Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the difference and consistency of kinematic variables for each athlete by selecting the official records of the world's elite female triple jumpers to evaluate the performance level. Methods Three athletes who won the prizes at the World Championships Daegu 2011 Women's Triple Jump were selected as the study subjects, and only the successful trials were used for analysis. Pearson's correlation analysis was conducted with the kinematic variables in the hop, step, and jump phase, respectively. Also, kinematic variables with statistically significant correlations between braking time and pushing time and related variables were described separately. The duty factor and support factor for the hop, step, and jump of support phases were calculated. Results The successful trials rate were 66.7% for Olha, 50% for Olga, and 83.3% for Caterine. In the last three stride distances of the approach run, Olha and Caterine had a “medium-long-short” pattern and Olga had a “long-short-medium” pattern. There was no difference in the duty factor value between hop and jump phases in the ‘hop-dominate’ technique type, but there was a difference in the jump phase in the ‘balance’ technique type, and the duty factor value in the step of both technique types was greater than that of hop and jump phases. As for the percentage of the support factor, Olha and Caterine had a characteristic that the percentage of braking time in step and jump phases was opposite. On the other hand, Olga had the same percentage for the hop and step phase, and a smaller percentage for the jump phase. Conclusion To increase the accuracy of the board touch-down, maintain a certain last stride(1SL) depending on the technique type. This consistency of the approach run increases reduces distance loss on the take-off board and increases the successful rate of each trial. The duty factor can judge both the performance level and the technique type of triple jump, and the support factor is a variable that can classify the technique types of hop, step, and jump phases. If both the relative time required for the triple jump and the variability of the support time(braking and pushing) for each phase are constant, the difference in records by trial will be small.


Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.


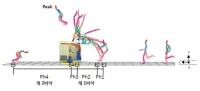
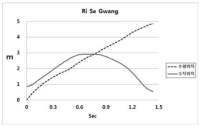
The aim of this study was to acquire essential information regarding Ri Se Gwang motion(element group Ⅱ, difficulty 6.4 point, double Tsukahara with tucked 1/1 twist), which Ri Se Gwang of North Korea performed during the final vault event of artistic gymnastic at Incheon Asian Game 2014, by analyzing motional characteristics. Firstly, Ri Se Gwang technique had second jump airborne time of 1.07 seconds and airborne height of 2.91m, which have great influences on the success of technique while having horizontal and vertical velocity of 2.73 m/s and 3.87 m/s, respectively, at the takeoff. These were sufficient jump motion for successful accomplishment of the technique however flight pattern was somewhat small which was mainly oriented vertically when compared to previous studies of Yeo and YANG Hak Seon 2 techniques. Secondly, blocking angle of vault contact was small at 9 degrees while having very small takeoff angle of 79 degrees. However, it had fast average trunk rotational velocity of 545 deg./s at the vault contact phase by rapidly bending trunk from the board takeoff until approaching the vault leading to achieve fast trunk rotational velocity of 452 deg./s after the take off in order to complete the airborne rotation successfully. Thirdly, the preparation phase of Ri Se Gwang technique had a distinct characteristics that the trunk was rapidly bent during the approach to the vault attempting aggressive blocking which leads to vertically oriented flight. It showed that this characteristic assists the motion of thigh snatch and the regulation of twist which strengthen airborne rotation for airborne rotational motion. And it also showed that sufficient landing and twist angles at the landing phase are possible with free rotational motion if the height of second jump reaches 3 m.







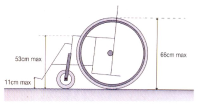
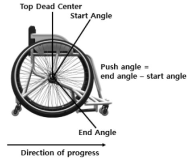
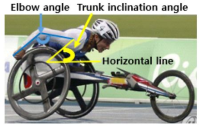
[Purpose] A potential issue for wheelchair sports are the characteristics of wheelchair design. The purpose of this review was to investigate the characteristics of design in wheelchair sports including the height of seat, camber and handrim size for improving the performance. [Results] The optimum height of seat related to trunk, arm length and handrim size. The lower seat showed the push efficient highly, while higher seat increased the energy expenditure. In energy expenditure, the optimum height of seat was 100-120° of elbow angle. Handrim size play the role in gear. The smaller handrim size acts like high gear, it gains disadvantages in acceleration, it gains advantages in maximum velocity. On the contrary, the higher handrim size acts like low gear, it gains disadvantages in maximum speed, it gains advantages in acceleration. The ratio of gear consideration in power and velocity. When increased camber enhanced the lateral stability, easier catch the handrim and easier arm motion. So it improved the energy expenditure and push technique. When increased camber enhanced the mechanical efficiency and stability, but it decreased the power. The racing wheelchair camber using the 8° and 10°. [Conclusion] Athletes, coaches and wheelchair experts are provided with insight in the performance effect of key wheelchair design settings, and they are offered a proven sensitive method to apply in sports practice, in their search for the best wheelchair-athlete combination.



PURPOSE This study examined Julsil impact on self-management and the moderating effect of achievement goal orientation in adolescent male athletes. METHODS Adolescent male athletes (n=248) registered with the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee participated in a survey. After exclusion of data from seven respondents who provided insincere responses, 241 responses were used for the final analysis. After verification of the measurement tool’s construct validity, technical statistical analysis and correlation analysis were performed. Finally, multiple regression analysis and PROCESS Macro (Model 1) were used to verify the research hypothesis. RESULTS 1) Male adolescent athletes’ Julsil and 2) task goal orientation had significant positive effects on self-management,, but ego goal orientation did not. 3) The moderating effect of task goal orientation on the relationship between Julsil and self-management was significant, but that of ego goal orientation was not. CONCLUSIONS 1) Male adolescent athletes’ Julsil and 2) task goal orientation had significant positive effects on self-management,, but ego goal orientation did not. 3) The moderating effect of task goal orientation on the relationship between Julsil and self-management was significant, but that of ego goal orientation was not.
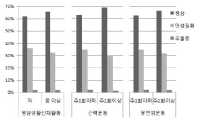
This study examined the association between physical activity (PA) and the prevalence of chronic disease and chronic depression. Additionally, the relationships between PA and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among general population, categorized by healthy, chronic disease and depression were investigated. Cross-sectional data includes 9,739 participants (4,351 males, 5,659 females, over 19 years old) who completed physical activity, chronic disease and HRQoL questionnaires from The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Complex samples frequency, descriptive, cross-tab and logistic analysis were used. Estimated prevalence of chronic disease and depression were significantly different between PA levels and frequency. Based on odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), participating in lower levels of daily PA including less resistance and flexibility exercise were associated with an increased likelihood of chronic disease. Less frequency of resistance PA was also associated with an increased likelihood of depression. Estimated prevalence of HRQoL was different according to PA in the healthy and chronic disease populations. Adjusted OR and confidence intervals represented through lower levels of daily PA and less frequency of resistance PA were associated with an increased likelihood of poor HRQoL in the chronic disease population. No significant OR between PA and HRQoL in the depression population was observed.


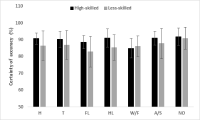
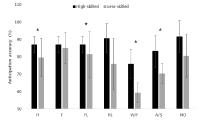
Purpose The purpose of this study was to establish the differences of anticipating accuracy and confidence according to fencing expertise and spatial occlusion region. Methods For the purpose of this study, the anticipation ability of 6 high-level fencing players and 6 low-level fencing players were analyzed. All subjects performed the 60 tasks of anticipating the attack positions(thorax, thigh, toe) from observing the fencing video screen using spatial occlusion technique. The spatial occlusion technique was used in 6 particular body of opponent’s movement. For statistic analysis, data was analyzed through independent T-test measure. Moreover, Paired t-test were used as follow-up analysis. Results The results of the study were as follows: In terms of accuracy anticipation, the main effect of expertise was significantly different. Specifically, when the spatial occlusion technique was applied in head, left leg, arm, and a foil, the accuracy of anticipation was significantly different. Moreover, comparing with no-occlusion condition, anticipation accuracy decreased when spatial occlusion technique was applied in arm and foil. In terms of confidence, there was no significant difference between level of expertise. Conclusions In order to effectively anticipate the opponent’s movement in fencing sports, it is necessary to focus on the visual cues of arm/shoulder, and the foil. Especially, focusing on the foil movement might provide the core informations on anticipation ability.



PURPOSE The quiet eye (QE) is defined as the final fixation time that is a specific target prior to initiating movement. This study aimed to identify the cause of QE in golf putting and to present an efficient practice method for improving putting skills. METHODS Thirty participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups. Each group practiced golf putting in different ways for two days. RESULTS The QE group showed a significant difference in putting scores, which was higher than that of the control group. The visual-occlusion group showed no difference compared to the other groups in terms of putting scores. The QE group showed a significant difference in terms of QE in the retention and competition tests compared to the pretest. The control group tended to have a slightly longer QE in competition tests compared to the pretest. The visualocclusion group showed no statistically significant difference in QE based on the period. All three groups had significantly longer swing times over the selected period. There was no significant difference in terms of the alpha power of the occipital lobe based on group and period. CONCLUSIONS The position of the visual-occlusion group became stable. However, the QE did not lengthen. The QE group had a longer QE. Furthermore, the control group that practiced with their eyes open tended to have longer QE. Therefore, QE may be related to visual-based cognitive processing rather than posturalkinematics. Finally, this study proved that QE practice is a more efficient method for novices in golf putting.
PURPOSE By analyzing trends in Taekwondo demonstrations, specifically in breaking and performances, to date, this study aims to offer timely insights and set the groundwork for future research. METHODS We used Korean abstracts from a total of 425 papers containing the keyword “Taekwondo demonstrations” spanning 20 years from April 2004 to April 2023. We employed Python 3.5.2 to conduct dynamic topic modeling (Latent Dirichlet Analysis, LDA) and to examine the correlation between the topic distribution by section and the publication year. RESULTS The main findings from the LDA are as follows. Topic 1 (10%): “The development of demonstrations: performance in culture and art, ” Topic 2 (11%): “The development of formalized rules and judgments in a demonstration event,” Topic 3 (08%): “A study on the educational courses and professionalism of Taekwondo coaches,” Topic 4 (11%): “Technical movements and kinematic characteristics,” Topic 5 (09%): “A study on marketing perspectives of demonstration performances,” and Topic 7 (33%): “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization.” In the correlation analysis between the topic share by section and the publication year, Topics 1 to 5 exhibited no statistically significant correlation. However, Topic 6, “A study on the attainment of events, training, and the psychological factors influencing athletes” and Topic 7, “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization,” also displayed a very statistically significant but negative correlation. CONCLUSIONS Future research should focus on studies on the psychological management of athletes during the performance of specific techniques and training methods. Further research considering the global characteristics of Taekwondo may be required.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) motion data produced through artificial intelligence-based user motion recognition technology with images obtained using a smartphone monocular camera. This was done to explore the possibility of developing an application that can improve the reliability of the measurement of physical activity performing motions and feedback provision. METHODS To check the accuracy of the artificial intelligence-based 3D motion analysis system that utilized a semi-supervised learning method, a commercialized 3D infrared motion analysis system measured and compared motions on three movement planes, motions with limited joint movement, and fast motions in a wide moving range. RESULTS The motions on the coronal and sagittal planes produced through the 3D motion analysis application showed very high measurement accuracy; however, the accuracy of the measurement of motions on the horizontal plane, which could not be measured directly with a camera, was relatively lower than that of the coronal and sagittal planes. Accuracy in measuring 3D motion was moderate in moving motions and low in motions with limited joint movement. CONCLUSIONS For the developed 3D motion analysis system to be used in online physical education, the types of physical activities included in the program should be comprehensively composed through the analysis of the content system of the physical education curriculum and the resultant physical activities.