
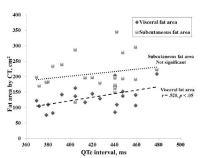
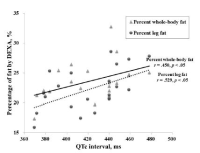
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between QTc interval and maximal oxygen consumption(V˙O2max) and body fat distribution in middle-aged men. Abnormal subjects (QTc interval, ≥440ms, n=10) and normal subjects(≤430ms, n=11) using QTc interval based on the Bazzet's equation were involved in the study. After overnight fasting, blood and blood pressure were measured. Abdominal fat area and regional fat compartment were measured by computed tomography(CT) and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry(DXA), respectively. For V˙O2max, the subjects underwent a maximal graded exercise test on a cycling ergometer. Abnormal group was significantly higher in SBP, basal insulin, HOMA-IR, and leg fat compared with normal. There was a significant relationship(r=.614, p=.03) between QTc interval and V˙O2max in all subjects. Also, partial correlation analysis showed a significant relationship(r=.480, p=.032) between the QTc interval and V˙O2max. Having a QTc interval outside normal range significantly worsened risk parameters for metabolic syndrome, in particular blood pressure and insulin resistance. Moreover, QTc interval was strongly correlated with cardiorespiratory fitness in middle-aged men. This study indicates that further study will be needed to assess the exercise training effects on QTc interval.


Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of a single corrective exercise (CEX) and corrective kinesio taping (CKT) on gait patterns, plantar pressure, balance, and pain in 20~30s female patients with moderate hallux valgus. Methods Twenty-one participants (age: 30.1±5.1 yrs; height: 164.1±4.8 cm; body weight: 56.7±6.8 kg; body mass index: 21.2±5.7 kg·m-2; hallux valgus angle: 27.2±6.1°) with hallux valgus was recruited and participated in three trials, i.e., CEX trial, CKT trial, and combined CEX and CKT (CEX+CKT) trial, repeatedly in a counter-balanced order. One week of wash-out period was placed between the trials to minimize the effect of the previous treatment on the next treatment. Variables related to gait pattern, plantar pressure, balance, and pain were measured during each treatment. We carried out repeated two way ANOVA on measured variables. Results 1) Regarding gait patterns, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant increases in the length of patients strides, the single support line during the stance phase, and significant reduction of the cadence. 2) Regarding gait cycle, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant reductions in the contact times of forefoot, midfoot, and heel. There was a significant reduction of double stance phase in CEX treatment. 3) Regarding foot pressure on gait, CEX+CKT treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of midfoot and heel. CEX treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of forefoot. 4) Regarding balance, CEX treatment and CKT treatments significantly increased one leg standing with eyes closed. 5) Pain was significantly reduced in CKT treatment and CEX+CKT treatments. Conclusions According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that a single CKT treatment was effective in reducing pain when walking and that plantar pressure, gait pattern, gait cycle, and balance were improved through a single bout of CEX treatments. Therefore, treatments by stage, starting with CKT treatments to reduce the pain, and then treating CEX to improve the gait pattern, gait cycle, foot pressure when walking, and balance ability, would be effective. Future research is warranted to identify the effects of long-term treatments.
PURPOSE This study sought to investigate the effects of passive warm-up on flexibility, exercise performance, and lactate oxidation rate in track and field athletes. METHODS A total of eight male athletes with more than three years of athlete experience were recruited as participants, and passive warm-up (PW) and active warm-up (AW) treatments were conducted in a single-group crossover study design. The participants performed thermal stimulation at 40°C for 20 minutes as a PW and performed a 60-70% HRmax cycle as an AW. Flexibility and exercise performance were measured after each treatment. Anaerobic power was measured using the Wingate test, and lactic acid concentration was measured. RESULTS Body temperature significantly increased in both PW and AW, and no significant difference was observed in exercise performance between treatments. Flexibility and lactic acid oxidation rate were significantly higher in PW than in AW. CONCLUSIONS In track and field sprinters, PW did not exhibit any significant difference in anaerobic power and exercise performance compared to AW even though no physical exercise was performed, and PW was effective in body temperature, lactic acid oxidation rate, and flexibility. PW suggests the possibility of replacing AW.
Circadian rhythm (CR) is an intrinsic process that changes in a cycle of approximately 24h/day to maintain body homeostasis. It is mainly controlled by the central command through the suprachiasmatic nucleus, and modern society features can disturb the central CR, contributing to various diseases. Recent studies have provided evidence that extrinsic factors, such as regular physical activity (RPA) and timerestricted feeding (TRF), can also alter the CR peripherally, emphasizing RPA and TRF as the non-therapeutic methods for circadian misalignment (CM). Therefore, this review scrutinizes the regulatory mechanism of CR and summarizes the relationships between CM and various diseases. In addition, by reviewing studies investigating the prevention or improvement of CM via RPA and TRF, the value of circadian biology research that can directly affect health, physical function, and lifespan is summarized. By introducing the scientific evidence for RPA and TRF to maintain and improve CR, we tried to emphasize the importance of regular exercise and healthy eating habits to people in the modern world who have difficulty maintaining CR.

[Purpose] This study aimed to investigate the structural relationships among event quality, spectators‘ destination image, country image, and behavioral intention in the international cycle competition, Tour de Korea 2017. [Methods] The questionnaire was structured in four dimensions: event quality (three sub-dimensions and twelve items), destination image (three items), country image (three items), and behavioral intention (four items). A total of 292 spectators from six hosting cities (Yeosu, Gunsan, Muju, Yeongju, Cheongju, and Seoul) during the event participated in this study. Factor analysis, reliability, validity, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were conducted utilizing SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0. [Results] This study indicated that event quality in an international sporting event was found to be the significant factor of spectators’ destination image and country image, which, in turn, significantly influenced the spectators’ intention to revisit to the place of the event and/or the event itself. [Conclusions] The findings of the present study contribute to theoretical understandings of event quality that predicts spectators’ behavioral intention and destination image in a global sporting event. Practically, this study also provides some important suggestions for practitioners who plan marketing strategies for international sporting events.

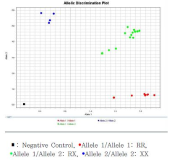
The ACTN3 R577X polymorphism has been associated with an elite athletes status. Several studies have determined that the R allele is connected with power-oriented athletic performance, whereas the nonfunctional XX genotype may give some beneficial effect for endurance performance. The main aim of the study was to determine the possible interaction between the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism and an power-oriented athlete status in Korean elite athletes(wrestling 31, judo 13, boxing 16, fencing 6, cycle 16, ≤400m athlete 18). Each athletes performed a 30-second WAPtest with a resistance equal to 7.5% for male and 5% for female body weight. Genotyping for the ACTN3 R577X (rs1815739) polymorphism was performed using the TaqMan approach. The ACTN3 R577X genotypes exhibited a HardyWeinberg equilibrium distribution in our population. The relative and absolute average power results of the 30-second Wingate test did not differ significantly among the genotypes. However, the relative peak power result of the Wingate test was significantly higher in the R-allele- dominant model groups than in the XX group in male but not female athletes. These results suggest that the ACTN3 R allele is associated with the relative peak power during the Wingate test in male Korean elite athletes.


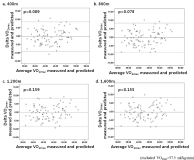
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the new indirect method assessing maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) using heart rate (HR) and accelerometer during walk exercise. Methods One hundred seven participants (55 male, 52 female) performed a graded exercise test to determine VO2max and two types of 1,600 m walk exercises (fast walk and pace controlled walk). The equations for estimating VO2max was developed by stepwise multiple regression. The validity of developed equations tested through the correlation between measured VO2max and estimated VO2max, was assessed by predicted residual sum of squares, and Bland-Altman plotting. Results VO2maxwas correlated with time, and HR/activity count per minute (ACM) measured in pace controlled walk exercise at all distance (400 m, 800 m, 1,200 m, 1,600 m). The equations were valid significantly and their multiple correlation coefficients or standard estimated error were similar to that Åstrand-Rhyming cycle ergometer test or Rockport 1 mile walk test. Using HR/ACM in pace controlled walk (400 m), it was possible to estimate VO2max(R2: 0.675, %SEE: 10.7). The equation was: VO2max=121.659+6.656×Gender-0.865×Age-9.540×Time-2460.952×HR/ACM (Gender, 0=female, 1=male: Time, hundredth of a minute: HR, heart rate: ACM, activity count per minute). Conclusion Estimation equations developed in this study are considered to estimate VO2max through a shorter distance, or a lower intensity of walk exercise. It is required studies to target a wide range of ages or to develop walk test on a lower bpm.

The purpose of this research is to provide the information about sports injury by surveying and analyzing a result, and to lead analytic and scientific training among the subjects being elite summer sport athletes. All sports injuries are recorded on injury report form and the following results were obtained. In Cycle sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. and In Table tennis sport, the prevalence of injuries of the ankle was highest due to the chronic fatigue. The prevalence of injuries of the shoulder, low back were highest due to the overuse of joints. In Badminton sport, the prevalence of injuries of low back, knees, ankles were highest by overtraining. In Gymnastics, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, ankles were highest. In Archery sport, there is a lot of injuries to the shoulder and neck. In Weight lifting sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, and ankles were highest. In Golf sport, the prevalence of injuries of knees, low back were highest. In Hockey sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Boxing sport, the prevalence of injuries of hands, shoulder, the low back were highest, In Judo sport, there are overall damage occurred in parts of the whole body, but the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Fencing sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. In Wrestling sport, although there is a difference slightly depending on freestyle and Greco-Roman, but the prevalence of injuries of knees, ankles, low back were highest. In Handball sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees were highest. In Taekwondo, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, feet were highest.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to section the stages of performance development based on the track and field athletes' performance records, derive the performance development span, which was a continuum of the development stages, and extract the psychological experience of the performance development span. METHODS In this study, 56 retired track and field athletes were provided with competition records, and 10 athletes participated in in-depth interviews. With the stage of performance development partitioned using long and short-term moving averages and regression slope in PRR, a continuous of performance development span was derived. To extract psychological experiences in the performance development span, a subject analysis was conducted after an in-depth interview. RESULTS First, the track and field athletes' performance development stage calculated short and long-term moving averages in the PRR. Based on the average difference in the regression slope of the initial 20% CPR in which the long-term moving average was not calculated, it was divided into beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods. Second, the performance development span was a continuum of the stage was of performance development, and the beginning period was 0 < PRR ≤ 7, it was a time when the competition record rises sharply. The rising period was 7 < PRR ≤ 60, which was a virtuous cycle time of growth athlete. The peak period was 60 < PRR ≤ 74, which was a time when the peak record was maintained. The decline period was 74 < PRR ≤ 100, which was a time when the competition record was downward. Third, throughout the performance development span physical intelligence of track and field athletes was based on their natural physical superiority, the technical skills rises and remains at its peak and then enters a downward trend. Competitional Intelligence aims to become personalization as it matures gradually while its competition management capability and game knowledge are immature. Psychological intelligence overcomes the initial psychological atrophy to form confidence, and after experiencing psychological burden at the peak, confidence decreases. In the environmental context, the competition record rises in the early stages, continues to rise, peaks, and enters a downward trend. CONCLUSIONS Track and field athletes' performance development span was implemented as a continuum of beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods, and the psychological experience of the performance development span formed a span of physical intelligence, competitional intelligence, psychological intelligence, and environmental context.