The results are as follow: The hit ratio were high in ‘cluster 5’ for artificial neural networks model(spectator satisfaction: 71.3%, future consumption behavior: 99.3%) and logistic regression(spectator satisfaction: 71.8%, future consumption behavior: 96.5%). Furthermore, cross-tabulation and one-way ANOVA was performed to understand the cluster's characteristic which had highest hit ratio about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. And through this marketing strategy was suggested.

The aim of the study was to examine the tracking of body composition and physical fitness in boys and girls for 6 years. Thirty-seven boys and girls participated throughout the study. All measurements were performed annually. Body height, body weight, circumferences and skinfold thicknesses were measured and skeletal maturity was assessed. Body composition and bone mineral density were measured by DXA. Nine physical fitness tests were administered. Results of the study showed that there are significant interaction effects of time and group for body height(p<.01), waist circumference(p<.001), and skinfolds at triceps(p<.01), suprailiac(p<.01), thigh(p<.001) and medial calf(p<.01). All anthorpometric variables except skinfold thickness increased during the study period. Significant interaction effects of time and group were found for percent body fat(p<.05) and bone mineral density(p<.01). Percent body fat and fat tissue increased in boys from 7 to 11 years, then decreased in 12 years. Lean tissue(p<.001), bone mineral content(p<.001) and bone mineral density(p<.001) increased both in boys and girls throughout the study. There were significant interaction effect of time and group on sit and reach, standing long jump and sit-ups. In conclusion, percent body fat and fat tissue increased until 11 years, lean tissue and bone mineral density increased throughout the study both in boys and girls.


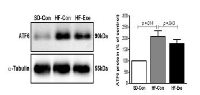
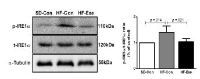
This study was to performed to the effect of 8-week endurance exercise influences on body weight, glucose tolerance and ER-stress in soleus of 16weeks Rats fed High-Fat diet. Rats were randomly assigned to 3 group; (1)Sprague-Dawley Control diet (SD-Con/n=4), (2)High-Fat diet Control (HF-Con/n=4), (3)High-Fat diet Exercise (HF-Exe/n=4). Exercise group ran on the treadmill for 30min/day at the level of 21m/min for 5days/week during 8weeks. Results showed that body weight and glucose tolerance of the HF-Con group was remarkably increased(p<.05) compared to other groups. However, HF-Exe group significantly decreased body weight and glucose tolerance compared to HF-Con group. Moreover, level of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺, which are main proteins of ER-stress were significantly increased in HF-Con group higher than other group, whereas HF-Exe group significantly decreased the expression of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺. Taken together, these finding suggested that the reduction of the body weight, glucose tolerance and unfolded protein response by treadmill exercise may represent a positive adaptation protecting against high-fat diet-induced ER stress.