Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the research topics of the articles which were published through European Sport Management Quarterly(ESMQ) from 2009 to 2018. The prior topic analysis studies of the ESMQ classified topics based on the key words using NASPE-NASSM SMPS categories. Therefore they couldn't fully reflect the content of the articles. Methods The topic modeling of the current study was conducted with the Latent Dirichlet Allocation(LDA) which generates topics based on the word usage in the article. A total of 265 articles were converted from 'pdf' format to 'txt' ANSI format for topic modeling analysis. The whole topic modeling process was done using R program and the model was set to generate 10 topics from the article. Results The 3 sport management experts were hired to label the name of the topics and the name of the topics are as follow : (1) Impact of mega sport event, (2) Cause-related marketing, (3) Factors affecting the results of the competition, (4) Managing sport organization, (5) European sport leagues, (6) Strategic management, (7) Sport economics, (8) Sport in communities, (9) Sport consumers, (10) Elite sports. It is not quite possible to compare the results of the current topic modeling results with the previous ones because of the methodological differences. However, even though the standards are different, Sport marketing topic showed the largest growth among the 10 topics extracted. Conclusions This study used the LDA probabilistic algorithm to analyze research topics, which made the analyses more objective and wholistic. However, the insights of the researchers were still needed to interpret and labeling the topics.
This study was to explore and confirm factors of sport psychology counseling needs in Korean elite coaches. In order to achieve this purpose, 56 elite coaches in Korean Olympic training center at Taereung and Jincheon responded on open-questionnaire and 260 coaches responded on survey. Open-ended questionnaire responses were analyzed by inductive content analysis and collected survey data were analyzed by exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, sport psychology counseling needs of elite coaches were competition preparation, negative athlete-coach relationship, athlete private problems, performance degradation, pressure on performance result, injury management, team cohesion degradation, motivation, training management, different gender athlete control, athletes drop out, pressure from outside, conflicts with colleagues, neglecting from athletes, feeling of incompetence, emotional control problem, and so on. Secondly, based on these responses, closed-ended questionnaire was developed, surveyed, and analyzed. Exploratory factor analysis illustrated that sports counseling needs of coaches were performance enhancement strategies, unreasonable pressure, negligence on training, coaching stress, competition result stress, conflicts with athletes. Finally, confirmatory factor analysis showed that construct of sport counseling needs illustrated appropriate fit indices values. The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on coaching education program and sport psychology counseling program development and application. Consequently, it will help coaches to control their mind at coaching in training and competitions.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify ACTN3 gene polymorphisms amongprofessional ssireum players by weight class and between elite and non-elite players,and to select genotype that matches the characteristics of the sport. METHODS The subjects of this study were 148 male athletes currently working as professionalssireum players. Chi-square test cross-tabulation analysis was conducted to examinethe differences in ACTN3 genotypes between weight classes and between elite andnon-elite players. RESULTS There were no significant differences in allele or genotypebetween ssireum players, but there were significant differences in R-allele and XXgenotype. CONCLUSIONS Players with the R-allele type of the ACTN3 gene weremore often classified as elite. Using this marker as a basis for organizing a playerselection and training programs would be more effective in training those that matchthe characteristics of elite players of the game.
Purpose This study seeks to explore the process where drop-out elite athletes collect their life skills obtained during their sports career and transfer them to their daily lives. Methods An open-ended questionnaire survey was conducted on a total of ninety retired elite athletes and the responses were analyzed. Based on the results of inductive analysis, five subjects were selected for a follow-up in-depth interview. The responses to the open-ended questionnaire were analyzed by the inductive content analysis method and the results from in-depth interviews by the deductive content analysis method. Results A total of 478 life skills were collected from the drop-out elite athletes and structuralized into four general categories: psychological skill, social skill, self-management skill, and goal-setting skill. The results of this study have revealed that life skills positively transferred to their future courses of lives and daily lives. Conclusion It is believed that the results of this study will be helpful to understanding the concept of sports life skills, studying the possibility of transfer, and provide the basic data for helping drop-out elite athletes with re-socialization and positive adaptation.
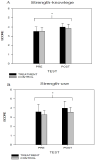
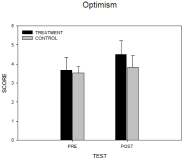
Purpose The goal of this study was to investigate the application effect of strength-based positive psychology intervention to elite archers. Methods Total of 20 elite archers participated in this study. Treatment group consisted of 10 elite archers participated in the strength-based positive psychology intervention for 8 weeks. Each individual responded the questionnaires in pre- and post-treatment sessions. Data were analyzed by repeated-measure ANOVA. Furthermore, archers participated in the program responded to in-depth interviews. Results According to the results, participants in strength-based positive psychology intervention showed that significantly increased strength knowledge, strength use, and optimism in the post–treatment compared to the pre-treatment session while control group did not show significant changes. In addition, archers perceived that there were positive effect on thinking ·coping and their self-confidence and self-esteem enhanced after participating the program. Conclusion The results of this study suggested that strength-based positive psychology intervention has positive impact on athlete’s wellbeing and perception of individuals strength and can be applicable to different sports field.

PURPOSE This study assessed elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness and developed reference standards for both their basic and specialized physical fitness. METHODS Data for analysis were collected from 870 athletes: from national teams, 123 elite Taekwondo athletes from the Performance Analysis and Assessment System (PAAS) administrator website (1999–2020); from regional sports centers, 731 collegiate and general division elite Taekwondo athletes (2015–2019); and from Y University, 16 elite Taekwondo athletes. Through measurement items’ selection and categorization, 20 physical fitness items were selected for the reference standards’ development, including 9 for basic fitness and 11 for specialized fitness. Taekwondo weight classes were divided into two: light + middle (fin, fly, bantam, feather) and middle + heavy (light, welter, middle, heavy). RESULTS Descriptive statistics for basic and specialized physical fitness items were categorized by gender and athletes’ fitness level. The reference standards’ development was aligned with existing standards, integrating the Cajori physical fitness 5-levels. It also introduced minimum physical fitness reference standards and target achievement reference standards for evaluating elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The reference standards proposed here can serve as objective indicators in selection of national representative athletes and also provide foundational data to establish fitness goals and evaluate future elite athletes’ physical fitness.

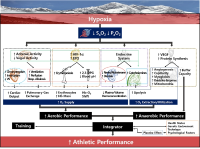
Purpose The purpose of this study is to emphasize the need for the establish and the use of altitude training center via examining exercise training method in natural or artificial altitude environment that is applied to various elite athletes in various advanced countries to maximize exercise performance and its effectiveness. Results Altitude training in natural or artificial altitude environment enhances aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance baesd on the hematological and nonhematological adaptations to hypoxic conditions. These altitude training methods can be classified into living high training high (LHTH), living high training low (LHTL), and living low training high (LLTH). LHTH (i.e., developed since the 1968 Mexico Olympics) and LHTL (i.e., developed in the 1990s by Levine and Stray-Gundersen) improve exercise performance via hematologic changes through erythropoiesis such as increased hemoglobin mass and erythrocyte volume. On the other hand, LLTH (i.e., has been developed variously since the 2000s) is composed continuous hypoxic training (CHT), intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) and repeated sprint training in hypoxia (RSH), and the altitude environment is constructed using a vacuum pump and a nitrogen generator. In general, LLTH method dose not induce hematological change in a short time within 3 hours. However, CHT and IHT enhance aerobic exercise capacity by improved exercise economy, supply and utilization of blood to tissues, capillary and mitochondrial densities, and oxidative enzyme activity through various biochemical and structural changes in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. RSH enhances anaerobic power and repetitive sprint performance by improving glycolytic enzyme, glucose transport, and pH control. In Korea, however, there are almost no facilities for altitude training that is applied to enhance athletic performance in advanced sports countries and recognition of the need for altitude training is also very poor. Conclusions Therefore, it is very urgent to develop altitude training for maximizing athletic performance in Korea and a lot of support and efforts are needed from the government and local governments.


PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on elite youth athletes by investigating their activities and eating habits before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study included 917 elite adult athletes from 19 sports and were grouped into 6. The questionnaire included items regarding demographics, physical activity, sleep, and eating habits before and after COVID-19. A total of 44 questions requiring subjective short answers were included. Statistical significance was set at p< 0.05. RESULTS After COVID-19, vigorous and moderate activity decreased across all sports; however, light activity increased in almost sports. Time spent sitting increased across all sports. The difference in the number of meals consumed varied among sports, and the number of competitions decreased in all sports. CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic appears to be finished but has not ended yet. Athletes must determine the best way to maintain their physical, physiological, and psychological states close to their original abilities. Determining this will provide the greatest impact on the return of athletes after COVID-19; this study will be helpful.
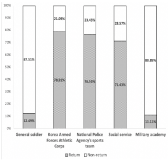
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the negative effects of long-term exercise (training and competition) suspension of male elite athletes due to compulsory military service on athletic performance, and to provide a basis for enhancing the importance of providing support systems and social conditions for maintaining athletic performance. Methods In this study, 17,418 male athletes aged 18 to 21 who were registered as athletes for the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee from 2003 to 2005 were enrolled. The athlete registration data includes information about the athlete's gender, age, sport and affiliation. According to the continuity of registration and belonging information, the compulsory military service type was classified into a manipulator. According to the form of Compulsory military service performed by male elite athletes, the return rate was confirmed and the career (year) was calculated. Results As a result of the survey, 12.49% of the athletes who served as general soldiers returned to the athletes after compulsory military service, showing a relatively low return rate compared to 78.91% of the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps, 76.55% of the National Police Agency's sports team, and 71.43% of the social service. Also, Athletes who served as general soldiers had a career of 2.46 years (± 1.94), while the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps was 10.21 years (± 3.58), the National Police Agency's sports team was 9.45 years (± 3.26), and the social service was 5.86 years (± 4.06), The exemption was 11.08 years (± 2.27), and the compulsory military service exception was 9.79 years (± 5.55). Conclusions Male elite athletes' decrease in athletic performance after compulsory military service is a natural result, as confirmed through the results of this study, and it is necessary to seek a support system between compulsory military service to maintain athletic performance.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to identify a sport-specific assessment for elite race walking athletes by comparing physiological responses to different types of walking graded exercise test (GTX) protocols. METHODS Six elite race walking athletes completed two types of walking protocols in a randomized crossover design with 1 week of interval between trials. Exercise time, oxygen uptake (VO2), ventilation (VE), and heart rate (HR) were measured in each trial; the lactate level was measured during the recovery period. RESULTS VO2, VE, and HR differed significantly between the trials (p<.01~.05). Exercise time (p<.01) and VO2 (p<.05) differed significantly between the walking protocols; however, VE and HR did not differ significantly. During the recovery period, lactate levels differed significantly between the trials (p<.01), but not the walking protocol. CONCLUSIONS These results suggest that modified walking GXT protocols were appropriate to assess elite race walking athletes.