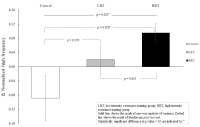
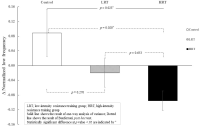
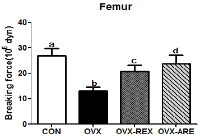
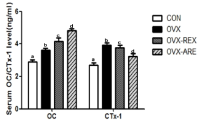
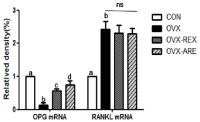
Purpose Osteoporosis is a systemic metabolic bone disease characterized by gradual decrease of bone mass and damage of the bone microstructure. In particular, postmenopausal osteoporosis is the most common type in women after menopause. This study aims to investigate the effects of combined exercise training on bone mineral density (BMD) and OPG/RANKL mRNA levels in ovariectomized rats. Methods A total of 40 Sprague-Dawley female rats were randomly divided into four groups: (1) CON (sham-operation, n=10), (2) OVX (ovariectomy, n=10), (3) OVX-REX (ovariectomy-resistance exercise, n=10), and (4) OVX-ARE (ovariectomy-combined aerobic and resistance exercise, n=10). Combined exercise training was performed on a treadmill and ladder adapted to rats in alternate days (4 days/wk, for 12 wk). Results Compared to the OVX group, all exercise treatments increased BMD and bone breaking force(p<0.05). In the bone turnover markers, serum C-terminal telopeptides of type-1 collagen (CTX-1) was significantly decreased in the exercise groups compared with OVX group and osteocalcin (OC) level was increased in the exercise groups (p<0.05). Additionally, in the exercise groups, expression of OPG mRNA was significantly increased compared with OVX group (p<0.05), and RANKL mRNA was slightly decreased but no significant between groups. Furthermore, OVX-ARE group showed more effects than OVX-REX group. Conclusions These results suggest that combined exercise may be a more effective therapeutic strategy to prevent and delay postmenopausal osteoporosis than resistance-only training.


Purpose The study examined the effects of a 12-week high intensity circuit training (HICT) on abdominal fat, physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese women. Methods Thirty obese women, aged 32-48 yrs, were recruited and randomly assigned to either HICT group (TR; n = 15) or control group (CON; n = 15). Subjects in the TR group participated in HICT of which resistance exercise and aerobic exercise were performed with a duration of 40 min/session and 3 sessions/wk for 12 weeks, whereas subjects in the CON group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns. Dependent variables included abdominal fat area, body composition, physical fitness, blood lipids profiles, and insulin resistance index. Analysis of variance with repeated measures with Bonferroni corrections was used to compare the outcomes between two groups. Results Main findings of the present study were as follows: 1) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant reductions in overall (i.e., body mass index and percent body fat) and abdominal obesity (i.e., waist circumference, total abdominal fat area, visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area-subcutaneous fat area ratio), 2) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in health-related physical fitness (i.e., muscular strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, balance, and cardiorespiratory endurance), and 3) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in fasting lipids, glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance. Conclusions The current findings of the study suggested that HICT would be an effective exercise intervention to improve metabolic complications associated with obesity and poor physical fitness in obese middle-aged women.




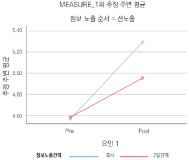
Purpose The purpose of the study was to examine the effect of exposure sequence and time gap between two exposures in image transfer in the context of sport sponsorship. Methods To accomplish the purpose of the study, one preliminary study and one main study were performed. The sample was drawn using a convenience sampling (33 for preliminary study and 120 for the main study). The data were analyzed using one sample t-test, repeated measure ANOVA(mixed design). Results The data for the main study indicated that the mean of the post-test was statistically higher than that of pre-test, which indicated that the image of the sporting event was transferred to the image of the brand Dell. This indicated that the image transfer actually took place although image similarity between sporting events and sponsoring brand was not conditioned. The hypotheses of the study were tested using a mixed design with exposure sequence and time gap between exposures as two between subject factors. The results indicated that the interaction was statistically significant. When two sponsorship information were given consecutively, the first sport event’s image was transferred more than the image of the secondly presented sport event, which indicated primacy effect. However, when the two sponsorship information was given with two days time gap, the image of the second sport event was transferred more than the first sport event’s image, which indicated a recency effect. Conclusions Two meaningful findins were delivered through the current study. First, even when there was no image similarity between sport event and brand, image transfer took place through sponsorship arrangement. Second, if primacy and recency effects are properly incorporated, image transfer can be achieved in a more effective way in sponsorship context.




Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the optimal model for winning medal on vault event of men's gymnastics. Specifically, decision tree analysis was used to explore, first, for the optimal conditions for qualifying top 8th player that have high possibility into final round, and second, for the optimal model for obtaining the medal of the vault event. Methods Data were collected for five official competitions (Olympics, Asian games, and International championship, etc.) organized by the Federation of International Gymnastics (FIG) from 2013 to 2016. In this study, the data of 626 vault players were collected. Also all of these players performed 921 vault skills for qualifying round or final round. Five predictor variables for estimating for qualifying into the final round and for obtaining the medal of the vault event were selected; nationality, difficulty score, acting score, additional penalty score, final score. Results The results is as follows. Overall, it was confirmed that the optimal model for entering into the final round was the difficulty score of vault event. The optimal model for entering into the final round estimates 81.2% when condition would be the 5.6 or higher of difficulty score and 8.6 or higher of the acting score. The optimal model for winning medals was 86.7%, which means that when condition would be the 6.0 or higher of difficulty score and no additional penalty score. Conclusions This models can be used as a basic data for establishing a strategy for medal acquisition of vault event of gymnastics.



[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of complex exercise and chromium supplement on healthe-related physical fitness, appetite regulating hormones, and diabetes risk factors in obese elementary school students. [Methods] The subjects were 32 obese elementary students over 25 kg/m2 to BMI, 8 complex exercise with high chromium supplement group (CE+HC), 8 complex exercise with low chromium supplement group (CE+LC), 8 complex exercise with placebo group (CE+PL), and 8 placebo group (PL). The subjects have performed the exercise program for 70 minutes a day and 3 times a week with aerobic and anaerobic exercise during 12 weeks. Also, low and high chromium supplement group took a peel 50 ug and 400 ug respectively at the same time and place. [Results] There were significant decreases in body fat to CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and significant increase in muscle mass compared with CE+PL (p<.05). However, there were no significant differences in body weight, BMI, muscular strength, muscular endurance, and flexibility between groups. For appetite regulating hormones, there is a significant difference to ghrelin in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and there were significant differences to glucose and insulin significantly decreased in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) in diabetes risk factors. [Conclusion] In conclusion, there were positive responses for body composition and diabetes risk factors for the twofold cases through complex exercise and high chromium supplement, but not for physical fitness and appetite regulating hormones.
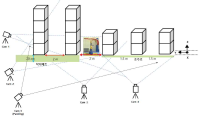
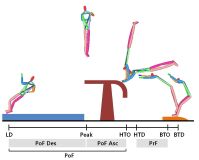
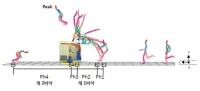
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to compare Yeo 2 vault and YANG Hak Seon vault to verify the possibility of YANG Hak Seon vault. [Methods] The YANG Hak Seon vault and Yeo 2 vault performed by five Korean national gymnastic athletes, and the photographic images were collected using a high-speed camera and their kinematic characteristics were analyzed by 3D image analysis. [Results] The main variable of the post-flight phase S1, S4, and S2 were similar to YANG Hak Seon vault. S1 showed the largest at shoulder angle and the highest body center of mass at horse take-off. S4 showed the smallest shoulder angle at horse take-off, slow twisting at the post-flight ascending period, but faster femoral rotation during horse contact. S2 showed the slowest twist velocity in the ascending period of the post-flight and the smallest rotational distance and twist distance at the peak. S3 showed the slowest horse take-off velocity, the least time in the post-flight phase, and the hip joint was flexed at the peak. [Conclusions] S1 is required to increase the twist velocity by narrowing the shoulder angle during post-flight. S4 is required to strong push-up and an increase in the twisting velocity in the post-flight ascending period. S2 is required to shorten the horse contact time and increase the horse take-off angle through powerful femoral rotation after board take-off. S3 will have to get enough power from the preparation phase.


[Purpose] This study aims to examine necessity and characteristics of the K-OVEP, and discuss ways of settle and spread the program stably through cases applied in school settings. [Methods] To do so, educational components and curriculum of the K-OVEP was represented by analyzing references, developmental materials, and program application. This study was examined through the application process and observation of long-term program of the K-OVEP from two types of educational fields, 2 elementary schools and 2 middle schools. In order to examine if the K-OVEP achieves the aim of the IOC and the K-OVEP, basic level study was conducted to 187 students who participated in the program in 2016. The questionnaire consisted of three categories; ‘cognition part’ through the Olympic games and the Olympic values, ‘value part’ regarding five educational themes of the OVEP, and ‘interest part’ asking interest and involvement in sports activities, participants answered the questionnaire before and after the education. [Results] We found that K-OVEP is an integrated value based educational program regarding Olympics, stresses personality education, encourages students to explore their career, and is a process oriented education. The results showed that the K-OVEP achieved the educational goals in every categories and questions, and educational effects in sports activity looked different among schools and the environments. [Conclusion] This study was performed to participants at first year of the introduction of the K-OVEP, so in order to keep track of learners’ significant change continuously, expansion of participants, steady development of various new programs, development of assessment tools, experts training and follow-up studies will be required.



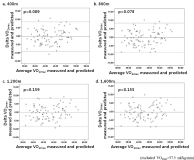
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the new indirect method assessing maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) using heart rate (HR) and accelerometer during walk exercise. Methods One hundred seven participants (55 male, 52 female) performed a graded exercise test to determine VO2max and two types of 1,600 m walk exercises (fast walk and pace controlled walk). The equations for estimating VO2max was developed by stepwise multiple regression. The validity of developed equations tested through the correlation between measured VO2max and estimated VO2max, was assessed by predicted residual sum of squares, and Bland-Altman plotting. Results VO2maxwas correlated with time, and HR/activity count per minute (ACM) measured in pace controlled walk exercise at all distance (400 m, 800 m, 1,200 m, 1,600 m). The equations were valid significantly and their multiple correlation coefficients or standard estimated error were similar to that Åstrand-Rhyming cycle ergometer test or Rockport 1 mile walk test. Using HR/ACM in pace controlled walk (400 m), it was possible to estimate VO2max(R2: 0.675, %SEE: 10.7). The equation was: VO2max=121.659+6.656×Gender-0.865×Age-9.540×Time-2460.952×HR/ACM (Gender, 0=female, 1=male: Time, hundredth of a minute: HR, heart rate: ACM, activity count per minute). Conclusion Estimation equations developed in this study are considered to estimate VO2max through a shorter distance, or a lower intensity of walk exercise. It is required studies to target a wide range of ages or to develop walk test on a lower bpm.


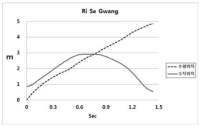
The aim of this study was to acquire essential information regarding Ri Se Gwang motion(element group Ⅱ, difficulty 6.4 point, double Tsukahara with tucked 1/1 twist), which Ri Se Gwang of North Korea performed during the final vault event of artistic gymnastic at Incheon Asian Game 2014, by analyzing motional characteristics. Firstly, Ri Se Gwang technique had second jump airborne time of 1.07 seconds and airborne height of 2.91m, which have great influences on the success of technique while having horizontal and vertical velocity of 2.73 m/s and 3.87 m/s, respectively, at the takeoff. These were sufficient jump motion for successful accomplishment of the technique however flight pattern was somewhat small which was mainly oriented vertically when compared to previous studies of Yeo and YANG Hak Seon 2 techniques. Secondly, blocking angle of vault contact was small at 9 degrees while having very small takeoff angle of 79 degrees. However, it had fast average trunk rotational velocity of 545 deg./s at the vault contact phase by rapidly bending trunk from the board takeoff until approaching the vault leading to achieve fast trunk rotational velocity of 452 deg./s after the take off in order to complete the airborne rotation successfully. Thirdly, the preparation phase of Ri Se Gwang technique had a distinct characteristics that the trunk was rapidly bent during the approach to the vault attempting aggressive blocking which leads to vertically oriented flight. It showed that this characteristic assists the motion of thigh snatch and the regulation of twist which strengthen airborne rotation for airborne rotational motion. And it also showed that sufficient landing and twist angles at the landing phase are possible with free rotational motion if the height of second jump reaches 3 m.







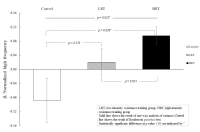
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.