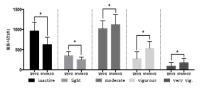
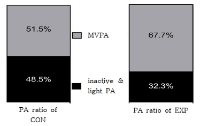
Active participation in Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity(MVPA) is the indicator of healthy development for adolescents. However, Korean adolescents’ MVPA have continuously declined, and Korean adolescents have lower levels of MVPA compared to adolescents in other countries. Considering this issue, the purpose of this study is to examine the effectiveness of SPARK M-SPAN program to promote adolescents’ MVPA in P.E. classes and to understand how the promotion of adolescents’ MVPA occurs. To collect data, this study used Sequential Mixed Method and GT3X accelerometers. A total of 168 adolescents (84 in an experimental group and 84 in a control group) participated in this study for the quantitative data analysis, and six students and a teacher were interviewed for the qualitative data analysis. Paired t-test showed that students in SPARK P.E. classes experienced the significant decreases of sedentary behaviors(-339.6 sec) and low intensity P.A.(-96.9 sec) at p<.05 and the significant increases of moderate(+99.3 sec), vigorous(+252.4 sec), and very vigorous intensity P.A.(+84.7 sec) regardless of gender difference at p<.05 except for female students’ moderate intensity P.A.. The qualitative data analysis showed that SPARK classes gave students positive learning environments and led them to experience enjoyment and achievement-orientated learning Key teaching strategies of SPARK program and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion section.

The purpose of this study was to examine the intensity of horseback riding as exercise (heart rate, oxygen intake, respiration exchange ratio, metabolism, energy expenditure) according to the tread of a horse such as walking, rising trotting, sitting trotting, and cantering. In this study, the subjects were 15 amateur horse riders. They participated in a 4-stage process(riding while the horse was walking, rising trotting, sitting trotting, and cantering) while wearing gas masks and heart rate belts for 5 minutes during each stage. Through this study, the average of heart rate, oxygen intake, respiration exchange ratio, metabolism, and energy expenditure in each stage of riding was attained and compared. The result of this study can be summarized as follows. First, the intensity of exercise by horse riding is significantly different depending on the tread of a horse. The intensity of exercise is increased as the speed of the horse's movements increased. Trotting and cantering show higher intensity than walking. Among the different treads of a horse, walking can be categorized as having an intermediate intensity of exercise, whereas trotting and cantering are categorized into a higher intensity. However, there are no significant differences in intensity between trotting and cantering. Second, there are no significant differences between male female participants in terms of intensity of exercise, but there are differences in the energy consumption per minute. The weight differences between male and female participants may be what cause this difference.

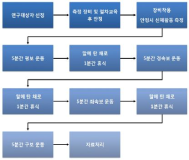
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of happiness improvement program on psychological variables which were happiness feeling, self-esteem, interpersonal relationship, internal-external locus of control, stress, coping, perceived performance and physiological variables such as cortisol and serotonin of collegiate badminton players. The participants consisted of 10 collegiate badminton players. Happiness improvement program for collegiate badminton players was developed by previous literatures, in-depth-interview, psychological test data, and consultation of happiness improvement experts. The happiness improvement program consisted of 12 intervention program: orientation, rapport development and the understanding happiness, self-esteem enhancement techniques, interpersonal relationship strategies, stress and coping management, peak performance methods, and action plan of happiness improvement program. Each program was applied to participants in about 90-120 minute a session(2-3 times session a week). The instruments of this study were made up of three broad categories: (a) psychological data, b) physiological data, and (c) qualitative data. Firstly, happiness improvement program significantly increased happiness feeling, self-esteem, internal-external locus of control, interpersonal relationship capability, coping skills of collegiate badminton players. Secondly, happiness improvement program significantly decreased stress of collegiate badminton players. Thirdly, participants positively perceived the effects of happiness improvement program on psycho-physiological variables. The limitations of this study and future implications were discussed.
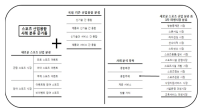
With coming industrial convergence era, there are the necessity of industrial convergence in sport industry. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to provide classification system and trend. This study applied case study method with semi-constructed interview, integrative literature review and observation. In addition, this study provide the conceptual framework for the classification system in sport industry related to industrial convergence. To conclusion, among the several criteria related to industrial convergence for product-new technology criterion, there are virtual sports, diagnosis valuation solution and exercise guide solution for participant sport market. In the case of new technology-service criterion, there are new media and virtual broadcasting for spectator sport market, and u-learning for participant sport market. For product-service criterion, there are complexity of sports facility and sportainment for spectator sport market, and virtual gaming sports and participatory tour for spectator and participant sport market. In addition, the trend of the sport industrial convergence has changed from leading media industry to converging with diverse industry areas.

PURPOSE This study aims to investigate the effects of three perceived benefits of physical activity classes on class satisfaction, college satisfaction, well-being, and workout intention, as well as the moderating effects of sports characteristics on the relationships between the benefits and outcomes. METHODS A total of 282 questionnaires were collected from university students enrolled in physical activity classes during the semester. Confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modelling (SEM), measurement invariance testing, and multi-group SEM were conducted using the Mplus 7.0. RESULTS Euphoric and social benefits positively affected class satisfaction. Class satisfaction, in turn, influenced college satisfaction, well-being, and workout intention. Sports characteristics moderated this relationship between the benefits of physical activity class and class satisfaction. CONCLUSIONS These findings offer practical insights for promoting student engagement and long-term participation in physical activity.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the decision-making process for consumers participating in sports centers based on an extended goal-directed behavior model (EMGB), and to provide empirical data for establishing effective operation strategies for sports centers, including additional risk perception of consumers during pandemic. METHODS A total of 446 surveys were used as the final sample. For data analysis, SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 were used for frequency analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model analysis. RESULTS Except for hypothesis 2 and 9, all of the hypothesis were chosen. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggested that extended goal-oriented behavior models can increase consumers' cognitive and emotional factors through emotional aspirations, suggesting that a lower risk perception of COVID19 increases their desire to participate in sports centers, and provides academic fundamental data on how to increase and activate sports centers.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the moderating effect of physical fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in older women. METHODS A total of 190 participants were categorized based on waisthip ratio (WHR) into high (50%) and low (50%) groups, as well as based on Z-score of fitness into high (25%; high fit), moderate (50%; moderate fit), and low (25%; low fit) groups. Logistic regression was used to assess the relative risk of MetS based on abdominal obesity and fitness levels, and moderation analysis using the Process macro was conducted to explore the moderating effect of fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and MetS risk factors. RESULTS After adjusting forcovariates, logistic regression showed that high WHR (odds ratio (OR)=2.721, p=0.004) led to a significantly higher risk of MetS compared with low WHR; the high fit group (OR=0.360, p=0.044) had a significantly lower risk of MetS compared wih the low fit group. Moderation analysis revealed that the impact of abdominal obesity on MetS risk factors varied depending on the level of fitness (β=-0.495, p=0.037), and the results remained significant after covariate adjustment (β=-0.458, p=0.049). CONCLUSIONS This study suggests that the risk of MetS from abdominal obesity can be mitigated by higher levels of physical fitness. These findings highlight the need for participation in regular physical activity to maintain a high level of fitness, along with proper nutritional intake, to prevent MetS in older women.
PURPOSE This study aims to investigate the effects of a 12-week equipment-based Pilates training on physical fitness, cardiovascular function, and vascular endothelial function in obese middle-aged women. METHODS Twenty-four women, aged 30-40 years with a body mass index ≥ 25 and percent body fat ≥ 30% were randomly assigned to one of two groups: the Pilates training group (TR; n=12); and control group (CON; n=12). The TR participants underwent three 50-minute equipmentbased Pilates training sessions per week for 12 weeks. Participants in the CON maintained their normal life patterns for the same intervention period. Variables regarding physical fitness, cardiovascular function, and vascular endothelial function were measured and compared pre-test and post-test u a two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) Regarding physique and body composition, participants’ body weight, body mass index, fat mass, percent body fat, waist circumference, hip circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio decreased significantly in the TR. 2) Regarding physical fitness, muscle strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and cardiorespiratory endurance increased significantly in the TR. 3) Regarding cardiovascular response, SV increased significantly in the TR. 4) Regarding vascular endothelial function, blood vessel diameter at rest and during vasodilation as well as blood flow volume during vasodilation decreased significantly in the CON, resulting in a significant interaction between group and test in FMD percentage. CONCLUSIONS It was concluded that the 12-week equipment-based Pilates program improved the physical fitness and vascular endothelial function in obese middle-aged women.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to compare the dynamic postural control of youth athletes with and without a history of lateral ankle sprains. METHODS Twenty-eight youth athletes (14 lateral ankle sprain, 14 healthy control) participated in this study. All participants answered the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure questionnaire and were subject to the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) for dynamic postural control evaluation to collect the joint angles of the lower extremity, a center of pressure (COP) path, and COP velocity. Independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test were performed to analyze the difference between the groups. RESULTS The lateral ankle sprain group (LAS) was found to have a long experience in participating in sports, and low Foot and Ankle Ability Measure scores were identified when compared to the healthy control (CON; p<0.05). LAS was observed with a short reach distance, less hip flexion, and dorsiflexion angles during the anterior direction of SEBT when compared to CON (p<0.05). Furthermore, LAS showed a slower anteroposterior and mediolateral center of pressure velocities in the posteromedial aspect of SEBT and a slower anteroposterior COP velocity in the posterolateral aspect of SEBT when compared to that of CON (p<0.05). There were no differences between the groups with respect to the other variables (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, decreased anterior reach distance of SEBT may be affected by changing the dynamic posture control strategy of the lower extremity joint on the sagittal plane in LAS.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate characteristics of levels of physical activity in considering gender and different types of competition-oriented physical activity classes using three-dimensional accelerometers. Methods A total of 981 students(505 male students, 476 female students) in six different types of physical education classes were participated in this study. All of the six different types of physical education classes were competition-oriented classes, and levels of physical activity were accessed by three-dimensional accelerometers. Data were analyzed using t-test and ANOVA. Results First, descriptive analyses of participation time of levels of physical activity showed that MVPA of physical education classes is 10.26 mins (22.89%) on average, and, MVPA showed differently in different types of physical education classes in the order of T ball(14.61 mins), flying disk(12.61 mins), soccer(10.78 mins), volley ball(10.56 mins), basketball(9.64 mins), and table tennis(5.73 mins). Second, female students showed significantly lower levels of MVPA in all the different types of physical education classes. Third, post-hoc analyses showed that significantly higher levels of MVPA were found in T ball physical education classes and significantly lower levels of MVPA were found in table tennis physical education classes, compared to other types of physical education classes. Conclusions MVPA in physical education classes is not satisfied with recommended MVPA, and MVPA in Korean physical education classes is lower than MVPA in same types of physical education classes in other countries. In addition, significant mean differences of MVPA are found between male and female students, and new sports physical education classes show higher levels of MVPA compared to classic sports physical education classes. These results indicate that competition oriented physical education classes widely used in Korea need to find ways to increase MVPA and to overcome different levels of MVPA between male and female students.