PURPOSE The quiet eye (QE) is defined as the final fixation time that is a specific target prior to initiating movement. This study aimed to identify the cause of QE in golf putting and to present an efficient practice method for improving putting skills. METHODS Thirty participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups. Each group practiced golf putting in different ways for two days. RESULTS The QE group showed a significant difference in putting scores, which was higher than that of the control group. The visual-occlusion group showed no difference compared to the other groups in terms of putting scores. The QE group showed a significant difference in terms of QE in the retention and competition tests compared to the pretest. The control group tended to have a slightly longer QE in competition tests compared to the pretest. The visualocclusion group showed no statistically significant difference in QE based on the period. All three groups had significantly longer swing times over the selected period. There was no significant difference in terms of the alpha power of the occipital lobe based on group and period. CONCLUSIONS The position of the visual-occlusion group became stable. However, the QE did not lengthen. The QE group had a longer QE. Furthermore, the control group that practiced with their eyes open tended to have longer QE. Therefore, QE may be related to visual-based cognitive processing rather than posturalkinematics. Finally, this study proved that QE practice is a more efficient method for novices in golf putting.
PURPOSE This study examined the effect of sports life skills and life skills transfer of student-athletes and coaches, applying Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM). METHODS Korean student-athletes and coaches from middle and high school sports teams participated in this study. There were 300 student-athletes (Mage=15.44, SD=1.64; male=218, female=82), with an average of 5.46 (SD=2.40) years of athletic career. Meanwhile, 33 coaches were (Mage=39.70, SD=8.36; male=26, female=7), with an average of 13.52 years of coaching career (SD=10.01). Measures included the Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA; Jang et al., 2020) and Korean Life Skills Transfer Survey (KLSTS; Lim et al., 2018). Descriptive analysis, correlation, and APIM were undertaken by using the SPSS and AMOS programs. RESULTS First, the correlation between athletes’ and coaches’ life skills was not significant. Second, athletes’ life skills significantly affected their life skills transfer, similar to coaches’ life skills significantly affecting their life skills transfer. Fourth, coaches’ life skills did not significantly influence athletes’ life skills transfer, and the converse was not true either. CONCLUSIONS This study verified the effect of life skills development for two groups of athletes and coaches, on transfer in sports, and attempted statistical verification of whether it affects sports life skills and transfer between athletes and coaches. Although no statistically significant results were found in the partner effect, it is meaningful in that, it provided important implications for conducting a follow-up study on the relationship between athletes and coaches. In other words, it is expected to be a cornerstone for research on building a new model, along with investigating the interactive relations between athletes and coaches on life skills in the sports field.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of trunk stabilization exercise (TSE) with abdominal expansion maneuver (AEM) that lasted for 8 weeks on postural stability and functional movement in college athletes. METHODS Twenty college athletes participated in the program (AEM=9, Control=11) and were subjected to 8-week TSE. The AEM group performed exercise by applying AEM techniques during TSE, and control group performed TSE without breathing-related instructions. Both groups measured postural stability with lower-quarter Y-balance test (LQYBT) and functional movement with functional movement screen (FMS) before and after applying TSE to verify the interaction before and after this study with the two groups. Two-way repeated analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the differences between groups and time for an absolute value of LQYBT and FMS, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests for post-hoc analysis. RESULTS As a result of the left and right LQYBT, there was a significant difference between the time x group (p=.041, p=.033), and post-hoc analysis indicated that there was a significant difference between the AEM and control groups (p=.000, p=,000). Furthermore, the FMS total score indicated that there was a significant difference between the time × group (p=.039), and the post-hoc analysis showed the AEM group had significant results (p=.001), while there were no significant results in the control group (p=.255). CONCLUSIONS Application of AEM during TSE seems to be effective with regard to postural stability and functional movement in college athletes.
PURPOSE High blood pressure and obesity pose significant health problems for older individuals. Previous studies showed that regular exercise improves physical fitness factors and decreases blood pressure and obesity. Therefore, this study investigated differences in blood pressure and obesity according to the physical fitness level of Korean older individuals using the National Fitness 100 data and used them to recognize the importance of maintaining physical fitness through regular physical activity or exercise for older individuals. METHODS From 2013 to 2019, a total of 218,848 subjects (men=74,271, women=144,577) aged ≥65 years who participated in the National Fitness 100 had their muscular strength, muscular endurance, cardiorespiratory endurance, balance, coordination, and flexibility measured, and they were ascribed a fitness level. Blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), percentage of bodyfat, and waist circumference were measured to compare the difference in fitness level. RESULTS There was a significant difference in the systolic and diastolic blood pressure in older men, and the diastolic blood pressure of older women by the fitness level (p<.001). In both older men and women, there was a significant difference in BMI, percentage of bodyfat, and waist circumference according to the fitness level (p<.001). CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, men and women showed different aspects in blood pressure, but Korean older individuals with having a high level of fitness managed their weight and body fat well. The decrease in obesity and improvement of physical fitness through regular physical activity and exercise could be a positive effect on maintaining health and extending healthy life years.
PURPOSE This study was designed to propose a quantitative base training evaluation method through alpine ski training monitoring using a triaxial accelerometer. METHODS Twelve Korean alpine ski athletes, six each in France and New Zealand, participated in this study. Activity data during training and daily living were collected for 7 days via the Actigraph GT9X. The collected data were downloaded through ActiLife Ver 6.13.1. Energy expenditure was calculated with Freedson (2011), and the resting metabolic rate was corrected using the Harris & Benedict (1918) formula. Further, the physical activity intensity classification criteria and METs formula of Freedson (1998) were used to classify hourly activity intensity. The collected data were organized by date, time, intensity, and energy expenditure using Microsoft Excel 2016. Differences between weekdays vs. weekends and skiing vs. physical training were analyzed through a paired sample t-test using Windows SPSS 23 with a significance level of a=.05. RESULTS First, both groups showed repetitive on and off high-intensity activities during scheduled ski training and competition. Second, moderate-intensity activities accounted for an average of 6-10%, and the weekly total time and intensity of MVPA was very high. Finally, the group from France showed differences in total energy expenditure during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05) and the energy expenditure of both ski training and physical training during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05). The New Zealand group showed a difference in total energy consumption during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05). CONCLUSIONS A systematic training program based on quantitative training evaluation should be developed for alpine ski athletes to maintain proper rest and exercise intensity levels.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training as an effective physical training method by analyzing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on the accuracy of perceived and actual distance as well as the correlation between the changes in the two variables. METHODS Thirty-six male college students took part in the experiment. Participants were beginners with no previous experience in golf or less than five times of experience. They were randomly assigned to one of three groups; proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control, maintaining the same sample size per group. The experiment was carried out in the order of pre-test, practice section, and post-test. In the pre-test, putting was tested to assess the accuracy of perceptual and actual distance in the 1-15m distance in a random order using a digital putting analyzer. In the practice section, proprioceptive-dependent and visual-dependent training groups practiced a total of 90 putting, six times per distance with the eyes closed or open. The post-test was the same as the pre-test. The accuracy of perceived and actual distance and the correlation between the changes in the two variables were analyzed using the calculated absolute errors. RESULTS The results of this study showed that there was no difference between groups in pre-test. In contrast, in post-test, the absolute error was significantly decreased in the order of proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control group in the three distance conditions. Besides, for the proprioceptive-dependent training group and visual-dependent training group, there was a significant positive correlation between the changes in the accuracy of perceived and actual distance. CONCLUSIONS These results provide insight into the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training for enhancing motor performance by showing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on perceived distance, actual distance, and the correlation between the two variables.
Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.

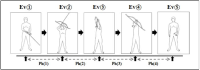
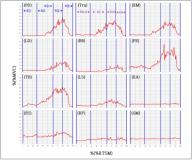
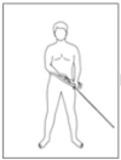
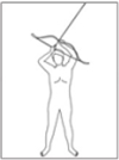
The past few decades has seen increasing kinematic studies using surface electoromyography (EMG) in archery, however there has been no such specific study in Korean traditional archery. The purpose of this study was to evaluate EMGs during archery shooting motion in Korean traditional archers. Ten men Korean traditional archers were participated, and divided into two groups according to the shooting stance; parallel stance group(PSG, n=5) and oblique stance group(OSG, n=5). The surface EMGs were measured 12 muscles during shooting motion of five events including Junbi(Set), Geogung(Set up), Manjak(Full draw), Balsi(Release), Machigi(Ending). At the result, muscle activity of posterior deltoid, trapezius, rhomboid major, latissimus dorsi, biceps brachii, forearm extensor bundle, triceps brachii, levator scapulae significantly increased at event of full draw and release, then significantly decreased again at event of ending, respectively(p<.01, p<.001). The muscle activity of erector spinae(ES) was also significantly increased at event of full draw and release(p<.01, p<.001), while no significant changes in muscles of rectus abdominis, rectus femoris(RF), gluteus maximus. As a result of comparing PSG and OSG, muscle activity of RF in OSG was higher than PSG at event of release(p<.05), it remained until event of ending(p<.05). On the other hand, the higher the tension of the bow, the higher the muscle activity of the draw arm at event of release(p<.05). These results suggest that when Korean traditional archery shooting, both side arm and back muscles are more activated than the abdomen, leg and hip muscles. The parallel stance might suppress the muscle activity of the lower extremities to twist the upper body. And the higher bowstring tension needs to increase of muscle strength in BB of draw arm.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of midsole hardness on gait mechanisms by wearing a backpack. Methods Ten healthy adult males(age:23.20±1.33yrs, heights: 1.72±0.03cm, weights: 67.60±5.95kg) participated in this study. Subjects walked at a speed of 1.5m/s in an 8m section wearing randomly selected midsole hardness (Soft, Medium, Hard) shoes and backpack (30% of body weight). For measurement of body movement, 10 infrared cameras (Vicon motion capture system, UK) and force plate (AMTI, ORG-6, US) were used. Results First, in the shock phenomenon change, the ground contact time was longer when wearing a backpack. Second, in the shock absorption strategy, the pack plantarflexion velocity at the ankle joint was faster in Hard than Soft, and the pack dorsiflexion moment decreased when wearing a backpack (p<.05). Also, the pack extension moment of the knee increased significantly when wearing a backpack. Fourth, in the mechanical negative work, the ankle joint performed less work than the medium soft, and the knee joint increased as the backpack was worn (p<.05). Conclusion As a result of this study, the difference in the hardness of the midsole used in this study does not seem to affect the biomechanical movement of gait even when wearing a backpack. In future studies, it is necessary to investigate the effect of the midsole through the presence or absence of shoes or inducing muscle fatigue.

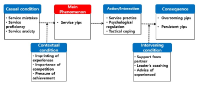
Purpose This study aims to investigate the experience of service yips in badminton players in depth through using grounded theory method. Methods We collected data from in-depth interviews with 14 participants in total, consisting of badminton players who experienced service yips, their doubles partners and coaches. The collected raw data were analyzed base on derive transcription, coding and paradigm models through grounded theory method. Results First, as a result, 59 concepts, 31 subcategories and 15 categories in regard to badminton service yips were deduced from open coding. Second, in axial coding, it was structured in a paradigm model by categories such as service yips, service mistakes, service proficiency, service anxiety, the imprinting experiences, the importance competition, the pressure of achievement, service practice, psychological control, tactical handling, support from partners, leaders’ coaching, advice from experienced ones, overcoming yips and persistent yips. Third, selective coding resulted in ‘Badminton service yips’ as the core category of this study. ‘Badminton service yips’ is a chronic performance impairment associated with badminton players making severe errors in swing motion on a service not intended by them that it is due to physiological or psychological symptoms such as hand tremors, overall body stiffness, arms stiffness, overstress, overanxiety, and concern over service mistakes. Conclusions We expect our study can be a theoretical foundation for understanding and explanation of ‘Badminton service yips’ and a useful reference for badminton players suffering from psychological difficulties caused by their service yips. The findings in this study should be considered for the development of potential strategies for overcoming the badminton service yips.
