PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effect of acute tart cherry juice intake on recovery after intermittent exercise in female field hockey athletes. METHODS Sixteen university female field hockey athletes were studied for a total of 3 days. The cohort was divided into 2 groups, placebo group (n=8, PLA) and the tart cherry juice group (n=8, TCJ), Each supplement was consumed 5 times over 48 hours. On the first day of the study, venous blood was collected before the test, and physical fitness variables (20m sprint, 5-0-5 agility, and Countermovement jump) were performed twice before and after the Yo-Yo Intermediate recovery test 1 to determine the degree of muscle damage and recovery of physical fitness factors. After all tests on Day 1, supplements (PLA, TCJ) were taken. After 24 hours, venous blood collection was performed, and after 48 hours, venous blood collection and physical element variables were measured to verify the effectiveness of tart cherry juice. RESULTS In the TCJ group, a significant effect was found over time in the 5-0-5 ability among the fitness variable items (p<.001) In Countermovement jump (CMJ), there was a significant effect over group and time (p<.001). Second, significant effects over group and time were shown in Interlukin-6 (IL-6) among variable items related to muscle damage and inflammation through venous blood collection (p<.05) and LDH (p<.001), and CK (p<.01) showed a tendency to decrease with time. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that acute tart cherry juice intake after intermittent exercise tends to reduce muscle damage and inflammation-related variables in female field hockey players, which could help them recover quickly, especially after hectic game schedules.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of an 8-week unstable surface Pilates training on physical fitness, abdominal muscle thickness, lumbar isokinetic muscle function, and pain in women aged 30–40 who are living a sedentary lifestyle and experiencing nonspecific low back pain. METHODS The training group (TR, n = 15) performed Pilates using small apparatuses on an unstable surface for 50 min/session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas the control group (n = 13) maintained their usual living pattern during the same intervention period. RESULTS 1) The body weight, body mass index, percent body fat, and fat mass decreased significantly in the TR, 2) whereas the hand grip strength, trunk extension, sit-andreach, and modified Schober test scores improved significantly. 3) The thickness of the external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis increased significantly in the TR. 4) Lumbar isokinetic flexor strength per body weight increased significantly in the TR. The endurance and endurance per body weight of the lumbar isokinetic extensor and lumbar isokinetic flexor also significantly increased in the TR. 5) The Korean Oswestry disability index (KODI) and the visual analog scale (VAS) score decreased significantly in the TR. 6) Significant negative correlations were found between the change rates in the KODI and nondominant hand grip strength, external oblique thickness, transversus abdominis thickness, and lumbar isokinetic extensor endurance. A significant negative correlation was found between the change rates in the VAS score and external oblique thickness. CONCLUSIONS The results revealed that the 8-week unstable surface Pilates training was beneficial in improving physical fitness, abdominal muscle thickness, lumbar isokinetic muscle function, disabilityindex, and pain levels in women aged 30–40 years who were having a sedentary lifestyle and experiencing nonspecific low back pain.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8-week aerobic exercise and polyphenol intake on body composition, cardiovascular response, vascular endothelial function, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in prehypertensive men. METHODS The study included twenty-eight males in their 20-30 years of age with prehypertension. Participants in the aerobic exercise + polyphenol intake group (EX + PP; n = 14) performed aerobic exercise three sessions/week, 30 min/session, at 65% of the heart rate reserve, and consumed polyphenol (grape seed extract 300 mg) for 8 weeks. Participants in the aerobic exercise + placebo intake group (EX + PL; n = 14) performed the same aerobic exercise; however, they consumed placebo instead of polyphenol. All independent variables were measured at pre-test and post-test, and the data were analyzed. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) SBP and MAP at rest decreased significantly in EX + PP, while MAP decreased significantly in EX + PL group. 2) In the EX + PP group, CO increased significantly, whereas DBP, MAP, and TPR decreased significantly during the hand grip exercise. In contrast, CO decreased significantly, while DBP and TPR increased significantly in the EX + PL group during the hand grip exercise. 3) Regarding vascular endothelial function, % FMD increased significantly in EX + PP group. 4) Sit-up increased significantly in both EX + PP and EX + PL groups; however, sit-and-reach in EX + PP group was significantly higher than that in EX + PL group at post-test. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study showed that the 8-week aerobic exercise would have positive effects on body composition, cardiovascular response, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in hypertensive men. Additionally, polyphenol intake would contribute more towards reduction of blood pressure at rest and during exercise and improvement of vascular endothelial function.

[Purpose] This study aimed to examine the effects of complex physical training on exercise and football performances in youth football players. [Methods] The subjects (n=16) were randomly assigned to either a complex physical training group (CPG, n=8) or a control group (CON, n=8). CPG was performed the complex physical training for 50 minute per day, and 2∼3 times per week, for 8 weeks. Exercise performance (health related physical fitness, skill related physical fitness, Y-balance and functional movement screen; FMS) and football performance (juggling, speed dribbling, shot passing, long kick and triple hop) were measured before and after 8 weeks complex physical training. [Results] Sit-up (p=0.002), sit and reach (p=0.040), 50-m run (p=0.031), side step (p=0.005), single-leg standing with eyes closed (p=0.040), plank (p=0.023), dominant composite score (p=0.002) and non-dominant composite score (p=0.005), deep squat (p=0.009), inline lunge (p=0.042), active straight leg-raise (p=0.015), rotary stability (p=0.049), total score(p=0.001), speed dribbling (p=0.030), dominant triple hop (p=0.001) and non-dominant triple hop (p=0.032) were statistical significant interactions between group and time. [Conclusion] Our findings indicate that complex physical training has beneficial effects on performance improvement of exercise and football in youth football players.

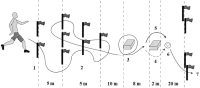
PURPOSE This study aimed to extract football coaches’ categories of performance evaluation factors (PEF) and examine the reflective characteristics of the football coaches’ player and casting judgments. METHODS PEF were extracted through an open-ended questionnaire and categorization from 80 AFC C or higher football coaches. Reflection was calculated in player and casting judgments through an analytic hierarchy process. The difference between the football coaches’ player and casting judgments was examined using SPSS 21.0. RESULTS First, the PEF of football coaches were categorized into four general categories: physical intelligence, psychological intelligence, growth potential, and competition intelligence. Second, the importance of football coaches’ player judgments were reflected by the PEF as football intelligence, situation judgment, football talent, tactical understanding, tactical operation, etc. The importance of the casting judgment were reflected by the PEF as tactical understanding, mediative skills, fitness, tactical operation, situation judgment, etc. Third, a statistically significant difference was noted between player and casting judgments. Football coaches tended to value growth potential and talent as sub-factors in the player evaluations. Football coaches’ PEF were aligned with the importance of player and casting judgments in psychological and competition intelligence as sub-factors such as skills, physical, attitude, passion, etc., but differed from physical intelligence and growth potential as sub-factors including mediative skills, physical, football talent, and tactical understanding. CONCLUSIONS In the football coaches’ player evaluations, the idealistic principle centered on growth potential. However, in the casting evaluation, the realistic principle centered on victory takes effect.
PURPOSE This study investigated the effect of non-linear periodization strength training on basic and professional fitness of national cross-country skiers. METHODS The body composition (height, weight, BMI, body fat %), basic physical strength (grip strength, lung capacity), anaerobic power (peak power, average power), graded exercise test (maximum heart rate, running time, VO2max, lactic acid), isokinetic strength (trunk strength), and 1RM (bench press, dead-lift, squat, shoulder press, leg curl, bicep curl, cable triceps extension) of nine national cross-country skiers (male: 5, female: 4) were measured. All analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0, Kruskal-Wallis H tests were applied to observe the changes by training methods. Mann-Whitney U tests were used as Post Hoc. RESULTS The results indicated that running time and VO2max post-test improved compared to that for the pre-test for graded exercise test. The lumbar extension strength of the post-test was higher than that for pre-test. There was no significant difference in other variables. CONCLUSIONS It is suggested that nonlinear periodization strength training can be expected to improve running time, VO2max, and trunk strength for cross-country athletes; however, it does not affect the overall changes.
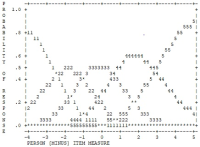
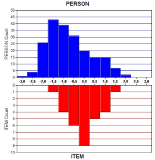
Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine item goodness-of-fit and the optimal categorization of an instrument measuring Korean elite young soccer player’s self-esteem using a two-facets Rasch model (item parameters and person parameters). Methods 10-item Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES) with five response categories was administered to 366 elite young soccer players from the Korea football association. The Rasch analysis was conducted by WINSTEPS 3.65. Results First, the model fit the data well. Second, 5-category rating scale did function well. Third, a item-person map illustrated the distribution of RSES items and person’s level of self-esteem. Fourth, the separation reliability of the items and person was shown to be an acceptable degree of confidence, respectively. Lastly, there was statistically significant difference in self-esteem between starting players and bench players, which supported the known-difference evidence of validity. Conclusion These findings provided additional support for the suitability of the RSES in assessing self-esteem of Korean elite young soccer players.


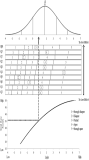
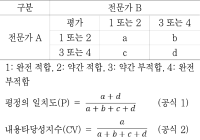
Purpose Common content knowledge(CCK) is composed of rules, techniques, and tactics. Such knowledge is a requirement for effective teaching of physical education (PE). There are, however, few validated tests of CCK. Thus, the purpose of this study was to develop a CCK test of soccer and evaluate the validity and reliability of the test using Rasch modeling (Rasch, 1980). Methods We developed thirty item common content knowledge test for soccer. Then, we used Rasch modeling to evaluate the validity and reliability of a test of soccer. Pre-service teachers (N=92) majoring in physical education and non-PE major (N=111) participated in this study. Results Thirty questions demonstrated good item-model fit. Moderately high internal consistency for person-ability and high internal consistency for item-difficulty are reported. Both Infit and Outfit statistics showed a good fit between the data and the Rasch model. Conclusions The analysis provides evidence to support the validity and reliability of this instrument as a CCK test of soccer. Limitations of the study were discussed and suggestions were provided to improve the test.

This study aims to suggest the guide line for weight category sports(Taekwondo, Judo, Wrestling, Weightlifting, and Boxing) who have to lose weight to pass weigh-in before games. Reference data was collected from RISS, Medline, PubMed, SciELO and effects of short term weight loss on physiological variables(body composition, physical fitness, blood components, oxidative stress and hormone, immune function) were analyzed. Also, weight loss procedures for weight category sports athletes were analyzed in details. The results of the research are as follows: weight category sports athletes prefer short term (3~5 days) weight loss methods (3~5%) with dietary control, sweating and exercise. Physical changes caused by the loss in body weight, fat-free mass, and BMI, however, do not affect body fat percentage. Different changes of physical strength element depend on weight reduction period. In short term weight loss method, anaerobic exercise capacity, muscular strength, and reaction time partially decrease and affect staying power. In contrast, long term weight loss method do not affect aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity. Furthermore, most of previous studies show that blood component change has negative effect on body water balance, stress-related hormone, and immune function. In conclusion, short term weight loss method negatively affects athletic performance of weight class competition athletic. Therefore, careful long term weight loss methods are recommended with dietetic consideration to prevent dehydration during weight loss period. Excessive weight loss on lightweight athlete should be prevented by institutional basis as well.
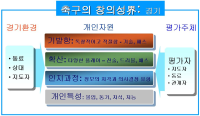
The purpose of this study was to explore a framework of understanding football performance. Researcher review was conducted to organize perspectives for football performance and drew implications as well as drift of football performance based on intelligence approach. Discussions for intelligence had been proceeded in concepts of learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence. Discussions of football performance approaches fitness, skill, and strategies in traditional intelligence aspects. The multiple intelligence perception discusses perspective, mentality, body, and analysis. The successful intelligence perspective deals with creativity, practical intelligence, and football talents. However, specific discussions for moral intelligence have not been progressed yet. FIFA’s social responsibility project and UEFA’s RESPECT campaign reflect that the discussions of football performance develops in a way of the moral intelligence. In European football, issues regarding value, such as RESPECT and against Racism, are currently emerging. Considering the change in the European football, the global football leagues will share the issues related to value in the near future. Given the fact that discussion for intelligence had been proceeded learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence, the moral intelligence will be a main concern in the further football performance discussion. The moral intelligence will be incorporated into football performance evaluations soon. Furthermore, teams and players will strive to place efforts in order for pursuing value and reputation as factors of performance.