PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.

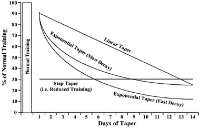
Purpose The aim of this study was to provide athletes and coaches on informations and benefits of a taper through evidence-based scientific studies and literatures in order to optimize an athlete’s top performance for the major competition. Methods Studies and literatures search was conducted using the databases RISS, KISS, SPORTDiscuss. Key words searched: taper AND(competition, OR performance, OR training, OR training). This study were eventually cited by 22 articles for results of this in total 100 articles. Results The training load is remarkably reduced during a taper. With a reduced training load, training intensity should be maintained during the taper. The training load reductions during the taper should be programmed with reducing training volume at 41% to 60% of pretaper training. The reduction of training frequency during a taper means that affect moderately trained athletes and highly trained subjects differently, reducing 30% to 50% of pretaper training and maintaining training frequencies, respectively. Detraining the duration of a taper is not easy. Most athletes is beneficial from a 2-week shorter or longer tapers, depending on their individual profiles of fitness loss, fatigue dissipation, and anxiety. The manipulations of this training program variables usually affect for most athletes and maximal performance gains. Conclusion Training intensity should be maintained during the taper, training volume reductions should be programmed at 41% to 60% of pretaper training. The reduction of training frequency could be reduced 30% to 50% of pretaper training, and most athletes is beneficial from a 2-week shorter or longer tapers. Future researches should be conducted the practical & effectual differences in individual and teamed-based sports after a taper procedure.


[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate the process of Jang Changsun’s winning gold medal in the 1966 Toledo World Amateur Wrestling Championship and its meaning. [Methods] Jang Changsun and Katsumura Yasuo who had competed with Jang Changsun for the gold medal were selected as participants, a player and an executive who had participated in the Championship were selected as informants. Data had been collected by in-depth interview were analyzed firstly by using the Patton(1991)’s data analysis method, and the following conclusions were obtained by comparing with preceding studies, press releases, reports etc. [Results] Jang Changsun won a gold medal through the three stages of desperate struggles. The first struggle was to loose weight. Jang Changsun lost three times more weight than other players through fasting treatment, intensive training and dehydration in order to secure an advantageous position in the competition. His second struggle was the sparring itself. He made his mind to win gold medal 2 years before the Championship and started to strengthen his physical fitness and polish up his techniques to fight with strong players from powerful nation of wrestling. He finished the sparring by winning 4 games and tieing 2 games resulting in the same deduction points with Katsumura. It was inevitable for him to fight desperately to lose weight again to get gold medal. He eventually won the gold medal by losing his weight until he fainted because of injuries and serious dehydration. [Conclusion] The first gold medalist Jang Changsun contributed a lot to development of Korean sports by offering chance to consider significance of improving elite player’s exercising environment, scientific coaching, gaining self-confidence to win medal, and realizing the importance of sports informations.


Purpose This study is a phenomenological research which tries to describe the subjective experience and to analyze multi-layered meanings, and it finds out the men's training experience and meaning. The purpose of this study is to investigate why the men do Yoga and what the subjective meaning of Yoga experience, and the study examines critically whether Yoga experience especially focused on women is against gender performance and dominant body discourse. Methods For the study, 6 middle & young-old aged men who do Yoga more than 6 months every week are selected as participants. Results The meaning of Yoga for middle & young-old aged men in their lives is as follows. First, it is hard for men to experience Yoga because of social and cultural background. Finding Yoga class which takes men's membership is difficult. Second, middle & young-old aged men's physical feature(interest in their health and disease) and personal background(women friendly daily life) become specific motivation to overcome the barrier to do Yoga. Third, Yoga is 'alterative training', not a training. Yoga is considered as a training which replaces the feature of training called men's sports previously. Fourth, Yoga has a meaning of 'healing' to have our own time. Fifth, Yoga is changed by itself in Yoga culture which is focused on women even though middle & young-old aged men do Yoga for a long time. Sixth, middle & young-old aged men realize that the feature of Yoga is not 'for only women', and they thought it is 'neutral training that men can do too.' Conclusion Consequently, the reason why middle & young-old aged men do Yoga is started from the motivation regarding physical characteristics and personal background, and the main purpose is to cure and to heal our bodies and mind. For them, Yoga means 'alternative training to fit their bodies' and 'their own time'. Moreover, old male adult's training experience and meaning are against gender performance in that it cause a crack in stereotyped gender sports area, but it is notable that there is no intention to resist the dominant gender body discourse.