Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an effective college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes. Methods A total of 160 student-athletes and 5 experts agreed to participate in this study. Four procedures were followed in this study: the needs assessment, the preliminary program development, and the application of the program. For the needs assessment, in-depth interviews were conducted, and the data were analyzed using an inductive reasoning process. Results The results of the needs investigation showed seven need factors and four interruption factors for college life adaptation. In addition, three need factors based on experience and seven interruption factors based on experience were found. The preliminary program was developed based on the needs assessment through the expert meeting, and the program consisted of four stages. Each stage consisted of three sessions, and each session contained a specific topic. The program was provided to nine freshman student-athletes in two months. As a result, the final program which consisted of four stages and thirteen sessions was developed after the reinforcement process based on evaluation of the preliminary program was conducted. Conclusions It is concluded that, the program is able to be expected to help them to understand their roles, have a better sense of responsibility and improve their self-esteem. Therefore, coaches and mental performance consultants should provide the college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes to reduce their stress and have a better college life.

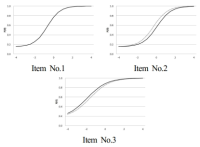
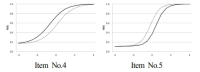
The purpose of this study was to analyze and confirm whether the items used in final paper and pencil test was determined to DIF when school sports clubs in each school operated by discriminatory curriculum in accordance with gender. Participants were 8th middle school students(male=135, female=141). They joined in school sports club every week from freshman to sophomore 1st semester. At that time, boys of them participated in soccer and basketball, and girls played dodge ball. They studied soccer unit at sophomore 1st semester, and had a final examination consisting of 5 soccer items. Using the data, differentially functioning item by the population difference between male and female were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. The results showed that Mantel-Haenszel method(using classical test theory), comparison of item characteristic curve and likelihood ratio test(using IRT) determined item number 4 and 5 to differentially functioning item. Finally, item number 4 were identified differentially functioning item in favor of male students in intensive qualitative analyses. That item have low content validity and application-level of cognitive behavior classification. The result provides that application-level item can be functioning differentially to female students with little sports experience than male students in paper and pencil test of PE.





PURPOSE This study investigated the perceptions and experiences of collegiate student-athletes with mental health concerns who are receiving sport psychology services. METHODS A total of 196 college student-athletes (98 male, 98 female) were recruited for the quantitative phase, while 14 athletes from 7 sports participated in the qualitative phase. This integrated approach sought to provide a comprehensive perspective on the research subject. The quantitative participants answered scales for depression (CES-D), anxiety (GAD-7), social support (NCAA RSSS), and mental help-seeking attitude (MHSAS), and the qualitative participants underwent in-depth interviews using a semistructured questionnaire based on a socioecological model. Quantitative data were examined using confirmatory factor analysis, reliability measures, independent t-test, and one-way analysis of variance via SPSS 28.0 and AMOS 28.0, and qualitative data were inspected through content analysis and expert meetings. RESULTS First, higher levels of depression, anxiety, and perceived social support were reported by female athletes as opposed to male athletes. Second, athletes in individual sports reported higher levels of social support than those in team sports. Third, athletes who planned to undergo future psychological counseling reported higher anxiety, social support, and helping attitudes than those with no plans to do so. Fourth, athletes who slept for more than seven hours reported lower levels of depression and anxiety and higher levels of perceived social support than those who slept for six hours or less. Fifth, freshman athletes reported higher depression levels than sophomore athletes. Sixth, student-athletes with no scholarships had higher anxiety levels than those with partial scholarships, who then reported higher perceived social support than those with full scholarships. Seventh, a lack of accessibility was the primary barrier to psychological service access for student-athletes. Eighth, engagement in interpersonal relationships was identified as a major stressor among student-athletes. CONCLUSIONS Differences in collegiate student-athletes’ mental health status as well as perceptions of and experiences in sport psychology services depend on various factors. These findings may serve as foundational data for improving sport psychology support services for collegiate student-athletes.