PURPOSE This study sought to explore elementary school (ES) teachers' avoidance of teaching model-based instruction (MBI) in physical education (PE) lessons. METHODS An open-ended questionnaire (n=93) and three focus group interviews (FGI ) were conducted with seven ES teachers. The collected data were analyzed using grounded theory analysis procedures (Strauss & Corbin, 1997). RESULTS Accordingly, we derived a grounded theory paradigm model composed of the core phenomenon (ES teacher’s avoidance of MBI in PE lessons), causal conditions (traditional difficulties of Elementary PE lessons, mismatch between MBI and ES teachers/PE lessons, lack of experience and teacher knowledge for/in MBI), contextual conditions (complex instructor organization, powerful trend of play), intervening conditions (value orientation for fun-focused PE, misunderstanding about PE curriculum), interactive strategies (focus on screening physical activities, preparing for PE lessons with YouTube rather than teacher guide book), and results (learner inclusive effects and de-curricularization). CONCLUSIONS ES teachers’ avoidance of MBI in PE lessons is a result of several reported problems with elementary PE lessons and is likely to be a recurring problem in the future. To encourage ES teachers’ MBI in PE lessons, efforts should be made to build practical knowledge of model use in pre- and in-service teacher education.
Purpose The purpose of this study was (1) to develop and to apply flipped learning strategies in Physical Education(PE) classes based on Sportscasting Model and (2) to examine the responses of students after PE lesson. Methods Participants were 10th high school students(N=216, male=115, female=101) in high school. Instruction strategies of flipped learning was developed after theoretical investigation, and the unit plans for curling and instructional materials were developed and applied. Open-ended questionnaires and in-depth interviews were used to collect the data. Qualitative content analysis combined with of structures in lesson was used to analyze the data. Results Results showed that (1) 11 instruction strategies of flipped learning were developed, (2) and the unit plan combining out-of class activities and in-class activities organically based on Sportscasting Model and instructional materials for unit of curling were developed and applied. In step of sportscasting, forcing relationship method-sportscasting based on the survey of students was developed and applied. (3) And 31 factors of Sportscasting Model and 15 factors of flipped learning were drawn from the analysis of questionnaires and interviews. Conclusion And to conclude, this research has a value of early study to develop and apply instruction strategies of flipped learning, the unit plan and instructional materials for combining Sportscasting Model with flipped learning organically. Discussions were provided in terms of the development of flipped learning applied in PE classes and responses of students.

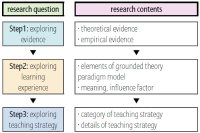
Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand learning experiences deeply and to prepare practical teaching strategies by reflecting the voices of the field. Methods For this, I used the logic and techniques of 'the grounded theory'. In particular, I used ‘the grounded theory paradigm model', which enables a holistic and systematic analysis of specific experiences to explore learning experiences and teaching strategies. I selected 10 male and female students who participated in art and physical activities as research participants. I collected data through literature review, in-depth interviews, and expert meetings, and analyzed using open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. Results First, I explored “the learning experience of art and physical activities in free-semester system", according to the elements of grounded theory paradigm model. It is composed of the ’causal condition’, ‘contextual condition’, ‘central phenomenon’, ‘interventional condition’, ‘interaction strategy’, and ‘results’. Second, based on this, I conducted "the teaching strategies for art and physical activities in free-semester system". These are composed of 'expansion strategy', 'diversity strategy', 'spontaneity strategy', and 'immersion strategy'. Conclusions The results of this study suggest that art and physical activities in free-semester system are leading to a positive change extended from the planned goals. In addition, various variables are structurally intertwined, and thus, it is considered that more strategic and systematic efforts are required in various dimensions for the successful application.


Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.